Private cloud environments offer enhanced security and control by dedicating resources exclusively to a single organization, making them ideal for sensitive data and compliance requirements. Hybrid multicloud architecture combines private clouds with multiple public cloud services, enabling greater flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency while supporting diverse workload demands. Selecting between private cloud and hybrid multicloud depends on an organization's priorities for control, security, and dynamic resource allocation.
Table of Comparison
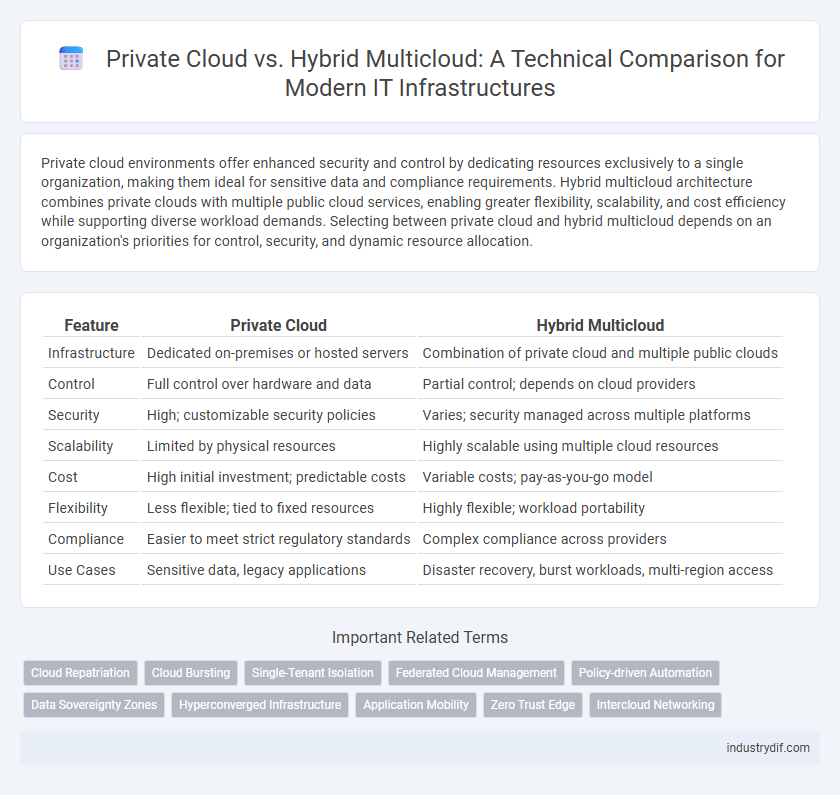
| Feature | Private Cloud | Hybrid Multicloud |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Dedicated on-premises or hosted servers | Combination of private cloud and multiple public clouds |
| Control | Full control over hardware and data | Partial control; depends on cloud providers |
| Security | High; customizable security policies | Varies; security managed across multiple platforms |
| Scalability | Limited by physical resources | Highly scalable using multiple cloud resources |
| Cost | High initial investment; predictable costs | Variable costs; pay-as-you-go model |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; tied to fixed resources | Highly flexible; workload portability |
| Compliance | Easier to meet strict regulatory standards | Complex compliance across providers |
| Use Cases | Sensitive data, legacy applications | Disaster recovery, burst workloads, multi-region access |
Definition of Private Cloud
Private cloud refers to a dedicated cloud computing environment exclusively operated for a single organization, offering enhanced security, control, and customization compared to public clouds. It is hosted either on-premises or by a third-party provider, ensuring that data, applications, and infrastructure remain isolated from other users. This setup enables enterprises to comply with regulatory requirements and optimize resource allocation while maintaining direct management over cloud assets.
Overview of Hybrid Multicloud
Hybrid multicloud infrastructure integrates multiple public clouds with private cloud environments, enabling organizations to optimize workload distribution and enhance flexibility. It provides unified management across different cloud platforms, improving scalability and reducing vendor lock-in risks. This approach supports advanced data governance, disaster recovery, and compliance by leveraging both on-premises resources and diverse cloud services.
Architecture Comparison
Private cloud architecture centralizes resources within a single organization's data center, offering enhanced control, security, and customization tailored to specific enterprise requirements. Hybrid multicloud architecture integrates private cloud infrastructure with multiple public cloud services, enabling dynamic resource allocation and workload portability while maintaining governance through unified management platforms. The architectural complexity of hybrid multicloud demands robust orchestration tools and standardized APIs to ensure seamless interoperability and compliance across diverse environments.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Private cloud environments offer enhanced control over data security and compliance by enabling organizations to enforce strict access controls, data encryption, and regulatory policies within a dedicated infrastructure. Hybrid multicloud architectures introduce complexity in security management due to distributed workloads across multiple public and private clouds, necessitating robust identity and access management, consistent encryption standards, and unified compliance monitoring tools. Enterprises must implement comprehensive security frameworks and automated compliance audits to address risks associated with data sovereignty, regulatory requirements, and cross-cloud vulnerability exposures in hybrid multicloud deployments.
Scalability and Flexibility
Private cloud environments offer robust security and control but often face limitations in scalability due to fixed infrastructure capacity. Hybrid multicloud architectures enhance scalability by distributing workloads across multiple public and private clouds, enabling dynamic resource allocation based on demand. Flexibility improves significantly in hybrid multicloud setups, allowing seamless integration of diverse services, rapid provisioning, and optimized workload management across varied environments.
