Legacy systems often struggle with inflexibility, limited integration capabilities, and high maintenance costs, making it difficult for businesses to adapt quickly to changing market demands. Postmodern ERP, by contrast, emphasizes modularity, cloud-based solutions, and seamless interoperability, enabling organizations to scale and innovate efficiently. This shift empowers companies to replace monolithic systems with agile, best-of-breed applications that improve responsiveness and reduce total cost of ownership.
Table of Comparison
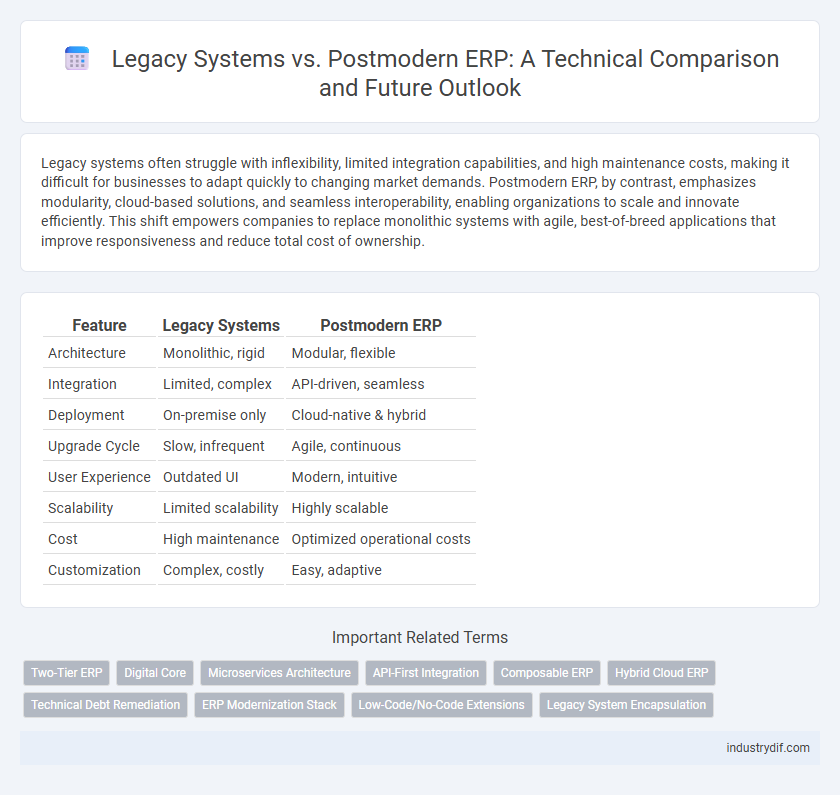
| Feature | Legacy Systems | Postmodern ERP |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Monolithic, rigid | Modular, flexible |
| Integration | Limited, complex | API-driven, seamless |
| Deployment | On-premise only | Cloud-native & hybrid |
| Upgrade Cycle | Slow, infrequent | Agile, continuous |
| User Experience | Outdated UI | Modern, intuitive |
| Scalability | Limited scalability | Highly scalable |
| Cost | High maintenance | Optimized operational costs |
| Customization | Complex, costly | Easy, adaptive |
Defining Legacy Systems in the Modern Enterprise
Legacy systems in the modern enterprise refer to outdated software and hardware platforms that continue to support critical business functions despite their limited flexibility and compatibility with current technologies. These systems are often characterized by monolithic architectures, reliance on outdated programming languages, and challenges in integration with newer applications, resulting in increased maintenance costs and operational risks. Modern enterprises face significant hurdles in aligning legacy systems with digital transformation initiatives, prompting a shift towards Postmodern ERP solutions that emphasize modularity, scalability, and cloud-native capabilities.
Key Features of Postmodern ERP Solutions
Postmodern ERP solutions offer modular architecture allowing seamless integration with best-of-breed applications, enabling greater flexibility compared to legacy monolithic systems. Cloud-native deployment supports real-time data access and scalability, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and agility. Advanced analytics and AI-powered automation within postmodern ERP improve decision-making and streamline business processes across diverse enterprise functions.
Integration Capabilities: Legacy vs Postmodern ERP
Legacy systems often suffer from limited integration capabilities due to outdated architectures and proprietary technologies, making it difficult to connect with modern applications and cloud services. Postmodern ERP, designed with modularity and open APIs, enables seamless integration across diverse platforms, enhancing real-time data exchange and scalability. This flexibility improves operational efficiency and supports agile business processes essential for competitive advantage.
Scalability and Flexibility: Comparative Analysis
Legacy systems often lack scalability due to rigid architectures and monolithic designs, limiting their ability to adapt to evolving business needs. Postmodern ERP solutions prioritize flexibility with modular components and cloud-native infrastructure, enabling seamless scalability and integration with emerging technologies. This architectural shift enhances responsiveness and supports continuous innovation in dynamic enterprise environments.
Security Considerations in Legacy and Postmodern ERP
Legacy systems often suffer from outdated security protocols, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches due to limited vendor support and infrequent security updates. Postmodern ERP architectures emphasize modularity and cloud integration, enabling more frequent security patches, advanced threat detection, and compliance with modern standards such as GDPR and SOC 2. Organizations adopting postmodern ERP benefit from enhanced encryption methods, identity and access management (IAM), and continuous monitoring, significantly reducing overall security risks compared to legacy environments.
