A logistics hub serves as a large-scale distribution center designed to consolidate inventory and streamline regional or national supply chains, optimizing transportation routes and reducing delivery times. Micro-fulfillment centers are smaller, strategically located facilities that leverage automation to quickly process online orders and support last-mile delivery in urban areas. Choosing between a logistics hub and a micro-fulfillment center depends on the balance between inventory volume, delivery speed, and geographic reach required for efficient transportation management.
Table of Comparison
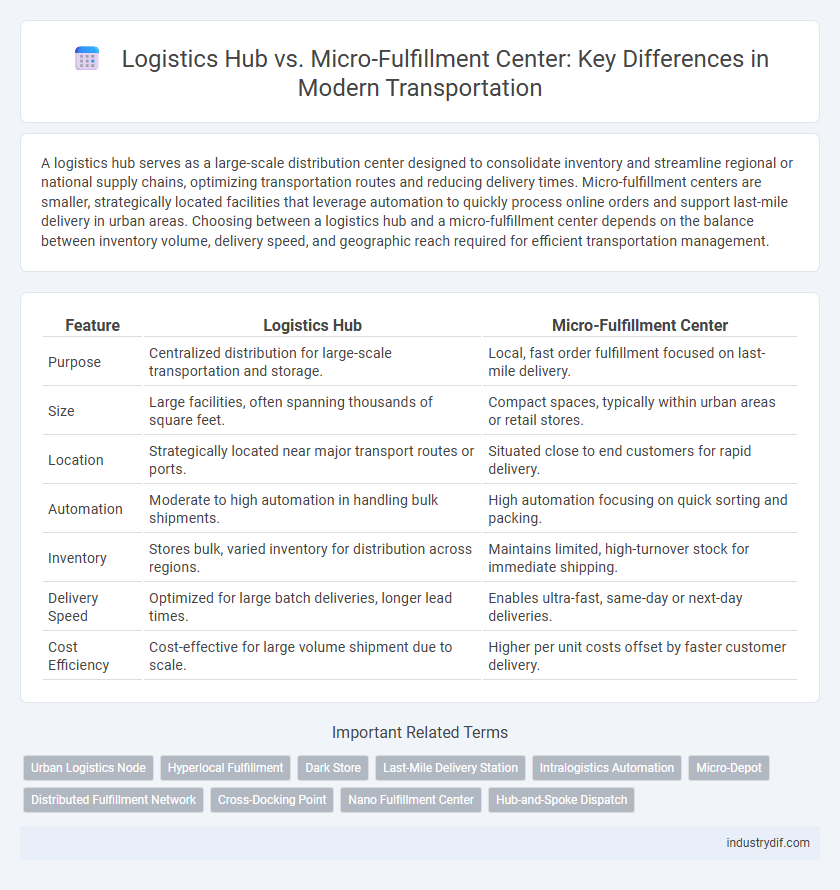
| Feature | Logistics Hub | Micro-Fulfillment Center |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Centralized distribution for large-scale transportation and storage. | Local, fast order fulfillment focused on last-mile delivery. |
| Size | Large facilities, often spanning thousands of square feet. | Compact spaces, typically within urban areas or retail stores. |
| Location | Strategically located near major transport routes or ports. | Situated close to end customers for rapid delivery. |
| Automation | Moderate to high automation in handling bulk shipments. | High automation focusing on quick sorting and packing. |
| Inventory | Stores bulk, varied inventory for distribution across regions. | Maintains limited, high-turnover stock for immediate shipping. |
| Delivery Speed | Optimized for large batch deliveries, longer lead times. | Enables ultra-fast, same-day or next-day deliveries. |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for large volume shipment due to scale. | Higher per unit costs offset by faster customer delivery. |
Overview: Defining Logistics Hubs and Micro-Fulfillment Centers
Logistics hubs serve as centralized locations that manage the storage, sorting, and distribution of large volumes of goods across extensive supply chains, optimizing transportation efficiency and reducing delivery times. Micro-fulfillment centers are compact, automated warehouses situated close to urban areas, designed to expedite last-mile delivery by quickly processing e-commerce orders. Both play critical roles in modern logistics, with hubs focused on bulk distribution and micro-fulfillment centers enhancing rapid, localized order fulfillment.
