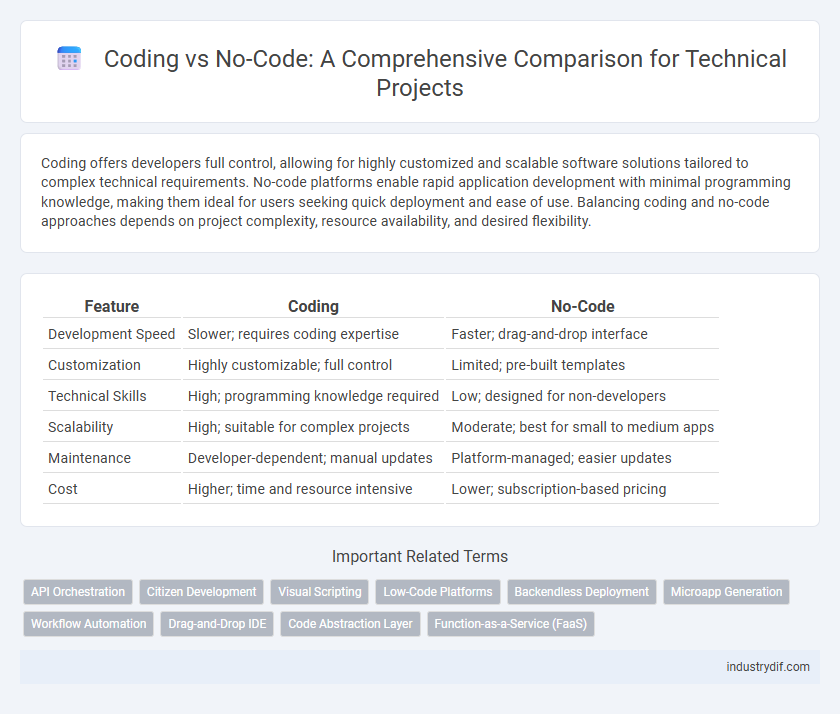
Coding offers developers full control, allowing for highly customized and scalable software solutions tailored to complex technical requirements. No-code platforms enable rapid application development with minimal programming knowledge, making them ideal for users seeking quick deployment and ease of use. Balancing coding and no-code approaches depends on project complexity, resource availability, and desired flexibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Coding | No-Code |
|---|---|---|
| Development Speed | Slower; requires coding expertise | Faster; drag-and-drop interface |
| Customization | Highly customizable; full control | Limited; pre-built templates |
| Technical Skills | High; programming knowledge required | Low; designed for non-developers |
| Scalability | High; suitable for complex projects | Moderate; best for small to medium apps |
| Maintenance | Developer-dependent; manual updates | Platform-managed; easier updates |
| Cost | Higher; time and resource intensive | Lower; subscription-based pricing |
Understanding Coding and No-Code Approaches
Coding involves writing and debugging algorithms using programming languages like Python, JavaScript, or Java to create customized, scalable software solutions. No-code platforms utilize visual interfaces and pre-built components, enabling users without programming skills to develop applications quickly and cost-effectively. Understanding the trade-offs between coding's flexibility and no-code's ease of use is essential for selecting the appropriate development approach based on project complexity and resource availability.
Key Differences Between Coding and No-Code Solutions
Coding solutions require proficiency in programming languages such as Python, JavaScript, or Java, enabling developers to create highly customized and scalable applications. No-code platforms leverage visual interfaces and pre-built components, allowing users without technical expertise to build functional software quickly and with less effort. Key differences include development speed, customization capabilities, and the need for technical knowledge, with coding offering greater flexibility and no-code focusing on accessibility and rapid deployment.
Technical Skills Required for Coding vs No-Code
Coding demands proficiency in programming languages such as Python, JavaScript, or C++, along with a deep understanding of algorithms, data structures, and software development principles. No-code platforms require minimal to no traditional coding skills, emphasizing user interface familiarity, logical workflow design, and platform-specific tools for application building. Technical skills for no-code focus on problem-solving through visual editors and integrations rather than syntax mastery or debugging complex code.
Speed and Efficiency in Development
No-code platforms accelerate development by enabling rapid prototyping and deployment with minimal technical expertise, significantly reducing time-to-market for applications. Traditional coding offers greater flexibility and customization but requires more time and specialized skills for debugging and optimization. Balancing speed and efficiency depends on project complexity, with no-code excelling in simple to medium applications and coding preferred for intricate, scalable systems.
Scalability and Customization Capabilities
Coding platforms offer superior scalability and customization capabilities by enabling developers to build intricate architectures tailored to specific business requirements. No-code solutions, while user-friendly and faster for initial deployment, often face limitations in handling complex logic and scaling beyond predefined templates. Enterprise-grade applications demanding high scalability and unique functionalities benefit significantly from traditional coding approaches.
