CI/CD automates software development workflows by continuously integrating code changes and deploying them through predefined pipelines, improving efficiency and reducing errors. GitOps extends this approach by using Git as the single source of truth for both application and infrastructure configurations, enabling declarative management and automated reconciliation in Kubernetes environments. This shift enhances transparency, security, and rollback capabilities by leveraging Git's version control to manage all deployment-related changes.
Table of Comparison
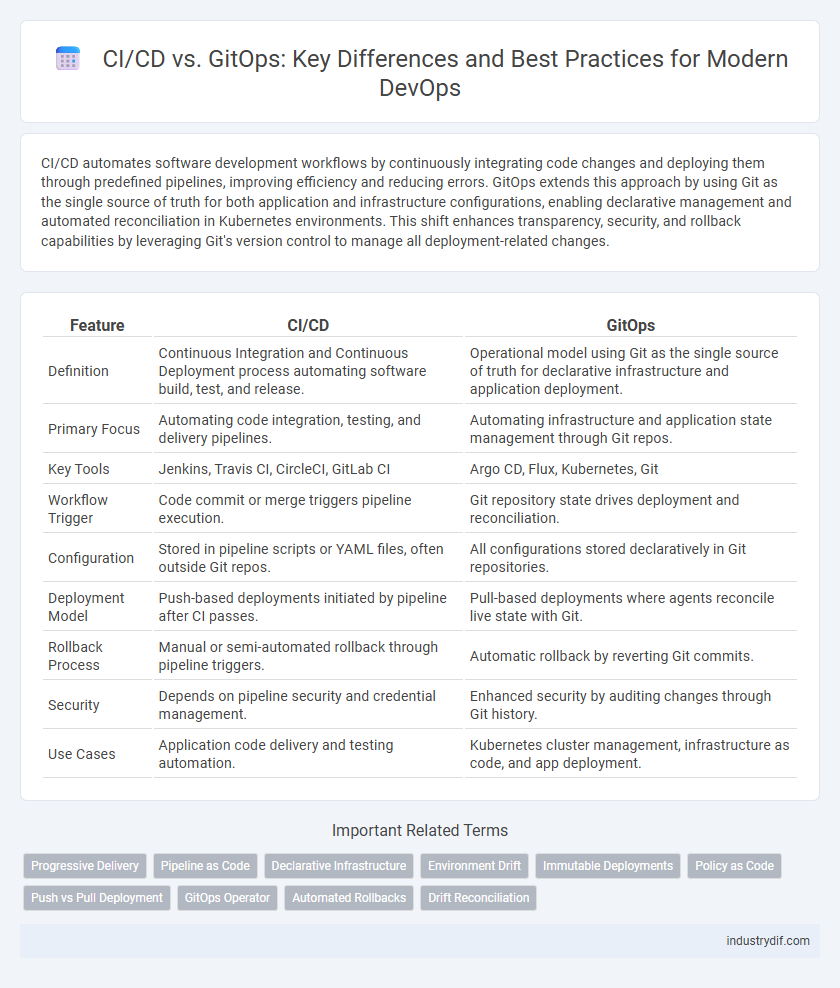
| Feature | CI/CD | GitOps |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment process automating software build, test, and release. | Operational model using Git as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application deployment. |
| Primary Focus | Automating code integration, testing, and delivery pipelines. | Automating infrastructure and application state management through Git repos. |
| Key Tools | Jenkins, Travis CI, CircleCI, GitLab CI | Argo CD, Flux, Kubernetes, Git |
| Workflow Trigger | Code commit or merge triggers pipeline execution. | Git repository state drives deployment and reconciliation. |
| Configuration | Stored in pipeline scripts or YAML files, often outside Git repos. | All configurations stored declaratively in Git repositories. |
| Deployment Model | Push-based deployments initiated by pipeline after CI passes. | Pull-based deployments where agents reconcile live state with Git. |
| Rollback Process | Manual or semi-automated rollback through pipeline triggers. | Automatic rollback by reverting Git commits. |
| Security | Depends on pipeline security and credential management. | Enhanced security by auditing changes through Git history. |
| Use Cases | Application code delivery and testing automation. | Kubernetes cluster management, infrastructure as code, and app deployment. |
Understanding CI/CD: Core Concepts and Workflow
CI/CD (Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment) automates software development by integrating code changes frequently, running automated tests, and deploying updates quickly to production environments. Core components include build automation, test automation, and deployment pipelines that ensure rapid feedback and continuous delivery of high-quality software. The workflow typically involves source code management, automated builds triggered by code commits, running tests, and automated or manual deployments, emphasizing efficiency and consistency in software delivery.