Core Functions: Operations of Each Model
Logistics hubs primarily focus on large-scale inventory storage, cross-docking, and long-haul transportation coordination to optimize supply chain efficiency and reduce delivery times. Micro-fulfillment centers specialize in rapid order processing and last-mile delivery by utilizing automated systems and proximity to end consumers to expedite e-commerce fulfillment. The operational distinction lies in logistics hubs managing bulk distribution across regions, while micro-fulfillment centers handle high-velocity, small-batch orders within urban areas.
Location Strategy: Urban vs. Regional Placement
Logistics hubs are typically located in regional areas with greater space availability, supporting large-scale distribution and efficient freight movement. Micro-fulfillment centers prioritize urban locations to reduce last-mile delivery time and enhance responsiveness to consumer demand. Strategic placement balances proximity to customers with operational efficiency to optimize supply chain performance.
Space and Infrastructure Requirements
Logistics hubs require extensive space and robust infrastructure to accommodate large-scale storage, cross-docking, and distribution activities, supporting high volumes of freight and complex supply chain operations. Micro-fulfillment centers demand significantly less space, often located within urban areas or retail environments, optimized for automated systems to enable rapid, small-batch order fulfillment. The contrast in space and infrastructure needs directly impacts site selection, operational costs, and the scalability of each facility type within the transportation and logistics network.
Technology Integration and Automation
Logistics hubs leverage advanced technology integration and automation to optimize large-scale inventory management, utilizing automated sorting systems, robotics, and AI-driven demand forecasting to enhance supply chain efficiency. Micro-fulfillment centers prioritize hyper-localized automation, employing compact robotics and real-time data analytics to accelerate order processing and last-mile delivery in urban environments. Both facilities integrate IoT and warehouse management systems, but micro-fulfillment centers focus on agility and speed, while logistics hubs emphasize volume and network optimization.
Inventory Management Differences
Logistics hubs manage large-scale inventory with centralized stock optimized for bulk shipments and long-term storage, supporting regional or national distribution networks. Micro-fulfillment centers operate with smaller, highly dynamic inventory tailored for rapid order fulfillment in urban areas, emphasizing speed and last-mile delivery efficiency. Inventory management in logistics hubs focuses on maximizing storage capacity and reducing transportation costs, while micro-fulfillment centers prioritize real-time inventory tracking and quick replenishment cycles.
Shipping Speed and Last-Mile Delivery
Logistics hubs streamline bulk shipping by consolidating inventory in centralized locations, enabling efficient long-haul transportation and volume-based cost savings. Micro-fulfillment centers prioritize rapid last-mile delivery by positioning goods closer to end consumers, drastically reducing transit times and enhancing same-day or next-day shipping speed. Combining centralized logistics hubs with strategically placed micro-fulfillment centers optimizes both shipping speed and the flexibility required for expedited last-mile delivery services.
Scalability and Flexibility in Operations
Logistics hubs offer extensive scalability by handling large volumes of goods across multiple transportation modes, enabling efficient regional distribution and long-term growth. Micro-fulfillment centers provide high operational flexibility by supporting rapid order processing and customizable inventory management closer to end consumers, ideal for urban and last-mile delivery demands. Both infrastructure types optimize supply chain responsiveness, but logistics hubs excel in bulk handling while micro-fulfillment centers enhance speed and adaptability at a localized scale.
Cost Considerations and Investment
A logistics hub typically requires a significant initial investment due to its large scale and infrastructure needs, encompassing warehousing, transportation, and cross-docking facilities. Micro-fulfillment centers demand lower capital expenditure by utilizing automated systems within smaller urban spaces, which reduces last-mile delivery costs. Cost considerations for logistics hubs favor bulk storage and distribution economies, while micro-fulfillment centers optimize investment in technology and speed, targeting faster order fulfillment and reduced inventory holding expenses.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Selecting between a logistics hub and a micro-fulfillment center depends on your business size, product type, and delivery speed requirements. Logistics hubs offer centralized inventory management and bulk shipping advantages, ideal for large-scale operations with extensive distribution networks. Micro-fulfillment centers prioritize quick order processing and last-mile delivery efficiency, making them suitable for e-commerce businesses targeting rapid local fulfillment.