Cost Efficiency Analysis
Private cloud environments offer predictable costs through dedicated infrastructure, reducing expenses related to external data transfer and compliance penalties. Hybrid multicloud setups incur variable costs due to dynamic resource allocation across multiple providers, often increasing operational complexity and cloud service fees. Cost efficiency in private cloud versus hybrid multicloud depends on workload patterns, with private clouds benefiting stable, high-demand applications and hybrid multiclouds optimizing short-term, scalable resource use.
Integration and Interoperability
Private cloud environments offer tightly controlled integration within a single infrastructure, ensuring high interoperability through uniform management and security protocols. Hybrid multicloud architectures enable seamless integration across multiple public and private clouds, leveraging APIs and standardized connectors to facilitate data sharing and workload portability. Effective interoperability in hybrid multicloud requires robust orchestration tools and compliance frameworks to maintain consistency and performance across diverse platforms.
Management and Automation Tools
Private cloud environments offer centralized management and automation tools that provide enhanced control over resource allocation, security policies, and compliance, streamlining IT operations within a single infrastructure. Hybrid multicloud solutions leverage orchestration platforms and unified management dashboards to automate workload distribution across diverse public and private clouds, optimizing performance and cost-efficiency. Advanced automation tools in hybrid multicloud environments facilitate seamless integration, continuous deployment, and policy enforcement, reducing manual interventions and operational complexities.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
Private cloud environments excel in industries requiring stringent data security and compliance, such as finance and healthcare, by offering dedicated resources and enhanced control over sensitive information. Hybrid multicloud architectures support dynamic workloads and scalability, ideal for enterprises in retail and technology sectors that need to balance on-premises infrastructure with public cloud resources for disaster recovery and workload optimization. Use cases include private clouds hosting critical applications with regulatory constraints, while hybrid multicloud setups enable real-time analytics and global reach for multinational corporations.
Future Trends in Cloud Deployment
Private cloud environments will evolve with enhanced automation, AI-driven resource management, and fortified security protocols tailored for sensitive data compliance. Hybrid multicloud strategies are projected to dominate future cloud deployment trends, offering seamless interoperability across diverse platforms to optimize workload distribution and cost efficiency. Emerging technologies such as edge computing and container orchestration will further drive the integration and scalability of hybrid multicloud infrastructures.
Related Important Terms
Cloud Repatriation
Cloud repatriation often occurs when organizations move workloads from public clouds back to private clouds to regain control, reduce costs, or meet regulatory requirements. Hybrid multicloud environments enable seamless workload mobility between private clouds and multiple public clouds, optimizing resource allocation and minimizing cloud repatriation risks.
Cloud Bursting
Cloud bursting enables private clouds to handle unexpected workloads by temporarily offloading excess demand to a hybrid multicloud environment, optimizing resource utilization and maintaining application performance. Hybrid multicloud architectures offer dynamic scalability and cost efficiency by seamlessly integrating on-premises private clouds with multiple public cloud services during peak traffic periods.
Single-Tenant Isolation
Private cloud environments ensure single-tenant isolation by dedicating hardware resources exclusively to one organization, enhancing security and compliance. Hybrid multicloud architectures combine private cloud isolation with public cloud scalability, enabling flexible resource allocation while maintaining strict data segregation through advanced network segmentation and encryption protocols.
Federated Cloud Management
Federated cloud management enables seamless integration and unified control across private cloud and hybrid multicloud environments by orchestrating workloads, policies, and security consistently. This approach enhances resource optimization, compliance adherence, and agility while minimizing operational complexity in distributed cloud infrastructures.
Policy-driven Automation
Policy-driven automation in private cloud environments enables centralized control with strict compliance, streamlining resource provisioning and workload management through predefined, organization-specific rules. Hybrid multicloud leverages policy-driven automation to orchestrate workloads across diverse cloud platforms, ensuring consistent governance, security, and optimized performance through dynamic policy enforcement.
Data Sovereignty Zones
Private cloud environments ensure strict data sovereignty by localizing data storage within defined geographic zones, complying with regional regulatory requirements. Hybrid multicloud architectures integrate multiple cloud services across diverse sovereignty zones while enabling secure data governance and dynamic workload distribution.
Hyperconverged Infrastructure
Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) enhances both private cloud and hybrid multicloud environments by consolidating compute, storage, and networking into a single system, improving scalability and management efficiency. Private clouds leverage HCI for dedicated, secure resource pools, whereas hybrid multicloud integrates HCI to seamlessly extend workloads across public and private platforms, optimizing flexibility and cost.
Application Mobility
Private cloud environments offer controlled application mobility within dedicated infrastructure, ensuring enhanced security and compliance for sensitive workloads. Hybrid multicloud architectures enable seamless application portability across diverse public and private clouds, optimizing resource utilization and reducing vendor lock-in.
Zero Trust Edge
Zero Trust Edge enhances security by enforcing strict access controls and continuous verification at the network perimeter, making it essential for hybrid multicloud environments where workloads span diverse cloud platforms and private infrastructure. In private cloud setups, Zero Trust Edge reduces internal threats by segmenting network access and minimizing lateral movement, ensuring robust protection within a single controlled environment.
Intercloud Networking
Private cloud environments offer dedicated infrastructure with enhanced security controls, while hybrid multicloud architectures integrate multiple public and private clouds to optimize workload distribution and scalability. Intercloud networking in hybrid multicloud setups enables seamless connectivity, low-latency data transfer, and unified management across diverse cloud platforms, enhancing operational agility and resilience.
Private Cloud vs Hybrid Multicloud Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com