Security Considerations: Coding vs No-Code
Custom coding enables granular control over security protocols, allowing developers to implement tailored encryption, access controls, and vulnerability patches. No-code platforms streamline development but may introduce risks due to limited transparency in underlying code and reliance on third-party security measures. Evaluating the security posture requires assessing platform compliance certifications, update frequency, and the ability to conduct independent security audits.
Cost Implications and Resource Allocation
Coding requires skilled developers, which increases labor costs and extends project timelines, especially for complex applications. No-code platforms reduce upfront expenses by enabling non-technical users to build solutions quickly but may incur hidden costs through limited customization and platform subscription fees. Efficient resource allocation depends on project complexity, budget constraints, and the need for scalability, with no-code favoring rapid deployment and coding supporting long-term flexibility.
Integration and API Compatibility
Coding offers extensive API compatibility and customization options, enabling seamless integration with complex systems and bespoke workflows. No-code platforms provide pre-built connectors and simplified API integration, ideal for rapid deployment but often limited in handling intricate or highly specialized APIs. Choosing between coding and no-code depends on the level of integration complexity and the need for tailored API functionality in a project.
Use Cases: When to Choose Coding or No-Code
Coding is ideal for complex, scalable applications requiring custom functionality, such as enterprise software, data-intensive platforms, and AI-driven systems. No-code platforms excel in rapid prototyping, simple workflows, and small business automation where speed and ease of deployment outweigh extensive customization. Organizations should evaluate project complexity, budget, user expertise, and long-term scalability to determine whether coding or no-code tools best fit their specific use cases.
Future Trends in Coding and No-Code Technologies
Emerging trends in coding emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate complex development tasks, enhancing productivity and precision. No-code platforms are evolving to support more sophisticated applications through modular components and AI-powered assistants, enabling non-developers to create enterprise-grade solutions. Hybrid models combining low-code frameworks with traditional coding are gaining traction, providing scalability and customization while accelerating time-to-market.
Related Important Terms
API Orchestration
API orchestration enables seamless integration and automation across multiple services, significantly enhancing both coding and no-code platforms' capabilities. While coding offers granular control and customization in API workflows, no-code solutions accelerate development by providing visual interfaces for API orchestration without extensive programming knowledge.
Citizen Development
Citizen development empowers non-technical users to create applications using no-code platforms, accelerating digital transformation while reducing reliance on professional developers. This approach enhances business agility by enabling faster prototyping and iteration, though complex, scalable solutions still often require traditional coding expertise.
Visual Scripting
Visual scripting bridges the gap between traditional coding and no-code platforms by allowing users to create logic flows through graphical interfaces without writing text-based code. This approach enhances accessibility for non-developers while maintaining flexibility for complex programming tasks through node-based representations.
Low-Code Platforms
Low-code platforms accelerate application development by enabling users to design software visually with minimal hand-coding, reducing dependency on specialized programming skills. These platforms integrate pre-built components and automation tools, improving deployment speed and fostering collaboration between developers and business users.
Backendless Deployment
Backendless enables rapid application deployment by offering a no-code platform that eliminates the need for traditional coding, significantly reducing development time and resource costs. Its visual interface supports backend logic, database management, and API integration, making it ideal for non-developers while maintaining scalability and performance comparable to coded solutions.
Microapp Generation
Microapp generation through coding enables precise customization and integration with existing systems, delivering tailored functionality for specific business needs. No-code platforms accelerate development cycles by allowing users to create microapps via intuitive interfaces, reducing dependency on technical expertise while maintaining scalability.
Workflow Automation
Workflow automation using coding offers unparalleled customization and integration capabilities, enabling complex, scalable solutions tailored to specific business logic. No-code platforms accelerate deployment and reduce technical barriers by providing intuitive interfaces, making automation accessible to non-developers with standardized workflows.
Drag-and-Drop IDE
Drag-and-drop IDEs enable rapid application development by allowing users to visually construct workflows and interfaces without writing code, significantly reducing development time and lowering the barrier for non-technical users. While traditional coding offers greater customization and control, drag-and-drop platforms optimize productivity for common tasks through pre-built components and intuitive design elements.
Code Abstraction Layer
Code abstraction layers simplify software development by hiding complex implementation details and providing reusable components, enabling faster deployment and easier maintenance. No-code platforms leverage these abstraction layers to allow users with minimal programming skills to create applications, while traditional coding offers full control and customization through direct manipulation of the underlying code.
Function-as-a-Service (FaaS)
Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) enables developers to deploy code in isolated functions without managing servers, offering granular scalability and efficient resource usage compared to traditional coding. No-code platforms integrating FaaS empower non-developers to automate workflows and create applications rapidly through visual interfaces while maintaining backend flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
Coding vs No-Code Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com