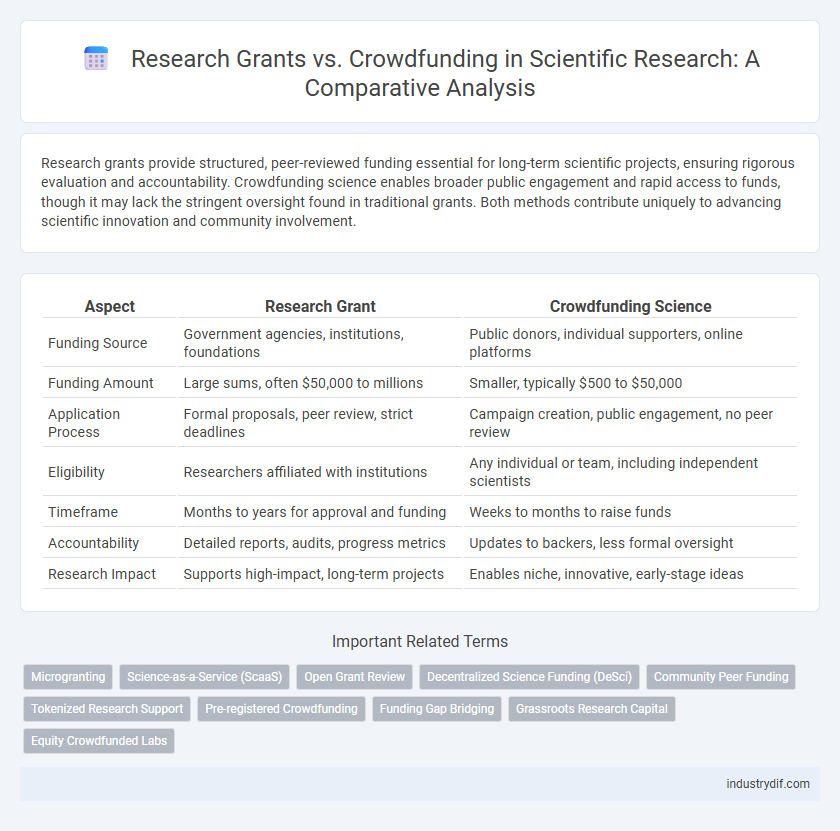
Research grants provide structured, peer-reviewed funding essential for long-term scientific projects, ensuring rigorous evaluation and accountability. Crowdfunding science enables broader public engagement and rapid access to funds, though it may lack the stringent oversight found in traditional grants. Both methods contribute uniquely to advancing scientific innovation and community involvement.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Research Grant | Crowdfunding Science |
|---|---|---|
| Funding Source | Government agencies, institutions, foundations | Public donors, individual supporters, online platforms |
| Funding Amount | Large sums, often $50,000 to millions | Smaller, typically $500 to $50,000 |
| Application Process | Formal proposals, peer review, strict deadlines | Campaign creation, public engagement, no peer review |
| Eligibility | Researchers affiliated with institutions | Any individual or team, including independent scientists |
| Timeframe | Months to years for approval and funding | Weeks to months to raise funds |
| Accountability | Detailed reports, audits, progress metrics | Updates to backers, less formal oversight |
| Research Impact | Supports high-impact, long-term projects | Enables niche, innovative, early-stage ideas |
Understanding Research Grants in Scientific Funding
Research grants provide structured, peer-reviewed funding from institutions like government agencies or scientific foundations, ensuring rigorous evaluation and accountability in scientific research. These grants often require detailed proposals, progress reports, and adherence to specific research objectives, offering stability and credibility to funded projects. Unlike crowdfunding, which relies on public contributions and may lack formal oversight, research grants prioritize scientific merit and long-term impact within the research community.
Exploring Crowdfunding as a Science Funding Model
Crowdfunding offers a democratized approach to science funding by enabling researchers to bypass traditional grant agencies and directly engage the public, which can accelerate innovation in niche or early-stage projects. Unlike research grants that undergo rigorous peer review and can be limited by conservative funding priorities, crowdfunding leverages social networks and digital platforms to raise capital quickly and often with greater flexibility. This model fosters community involvement and transparency, potentially expanding public interest and support for scientific research beyond conventional funding mechanisms.
Key Differences Between Grants and Crowdfunding
Research grants are typically sourced from governmental agencies, academic institutions, or foundations, providing substantial, pre-approved funding after rigorous peer review. Crowdfunding science relies on public contributions via online platforms, often emphasizing broader community engagement and lower funding thresholds. Unlike grants, crowdfunding requires active promotion and can offer greater flexibility but less financial stability and formal accountability.
Eligibility Criteria for Scientific Research Grants
Eligibility criteria for scientific research grants typically include the applicant's academic credentials, affiliation with recognized research institutions, and the alignment of the project with the funding body's priorities. Grant applications often require detailed project proposals, preliminary data, and evidence of the research team's expertise to ensure the scientific merit and feasibility of the study. Unlike crowdfunding, which is open to a wider audience and less formal, grant eligibility strictly enforces standards to support high-impact, peer-reviewed scientific endeavors.
Crowdfunding Campaign Strategies for Scientists
Effective crowdfunding campaign strategies for scientists include clearly articulating the research goals, demonstrating the potential impact, and engaging with a broad audience through multimedia presentations. Leveraging social media platforms and establishing a compelling narrative around the scientific problem can significantly increase funding success. Transparency about budget allocation and regular updates foster donor trust and sustained financial support.
