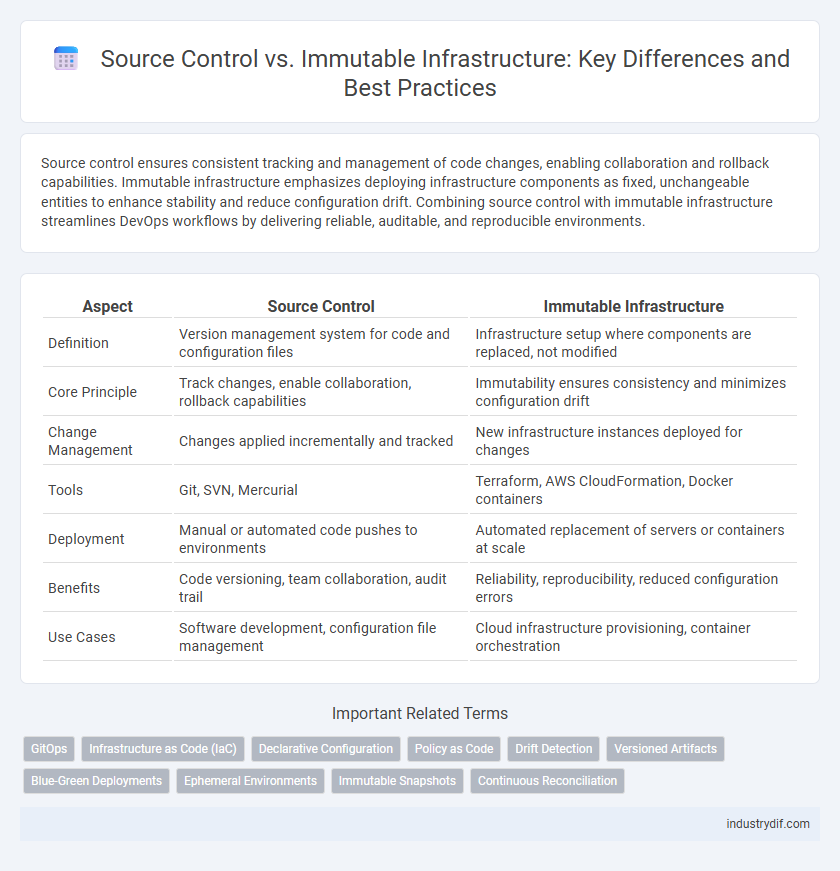
Source control ensures consistent tracking and management of code changes, enabling collaboration and rollback capabilities. Immutable infrastructure emphasizes deploying infrastructure components as fixed, unchangeable entities to enhance stability and reduce configuration drift. Combining source control with immutable infrastructure streamlines DevOps workflows by delivering reliable, auditable, and reproducible environments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Source Control | Immutable Infrastructure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Version management system for code and configuration files | Infrastructure setup where components are replaced, not modified |
| Core Principle | Track changes, enable collaboration, rollback capabilities | Immutability ensures consistency and minimizes configuration drift |
| Change Management | Changes applied incrementally and tracked | New infrastructure instances deployed for changes |
| Tools | Git, SVN, Mercurial | Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, Docker containers |
| Deployment | Manual or automated code pushes to environments | Automated replacement of servers or containers at scale |
| Benefits | Code versioning, team collaboration, audit trail | Reliability, reproducibility, reduced configuration errors |
| Use Cases | Software development, configuration file management | Cloud infrastructure provisioning, container orchestration |
Understanding Source Control in Modern Development
Source control systems like Git and Mercurial provide version tracking and collaboration tools essential for modern software development workflows. By maintaining a history of code changes, source control enables team collaboration, code review, and rollback capabilities, ensuring code integrity and traceability. Integrating source control with continuous integration and deployment pipelines streamlines development processes and supports agile practices.
Key Principles of Immutable Infrastructure
Immutable infrastructure emphasizes creating and deploying servers or components that are never modified after deployment, ensuring consistency and traceability across environments. Key principles include version-controlled, automated provisioning, and the elimination of configuration drift by replacing rather than updating resources. This approach contrasts with traditional source control systems that track code changes but do not enforce immutability of the deployed infrastructure itself.
Differences: Source Control vs Immutable Infrastructure
Source control manages code versions by tracking and storing changes in repositories like Git, enabling collaboration and rollback capabilities. Immutable infrastructure, in contrast, involves deploying fixed, unchangeable server instances where updates require replacing the entire infrastructure unit rather than altering existing ones. This fundamental difference ensures source control focuses on code lifecycle management, while immutable infrastructure emphasizes consistency, repeatability, and minimizing configuration drift in production environments.
Benefits of Source Control for Technical Teams
Source control systems enhance collaboration by providing a centralized repository that tracks code changes, enabling multiple developers to work concurrently without conflicts. They improve code quality through version history, facilitating easy rollback, auditing, and continuous integration workflows. Source control also boosts transparency and accountability by linking code modifications to specific team members, streamlining project management and debugging processes.
Advantages of Adopting Immutable Infrastructure
Immutable infrastructure enhances system reliability by ensuring that servers are replaced rather than modified, minimizing configuration drift and reducing deployment errors. It enables seamless rollbacks and faster recovery times through consistent environment replication, improving operational efficiency. This approach also strengthens security by limiting unauthorized changes and promoting version-controlled deployment artifacts.