What is GitOps? Principles and Methodology
GitOps is a modern operational framework that uses Git repositories as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application deployment. It follows principles such as version control for all configuration changes, automated reconciliation loops to ensure the desired state, and continuous deployment driven by pull requests. This methodology enhances reproducibility, auditability, and reliability by leveraging Git-native workflows combined with Kubernetes operators or similar automation tools.
Key Differences Between CI/CD and GitOps
CI/CD automates the software delivery process through continuous integration and continuous deployment pipelines, focusing on code build, test, and release stages. GitOps leverages Git repositories as the single source of truth for infrastructure and application configurations, enabling automated deployments via pull requests and declarative infrastructure management. Key differences include CI/CD's pipeline-centric approach versus GitOps' declarative, version-controlled infrastructure synchronization driven by Git workflows.
Deployment Automation: CI/CD vs GitOps Approaches
CI/CD pipelines automate deployment by continuously integrating code changes and delivering them to production through scripted workflows and testing stages. GitOps leverages Git repositories as the single source of truth, using declarative configurations and automated reconciliation loops to manage and deploy infrastructure and applications. While CI/CD emphasizes pipeline-driven deployments, GitOps prioritizes version-controlled infrastructure states for consistent and auditable rollbacks.
Infrastructure as Code in CI/CD and GitOps
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) in CI/CD automates deployment through scripted pipelines that validate, test, and apply configuration changes continuously. GitOps extends IaC by using Git as the single source of truth, enabling declarative infrastructure management and automated synchronization between the Git repository and the production environment. This approach enhances auditability, rollback capabilities, and ensures consistent infrastructure states by leveraging version-controlled manifests and Kubernetes operators.
Managing Environments: Process Comparison
CI/CD pipelines automate application deployment by sequentially managing environment configurations through scripted stages, ensuring consistency and minimizing manual intervention. GitOps leverages declarative infrastructure stored in Git repositories to manage environments, enabling automatic synchronization and auditability of changes directly through version control. This process comparison highlights GitOps' advantage in providing a single source of truth and enhancing environment drift detection compared to traditional CI/CD workflows.
Version Control Strategies: CI/CD vs GitOps
Version control strategies in CI/CD primarily center on automating build and deployment pipelines triggered by code commits within repositories, ensuring continuous integration and continuous delivery throughout the software lifecycle. GitOps extends these principles by using Git repositories as the single source of truth, managing infrastructure and application configurations declaratively through pull requests and automated synchronization tools. This approach enhances auditability and rollback capabilities by treating infrastructure changes as versioned code artifacts, enabling streamlined operations and increased collaboration between development and operations teams.
Security and Compliance Considerations
CI/CD pipelines automate software delivery but often require complex security configurations to prevent vulnerabilities during build and deployment stages. GitOps enhances security and compliance by enforcing declarative infrastructure changes through version-controlled repositories, enabling audit trails and policy enforcement via tools like Kubernetes Admission Controllers and OPA Gatekeeper. Integrating GitOps with CI/CD ensures continuous deployment processes remain transparent and traceable, reducing risks of unauthorized changes and improving regulatory compliance.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Team
CI/CD pipelines automate software delivery through scripted workflows, providing flexibility for diverse development environments, while GitOps leverages Git as the single source of truth for infrastructure and application deployments, enhancing auditability and consistency. Selecting the right approach depends on team expertise, scale, and operational requirements; CI/CD suits teams needing customizable pipelines, whereas GitOps excels in Kubernetes-centric environments prioritizing declarative management. Evaluating factors like tool integration, deployment frequency, and rollback capabilities ensures alignment with your team's productivity and reliability goals.