Related Important Terms
Urban Logistics Node
A logistics hub serves as a large-scale transportation and distribution center facilitating the efficient movement of goods across long distances, while a micro-fulfillment center optimizes last-mile delivery by operating smaller, automated facilities within urban areas. Urban logistics nodes leverage micro-fulfillment centers to reduce delivery times, lower transportation costs, and minimize environmental impact in densely populated cities.
Hyperlocal Fulfillment
Logistics hubs serve as centralized distribution points managing large-scale inventory flow, whereas micro-fulfillment centers operate within urban areas to enable hyperlocal fulfillment by quickly processing and delivering orders to nearby customers. Hyperlocal fulfillment through micro-fulfillment centers reduces last-mile delivery time, lowers transportation costs, and enhances customer satisfaction by leveraging proximity to end consumers.
Dark Store
Dark stores operate as micro-fulfillment centers designed for rapid, local delivery, streamlining inventory management and reducing last-mile transit times. Unlike traditional logistics hubs, dark stores prioritize immediate consumer demand fulfillment through automated systems and strategic urban locations.
Last-Mile Delivery Station
A logistics hub serves as a centralized distribution center handling large-scale inventory storage and bulk shipments, while a micro-fulfillment center operates closer to urban areas, enabling faster processing and delivery of smaller, last-mile orders. Last-mile delivery stations prioritize proximity to customers, reducing transit times and increasing delivery efficiency by leveraging micro-fulfillment centers' compact footprint and automated systems.
Intralogistics Automation
Logistics hubs serve as centralized nodes integrating large-scale intralogistics automation systems such as automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and conveyor networks to optimize bulk inventory handling and distribution efficiency. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage advanced robotics and AI-driven picking technologies to enable rapid, high-density order processing within urban areas, reducing last-mile delivery times and operational costs.
Micro-Depot
Micro-depots, integral to urban logistics, enable last-mile delivery efficiency by serving as compact distribution points that reduce transit times and costs compared to traditional logistics hubs. These facilities enhance supply chain responsiveness in densely populated areas by facilitating rapid order fulfillment and minimizing urban congestion through localized inventory storage.
Distributed Fulfillment Network
A distributed fulfillment network leverages both logistics hubs and micro-fulfillment centers to optimize delivery speed and inventory management, with logistics hubs serving as centralized storage and sorting facilities while micro-fulfillment centers enable faster last-mile delivery within urban areas. This hybrid model enhances supply chain efficiency by balancing bulk inventory consolidation with agile, localized order processing.
Cross-Docking Point
A logistics hub serves as a central cross-docking point where goods are quickly transferred between inbound and outbound transportation, minimizing storage time and improving supply chain efficiency. In contrast, a micro-fulfillment center focuses on rapid order assembly and last-mile delivery, handling smaller inventory volumes closer to the end customer rather than acting primarily as a transfer node.
Nano Fulfillment Center
Nano fulfillment centers, a compact evolution of logistics hubs, streamline last-mile delivery by focusing on hyper-local inventory storage and rapid order processing. Unlike traditional micro-fulfillment centers, nano fulfillment centers optimize space within urban settings, enhancing delivery speed and reducing transportation costs for e-commerce and retail sectors.
Hub-and-Spoke Dispatch
Logistics hubs serve as central nodes in the hub-and-spoke dispatch model, optimizing the aggregation and redistribution of goods across wide geographic areas, whereas micro-fulfillment centers provide rapid, localized order processing closer to the end consumer. This structure enhances delivery efficiency by leveraging large-scale inventory consolidation at logistics hubs and swift last-mile fulfillment through micro-fulfillment centers.
Logistics hub vs micro-fulfillment center Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com