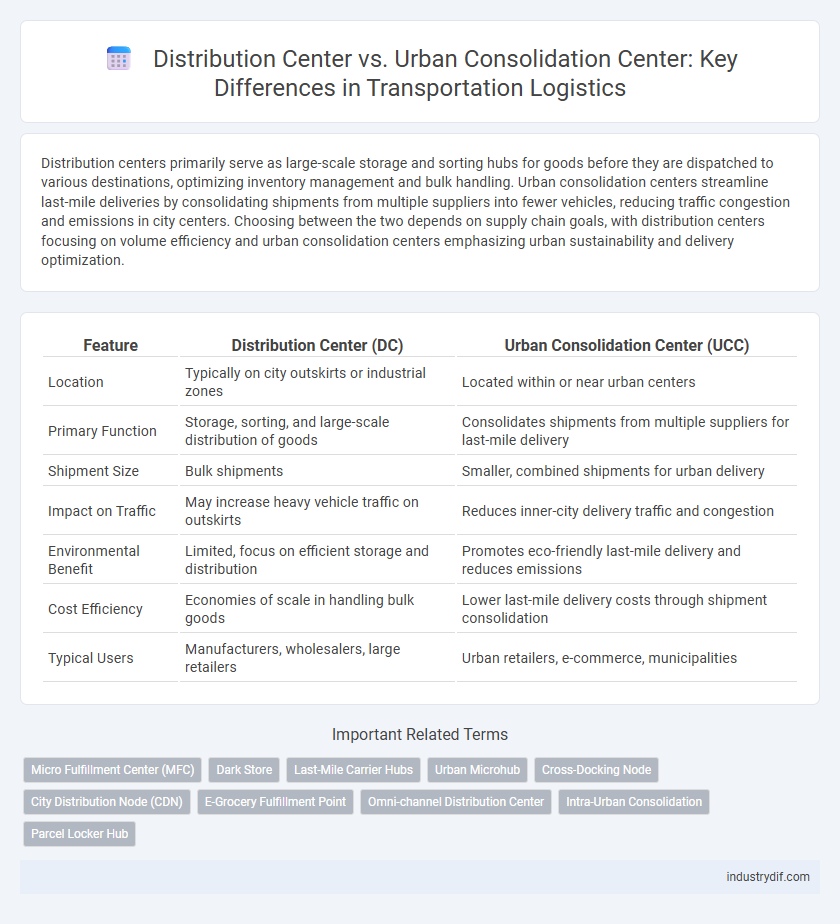
Distribution centers primarily serve as large-scale storage and sorting hubs for goods before they are dispatched to various destinations, optimizing inventory management and bulk handling. Urban consolidation centers streamline last-mile deliveries by consolidating shipments from multiple suppliers into fewer vehicles, reducing traffic congestion and emissions in city centers. Choosing between the two depends on supply chain goals, with distribution centers focusing on volume efficiency and urban consolidation centers emphasizing urban sustainability and delivery optimization.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Distribution Center (DC) | Urban Consolidation Center (UCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Typically on city outskirts or industrial zones | Located within or near urban centers |
| Primary Function | Storage, sorting, and large-scale distribution of goods | Consolidates shipments from multiple suppliers for last-mile delivery |
| Shipment Size | Bulk shipments | Smaller, combined shipments for urban delivery |
| Impact on Traffic | May increase heavy vehicle traffic on outskirts | Reduces inner-city delivery traffic and congestion |
| Environmental Benefit | Limited, focus on efficient storage and distribution | Promotes eco-friendly last-mile delivery and reduces emissions |
| Cost Efficiency | Economies of scale in handling bulk goods | Lower last-mile delivery costs through shipment consolidation |
| Typical Users | Manufacturers, wholesalers, large retailers | Urban retailers, e-commerce, municipalities |
Understanding Distribution Centers: Key Functions
Distribution centers serve as pivotal hubs in supply chain management by efficiently receiving, storing, and dispatching products to retailers or end customers, ensuring optimized inventory control and order fulfillment. These facilities utilize advanced warehouse management systems (WMS) to streamline operations such as picking, packing, and sorting, which reduces lead times and enhances accuracy. Urban consolidation centers complement these by consolidating deliveries in dense city areas, minimizing traffic congestion and lowering carbon emissions while supporting last-mile distribution efficiency.
What are Urban Consolidation Centers?