Future Trends in CI/CD and GitOps
Future trends in CI/CD emphasize increased automation through AI-driven pipelines and enhanced security integration to address evolving cyber threats. GitOps is expected to advance with improved declarative management, leveraging Kubernetes-native tools for seamless cloud-native deployments and real-time observability. Both methodologies will converge towards unified frameworks that optimize scalability, reliability, and developer experience in complex software delivery environments.
Related Important Terms
Progressive Delivery
Progressive Delivery in CI/CD frameworks enhances software deployment by enabling incremental feature releases and real-time monitoring, reducing risk and improving feedback loops. GitOps extends this approach by leveraging declarative infrastructure and automated pull requests, ensuring consistency and traceability in progressive rollout strategies.
Pipeline as Code
Pipeline as Code in CI/CD enables automated, script-driven workflows for continuous integration and delivery, promoting flexibility and customization. GitOps extends this model by using Git repositories as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and deployment pipelines, enhancing version control and auditability.
Declarative Infrastructure
GitOps leverages declarative infrastructure to automate CI/CD pipelines by using version-controlled configuration files that define the desired system state, enabling continuous synchronization and enhanced rollback capabilities. Unlike traditional CI/CD, which often relies on imperative scripts, GitOps ensures greater consistency, auditability, and scalability through infrastructure-as-code principles integrated with Kubernetes-native tools.
Environment Drift
CI/CD pipelines automate code deployment but can struggle to prevent environment drift due to manual configuration updates and inconsistent state management. GitOps enforces declarative infrastructure through version-controlled repositories, ensuring continuous synchronization and reducing environment drift by automatically reconciling differences between the desired and actual states.
Immutable Deployments
Immutable deployments in CI/CD pipelines ensure each release is a new, unaltered artifact, preventing configuration drift and enhancing rollback capabilities. GitOps extends this principle by using declarative Git repositories as the single source of truth, automating immutable infrastructure deployment and continuous delivery with improved auditability and security.
Policy as Code
Policy as Code in CI/CD automates security and compliance checks by embedding policies directly into pipeline scripts, enabling continuous enforcement during software delivery. GitOps extends this concept by storing policies as declarative code in repositories, ensuring version-controlled, auditable, and consistent policy application across infrastructure and application environments.
Push vs Pull Deployment
CI/CD pipelines typically use push deployments where code changes are actively pushed to production environments, enabling rapid delivery and immediate feedback. GitOps relies on pull deployments by having the target environment continuously pull and reconcile desired states from a Git repository, ensuring declarative, auditable, and automated infrastructure management.
GitOps Operator
GitOps Operator automates deployment and management of Kubernetes clusters by applying Git repository changes as the single source of truth, enhancing CI/CD pipelines with declarative infrastructure and continuous reconciliation. This approach improves reliability and security by enabling version-controlled, auditable, and consistent environment configurations.
Automated Rollbacks
CI/CD pipelines enable automated rollbacks by integrating continuous testing and monitoring tools that detect failures and trigger rollback procedures to previous stable versions. GitOps enhances this process by using declarative configurations stored in Git repositories, ensuring automatic rollback synchronization through version-controlled state reconciliation.
Drift Reconciliation
GitOps automates drift reconciliation by continuously monitoring declarative infrastructure states in the Git repository and enforcing consistency in the cluster, minimizing configuration drift. CI/CD pipelines primarily handle application delivery and testing but often require additional tooling or manual intervention to detect and resolve infrastructure drift effectively.
CI/CD vs GitOps Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com