Pros and Cons of Research Grants vs Crowdfunding
Research grants provide substantial funding with rigorous peer review ensuring project credibility and long-term support, but they often involve complex application processes and limited flexibility in fund usage. Crowdfunding offers rapid access to funds and enables direct public engagement and outreach, yet it may result in unpredictable funding amounts and lacks formal scientific validation. Balancing traditional grants with crowdfunding can diversify funding sources, though each method presents trade-offs between reliability and accessibility.
Impact on Scientific Innovation and Collaboration
Research grants provide structured funding that supports long-term scientific innovation by enabling comprehensive projects with rigorous peer review, fostering collaboration among established research institutions. Crowdfunding science introduces diverse funding sources and community engagement, accelerating niche or early-stage projects while enhancing public participation in the scientific process. Both models uniquely impact innovation and collaboration, with grants emphasizing stability and scale, and crowdfunding driving agility and democratization in research initiatives.
Financial Sustainability in Scientific Research Funding
Research grants provide structured financial sustainability for scientific research by offering substantial, multi-year funding secured through competitive peer review processes. Crowdfunding science offers flexible, project-specific funding driven by public interest but often lacks long-term financial reliability and scalability. Balancing grant funding with crowdfunding can diversify resources, yet grants remain the cornerstone for sustained, large-scale scientific innovation.
Transparency and Accountability in Funding Processes
Research grants typically involve rigorous peer-review processes ensuring transparency and accountability through detailed proposal evaluations and strict reporting requirements. Crowdfunding science relies on direct public engagement, promoting transparency by openly sharing project progress and outcomes but often lacks standardized accountability mechanisms. Combining both methods can enhance funding integrity by leveraging institutional oversight alongside community-driven openness.
Future Trends: Hybrid Approaches in Science Funding
Emerging hybrid approaches in science funding combine traditional research grants with crowdfunding platforms to diversify financial support and increase public engagement in scientific projects. This model leverages institutional funding stability alongside grassroots enthusiasm, enabling more dynamic allocation of resources tailored to both fundamental research and innovative, high-risk studies. Future trends indicate a rise in platform integrations that facilitate seamless collaboration between grant agencies and crowd contributors, optimizing transparency, accessibility, and impact measurement.
Related Important Terms
Microgranting
Microgranting in scientific research offers targeted, small-scale funding that accelerates innovative projects and exploratory studies often overlooked by traditional research grants. Unlike conventional grants that require extensive proposals and longer approval times, microgrants enable rapid disbursement of resources, fostering early-stage experimentation and increasing inclusivity in research funding.
Science-as-a-Service (ScaaS)
Research grants provide structured funding through institutional channels often requiring rigorous peer review and long-term project commitments, while crowdfunding science leverages public engagement and small contributions to accelerate innovation and democratize access to research opportunities. Science-as-a-Service (ScaaS) integrates both models by offering flexible, on-demand scientific resources and funding platforms that optimize project scalability, transparency, and stakeholder collaboration.
Open Grant Review
Open grant review fosters transparency and collaborative input in research funding, contrasting with traditional research grants that rely on closed, expert-only panels. Crowdfunding science engages diverse public stakeholders, democratizing funding decisions but often lacks the rigorous peer evaluation integral to open grant review processes.
Decentralized Science Funding (DeSci)
Decentralized Science Funding (DeSci) leverages blockchain technology to democratize research grants, allowing scientists to receive direct support from a global community without traditional institutional gatekeeping. Crowdfunding in DeSci accelerates innovation by enabling transparent, peer-to-peer funding mechanisms that reduce bureaucratic overhead and increase accessibility compared to conventional research grant systems.
Community Peer Funding
Community peer funding in science, such as crowdfunding, leverages a broad base of individual contributors to finance research projects, promoting public engagement and diverse funding sources. Research grants typically involve peer-reviewed assessment by experts, ensuring rigorous evaluation but often limiting innovation to established academic priorities.
Tokenized Research Support
Tokenized research support leverages blockchain technology to transform traditional research grants by enabling fractional ownership and transparent funding flows, enhancing researcher accountability and public engagement. Crowdfunding science through tokenization democratizes investment in innovation, allowing diverse stakeholders to directly contribute and benefit from scientific advancements while ensuring secure, traceable transactions.
Pre-registered Crowdfunding
Pre-registered crowdfunding in scientific research improves transparency and reproducibility by requiring detailed study protocols before funding acquisition, contrasting with traditional research grants that often rely on retrospective peer review. This approach fosters community engagement and accountability, potentially accelerating scientific discovery through direct public involvement and early validation of research hypotheses.
Funding Gap Bridging
Research grants provide structured, peer-reviewed funding crucial for large-scale scientific projects, while crowdfunding platforms offer flexible, rapid financial support for niche or preliminary studies; combining both methods effectively bridges the funding gap by addressing limitations of traditional grant cycles and democratizing access to capital. This hybrid approach enhances innovation by enabling continuous research momentum and fostering direct community engagement in scientific endeavors.
Grassroots Research Capital
Research grants typically provide substantial funding with stringent peer-review processes, supporting established scientific projects, while crowdfunding science offers grassroots research capital that empowers early-stage or niche studies through public contributions. Crowdfunding platforms democratize funding access, enabling scientists to bypass traditional gatekeepers and directly engage with a community invested in grassroots innovation and exploratory research.
Equity Crowdfunded Labs
Equity crowdfunded labs enable researchers to raise capital by offering stakeholders ownership shares, contrasting with traditional research grants that provide non-repayable funding typically from government or institutional sources. This model democratizes investment in scientific innovation, aligns researcher and investor interests, and accelerates translational research by leveraging public engagement and financial commitment.
Research Grant vs Crowdfunding Science Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com