Urban Consolidation Centers (UCCs) are strategically located facilities in metropolitan areas designed to consolidate shipments from multiple suppliers into fewer, larger deliveries. This process reduces urban freight traffic, decreases emissions, and enhances delivery efficiency by minimizing the number of individual trucks entering congested city zones. UCCs support sustainable urban logistics by enabling last-mile deliveries with smaller, cleaner vehicles or cargo bikes, improving overall transportation management in dense urban environments.
Core Differences Between Distribution Centers and Urban Consolidation Centers
Distribution centers are large-scale facilities designed for storing, sorting, and dispatching goods to various locations, prioritizing inventory management and bulk shipments. Urban consolidation centers operate within city limits, focusing on reducing urban freight traffic by consolidating shipments from multiple suppliers into fewer, more efficient deliveries to retailers or end customers. The core difference lies in their operational scope: distribution centers function as regional hubs with extensive storage, whereas urban consolidation centers emphasize last-mile delivery optimization and environmental sustainability in congested urban environments.
Strategic Locations: DCs vs UCCs
Distribution Centers (DCs) are strategically located on the outskirts of cities or near major highways to facilitate large-scale storage and efficient regional transportation, optimizing long-haul and bulk cargo movement. Urban Consolidation Centers (UCCs) are positioned within urban areas to streamline last-mile delivery by consolidating shipments from multiple carriers, reducing traffic congestion and carbon emissions. The strategic placement of DCs supports wide-area distribution networks, while UCCs enhance delivery efficiency and sustainability within dense city environments.
Role in the Supply Chain: DCs vs UCCs
Distribution Centers (DCs) serve as large-scale hubs focused on inventory storage, order fulfillment, and large shipment handling to streamline long-distance transportation and regional distribution. Urban Consolidation Centers (UCCs) function as localized nodes that aggregate goods from multiple suppliers to reduce urban freight traffic, enhance delivery efficiency, and minimize environmental impact in densely populated city areas. While DCs optimize supply chain efficiency through bulk logistics and warehouse management, UCCs emphasize last-mile delivery improvements and traffic decongestion in metropolitan zones.
Benefits of Using Distribution Centers
Distribution centers streamline inventory management by consolidating goods from multiple suppliers, enabling faster order fulfillment and reducing transportation costs through bulk shipments. They enhance supply chain efficiency by providing centralized storage, which minimizes stockouts and improves demand forecasting accuracy. Using distribution centers supports scalability and flexibility in logistics operations, facilitating quicker responses to market changes and customer demands.
Advantages of Urban Consolidation Centers in Urban Logistics
Urban Consolidation Centers (UCCs) significantly reduce last-mile delivery costs and emissions by consolidating shipments from multiple carriers into fewer, fuller loads. UCCs improve urban traffic flow and decrease congestion, enhancing overall city air quality and minimizing delivery times compared to traditional Distribution Centers. The centralized location of UCCs facilitates efficient use of low-emission vehicles, supporting sustainable urban logistics and regulatory compliance.
Challenges Faced by Both Facility Types
Distribution centers and urban consolidation centers both face significant logistical challenges, including space constraints and traffic congestion that impact efficient goods handling and delivery. Distribution centers struggle with high inventory turnover and the need for rapid order fulfillment to meet e-commerce demands. Urban consolidation centers must address regulatory restrictions, limited operating hours, and coordinating multiple carriers to reduce urban freight traffic and emissions.
Impact on Last-Mile Delivery Operations
Distribution centers optimize last-mile delivery by centralizing inventory and enabling bulk shipments, which reduces overall transportation costs but can increase delivery time due to long-distance transportation. Urban consolidation centers improve last-mile delivery efficiency by consolidating shipments within city limits, decreasing traffic congestion and emissions while enhancing delivery speed and reliability. The choice between these facilities depends on balancing cost-efficiency with urban sustainability and customer service goals.
Choosing the Right Facility for Your Transportation Needs
Selecting the right facility between a Distribution Center (DC) and an Urban Consolidation Center (UCC) depends on your supply chain priorities and urban delivery challenges. Distribution Centers excel in large-scale storage and regional order fulfillment, optimizing inventory management and transportation costs across broader areas. Urban Consolidation Centers focus on last-mile delivery efficiency and reduced urban congestion by aggregating shipments closer to city centers, making them ideal for businesses aiming to enhance sustainability and minimize delivery times in dense metropolitan areas.