Total Cost of Ownership: Legacy Systems vs Postmodern ERP
Legacy systems often incur higher total cost of ownership (TCO) due to expensive maintenance, limited scalability, and costly integrations. Postmodern ERP minimizes TCO by leveraging modular architecture, cloud-based services, and easier customization, which reduces infrastructure and update expenses. Organizations adopting postmodern ERP benefit from lower operational costs and enhanced agility compared to the rigid and costly legacy systems.
Migration Challenges from Legacy to Postmodern ERP
Migrating from legacy systems to postmodern ERP involves significant challenges such as data integration complexities, system compatibility issues, and maintaining business continuity during the transition. Legacy systems often utilize outdated architectures and proprietary formats, complicating data extraction and transformation processes essential for postmodern ERP platforms. Effective migration requires robust change management strategies, comprehensive testing frameworks, and phased implementation plans to minimize operational disruptions and ensure seamless system interoperability.
Customization: Limitations and Opportunities
Legacy systems often impose rigid customization limitations due to outdated architectures and proprietary codes, restricting businesses from adapting quickly to evolving processes. Postmodern ERP solutions offer modular and flexible customization options through APIs and cloud-based integrations, enabling tailored workflows and scalability. This shift enhances operational agility while reducing dependency on extensive IT resources and lengthy upgrade cycles.
Impact on Business Agility and Innovation
Legacy systems often hinder business agility due to rigid architectures and limited integration capabilities, causing delays in responding to market changes. Postmodern ERP solutions promote innovation by enabling modular deployment, cloud scalability, and real-time data access, which accelerate decision-making and adaptability. Companies leveraging postmodern ERP platforms experience enhanced operational flexibility and faster implementation of emerging technologies.
Future Trends: The Evolution Beyond Postmodern ERP
Emerging future trends indicate a shift beyond Postmodern ERP towards hyper-modular, AI-driven platforms that leverage blockchain for enhanced security and decentralized data management. Legacy systems are increasingly inadequate for real-time analytics and agile business processes, prompting enterprises to adopt cloud-native ERPs with embedded machine learning capabilities. The evolution emphasizes interoperability, personalization, and continuous innovation to meet dynamic market demands and digital transformation goals.
Related Important Terms
Two-Tier ERP
Two-Tier ERP architecture integrates legacy systems at the headquarters with modern, cloud-based ERP solutions at subsidiary levels, enhancing flexibility and scalability without disrupting existing core operations. This approach allows enterprises to maintain stable legacy infrastructure while adopting innovative postmodern ERP capabilities for localized agility and faster deployment.
Digital Core
Legacy systems often rely on monolithic architectures that hinder agility and scalability, while Postmodern ERP leverages a flexible digital core to enable seamless integration, real-time data processing, and modular innovation. The digital core in Postmodern ERP acts as a centralized platform that harmonizes cloud-based services, AI-driven analytics, and IoT connectivity, transforming enterprise workflows and enhancing decision-making efficiency.
Microservices Architecture
Legacy systems typically rely on monolithic architectures that hinder scalability and flexibility, while Postmodern ERP leverages microservices architecture to enable modular, independently deployable components. This shift improves fault isolation, accelerates updates, and supports seamless integration with cloud-native technologies.
API-First Integration
Legacy systems often rely on monolithic architecture with limited API capabilities, restricting seamless data exchange and real-time integration. Postmodern ERP emphasizes API-first integration, enabling modular connectivity, enhanced interoperability, and agile adaptation to evolving business requirements.
Composable ERP
Legacy systems often suffer from rigid architectures and limited integration capabilities that hinder agility and scalability in enterprise environments, whereas composable ERP in postmodern ERP frameworks enables modular, API-driven components that accelerate customization and seamless interoperability. This composable approach leverages microservices and cloud-native technologies, empowering businesses to adapt quickly to changing market demands while reducing implementation time and total cost of ownership.
Hybrid Cloud ERP
Hybrid Cloud ERP integrates the robust functionalities of legacy systems with the flexibility of postmodern ERP architectures, enabling organizations to leverage on-premises stability alongside scalable cloud services. This approach enhances data interoperability, facilitates real-time analytics, and supports modular deployment, driving digital transformation while preserving critical legacy investments.
Technical Debt Remediation
Legacy systems often accumulate significant technical debt due to outdated architectures and rigid integrations, resulting in increased maintenance costs and reduced scalability. Postmodern ERP solutions enable technical debt remediation through modular design and cloud-based flexibility, improving system agility and reducing long-term operational risks.
ERP Modernization Stack
Legacy systems often struggle with scalability and integration limitations, hindering agile business processes, whereas Postmodern ERP leverages cloud-native architectures, microservices, and API-driven integrations to enable modular, flexible, and scalable ERP modernization stacks. This shift enhances real-time data analytics, seamless third-party application compatibility, and continuous deployment, driving faster innovation cycles and reduced total cost of ownership.
Low-Code/No-Code Extensions
Legacy systems often lack flexibility and require extensive coding for modifications, hindering rapid adaptation to evolving business needs. Postmodern ERP platforms leverage low-code/no-code extensions, enabling faster customization, streamlined integration, and empowering users with minimal technical expertise to innovate workflows efficiently.
Legacy System Encapsulation
Legacy system encapsulation involves wrapping outdated software components in modern interfaces to preserve core functionality while enabling integration with Postmodern ERP architectures. This approach minimizes disruption, allowing businesses to leverage legacy data and processes within scalable, modular ERP environments that support cloud services and agile workflows.
Legacy Systems vs Postmodern ERP Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com