Common Use Cases for Source Control
Source control is primarily used for managing code versions, enabling collaboration among development teams, and tracking changes over time to ensure software reliability. It supports continuous integration and deployment pipelines by storing configuration files, infrastructure-as-code scripts, and application source code in repositories like Git. Common use cases include branching strategies for feature development, rollback capabilities during incident response, and audit trails for compliance and code reviews.
Real-World Applications of Immutable Infrastructure
Immutable infrastructure enhances deployment consistency by ensuring that every server or component is replaced rather than modified, reducing configuration drift and deployment errors. Real-world applications include cloud-native environments like Kubernetes and Docker, where containers are routinely redeployed to maintain a consistent and reliable state. Enterprises leverage immutable infrastructure to streamline CI/CD pipelines, improve rollback capabilities, and enhance security by minimizing unauthorized changes.
Integrating Source Control with Immutable Infrastructure
Integrating source control with immutable infrastructure enhances deployment reliability by ensuring all infrastructure configurations are versioned and auditable within repositories like Git. This approach enables continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines to automatically provision and update immutable infrastructure components using tools such as Terraform or AWS CloudFormation. By linking source control changes directly to infrastructure deployments, organizations achieve improved traceability, rollback capability, and consistency across development, testing, and production environments.
Challenges and Pitfalls in Source Control Management
Source control management faces challenges such as merge conflicts, complex branching strategies, and limited traceability in large-scale, distributed teams. Inconsistent commit messages and inadequate automation can lead to code divergence and deployment errors. Additionally, maintaining synchronization between source control and dynamic infrastructure changes complicates configuration drift management.
Best Practices for Transitioning to Immutable Infrastructure
Transitioning to immutable infrastructure requires integrating source control systems such as Git to manage declarative infrastructure-as-code configurations, ensuring versioning and auditability. Emphasize automated pipelines for continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) to enforce consistent, repeatable infrastructure provisioning without manual changes. Adopting infrastructure immutability best practices involves using containerization tools like Docker and orchestration platforms such as Kubernetes to replace mutable components with immutable artifacts, streamlining rollback and scaling processes.
Related Important Terms
GitOps
GitOps leverages source control systems like Git to manage and automate infrastructure provisioning through declarative configurations, ensuring infrastructure remains consistent and auditable. By treating infrastructure as code stored in Git repositories, GitOps enables immutable infrastructure practices where any changes are versioned, reviewed, and automatically applied, reducing configuration drift and improving reliability.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Source Control systems provide versioning, collaboration, and traceability for Infrastructure as Code (IaC) configurations, ensuring reliable management of infrastructure changes. Immutable Infrastructure leverages IaC to deploy consistent, unchangeable server instances, enhancing system stability and simplifying rollback by replacing rather than modifying resources.
Declarative Configuration
Declarative configuration enables source control systems to manage infrastructure as code, ensuring versioned, auditable, and reproducible changes that align with immutable infrastructure principles. By defining desired states, declarative models reduce configuration drift and simplify rollback processes in immutable infrastructure deployments.
Policy as Code
Policy as Code integrates with source control systems to enforce automated validation and compliance of infrastructure changes, ensuring that immutable infrastructure configurations are consistently applied and auditable. Embedding policies directly into version-controlled repositories enables seamless collaboration, versioning, and rollback capabilities essential for managing immutable infrastructure at scale.
Drift Detection
Source control enables precise tracking of configuration changes through versioned code repositories, facilitating early identification of drift by comparing desired versus actual states. Immutable infrastructure eliminates configuration drift by redeploying fresh instances, ensuring environments remain consistent and enabling straightforward detection of deviations by enforcing state immutability.
Versioned Artifacts
Versioned artifacts play a critical role in source control by enabling precise tracking and rollback of code changes, fostering reproducibility and auditability. In immutable infrastructure, these artifacts ensure consistent and predictable deployments by packaging application binaries and configuration files into unchangeable, versioned units that prevent configuration drift.
Blue-Green Deployments
Source control systems manage code versioning and collaboration, ensuring consistent blue-green deployment configurations are tracked and reproducible. Immutable infrastructure leverages unchangeable server instances to rapidly switch between blue and green environments, minimizing downtime and deployment risks.
Ephemeral Environments
Ephemeral environments leverage immutable infrastructure principles to ensure that each deployment is consistent, reproducible, and free from configuration drift, enhancing reliability during development and testing cycles. Source control systems track infrastructure-as-code configurations and version changes, enabling automated provisioning of these transient environments with precise state management and rollback capabilities.
Immutable Snapshots
Immutable snapshots provide a robust mechanism for preserving infrastructure states by capturing exact system configurations at a specific point in time, ensuring consistency and enabling rapid recovery. Unlike traditional source control which tracks code changes, immutable infrastructure snapshots encapsulate entire environments, minimizing drift and enhancing reliability in deployment pipelines.
Continuous Reconciliation
Continuous reconciliation in source control ensures infrastructure state aligns with versioned code repositories, enabling automated drift detection and rollback. Immutable infrastructure complements this by deploying consistent, non-modifiable resources, reducing configuration drift and enhancing system reliability.
Source Control vs Immutable Infrastructure Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com