Related Important Terms
Micro Fulfillment Center (MFC)
Micro Fulfillment Centers (MFCs) optimize last-mile delivery by integrating automated storage and retrieval systems within Distribution Centers (DCs) or Urban Consolidation Centers (UCCs), significantly reducing delivery times and costs in dense urban areas. Unlike traditional DCs that handle bulk inventory, MFCs focus on rapid order fulfillment in UCCs, streamlining urban logistics and minimizing congestion.
Dark Store
A Distribution Center primarily handles bulk storage and large-scale order fulfillment for various retail locations, whereas an Urban Consolidation Center focuses on aggregating shipments in dense city areas to reduce congestion and improve last-mile delivery efficiency. Dark Stores operate as specialized urban fulfillment hubs, often similar to Urban Consolidation Centers, optimizing rapid delivery by functioning exclusively as inventory points without customer-facing retail services.
Last-Mile Carrier Hubs
Distribution Centers serve as large-scale logistics facilities focused on sorting, storing, and dispatching goods over long distances, whereas Urban Consolidation Centers specialize in aggregating shipments within city limits to streamline last-mile delivery. Last-mile carrier hubs in Urban Consolidation Centers enhance efficiency by reducing traffic congestion, lowering emissions, and enabling faster deliveries through optimized route planning and consolidated freight loads.
Urban Microhub
Urban microhubs serve as localized distribution points within urban consolidation centers, significantly reducing last-mile delivery distances and congestion in dense city environments. By clustering shipments for multiple carriers, these microhubs optimize transportation routes, lower delivery costs, and enhance sustainability in urban freight logistics.
Cross-Docking Node
A Distribution Center primarily functions as a storage hub where goods are received, sorted, and held before being dispatched, whereas an Urban Consolidation Center operates as a cross-docking node that consolidates shipments from multiple suppliers for direct, efficient delivery to urban end points, minimizing storage time. Cross-docking at Urban Consolidation Centers reduces transportation costs and environmental impact by streamlining last-mile delivery with faster turnover and optimized load combinations.
City Distribution Node (CDN)
A City Distribution Node (CDN) serves as a strategic urban logistics hub that streamlines last-mile delivery by consolidating shipments within metropolitan areas, enhancing efficiency and reducing traffic congestion. Unlike traditional distribution centers, CDNs optimize urban freight flows by leveraging proximity to end consumers, supporting sustainable transportation and faster delivery times.
E-Grocery Fulfillment Point
A Distribution Center (DC) serves as a large-scale warehouse facilitating bulk storage and long-distance transportation, while an Urban Consolidation Center (UCC) operates as a strategically located facility within city limits designed to aggregate shipments for last-mile delivery. In e-grocery fulfillment, UCCs optimize urban logistics by reducing delivery times and carbon emissions through consolidated loads, contrasting with DCs that primarily support inventory management and regional distribution.
Omni-channel Distribution Center
An Omni-channel Distribution Center integrates inventory and fulfillment processes across multiple sales channels, enabling faster, more flexible deliveries to end customers and retail locations, unlike Urban Consolidation Centers which primarily focus on reducing last-mile congestion by consolidating shipments in dense urban areas. This strategic alignment enhances supply chain efficiency by minimizing transit times and optimizing inventory allocation across brick-and-mortar stores, e-commerce platforms, and direct-to-consumer shipments.
Intra-Urban Consolidation
Intra-urban consolidation involves centralizing shipments within city boundaries to optimize last-mile delivery efficiency, often utilizing Urban Consolidation Centers (UCCs) that reduce traffic congestion and emissions by pooling loads from multiple suppliers. Distribution Centers (DCs) primarily focus on bulk storage and regional distribution, whereas UCCs specialize in facilitating sustainable and streamlined intra-city cargo handling through coordinated freight consolidation.
Parcel Locker Hub
A Distribution Center (DC) serves as a large-scale facility for sorting and dispatching bulk shipments across wide geographic regions, while an Urban Consolidation Center (UCC) focuses on streamlining last-mile deliveries in dense city areas by aggregating parcels to reduce traffic and emissions. Parcel Locker Hubs, integral to UCCs, provide secure, automated pick-up points that enhance delivery efficiency, reduce failed delivery attempts, and support sustainable urban logistics.
Distribution Center vs Urban Consolidation Center Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com