Freight logistics typically involve the large-scale movement of goods through global supply chains, emphasizing efficiency in bulk transportation and long-distance delivery. Micro-fulfillment centers prioritize speed and localization, enabling rapid order processing and last-mile delivery within urban areas. Comparing the two highlights a shift from high-volume, centralized distribution toward agile, customer-centric delivery models.
Table of Comparison
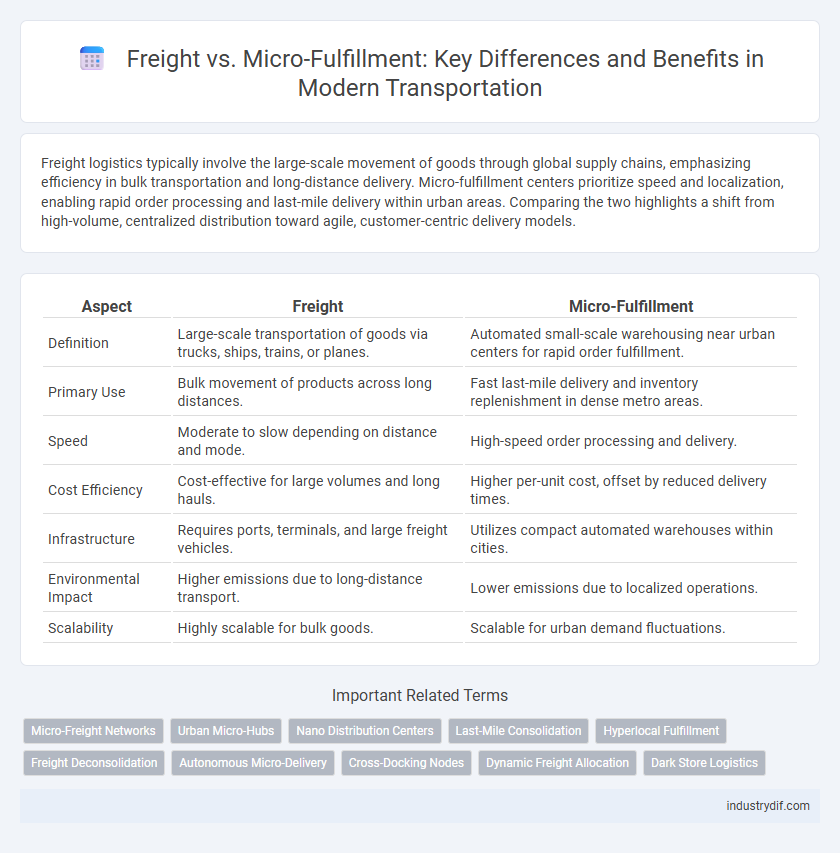
| Aspect | Freight | Micro-Fulfillment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large-scale transportation of goods via trucks, ships, trains, or planes. | Automated small-scale warehousing near urban centers for rapid order fulfillment. |
| Primary Use | Bulk movement of products across long distances. | Fast last-mile delivery and inventory replenishment in dense metro areas. |
| Speed | Moderate to slow depending on distance and mode. | High-speed order processing and delivery. |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for large volumes and long hauls. | Higher per-unit cost, offset by reduced delivery times. |
| Infrastructure | Requires ports, terminals, and large freight vehicles. | Utilizes compact automated warehouses within cities. |
| Environmental Impact | Higher emissions due to long-distance transport. | Lower emissions due to localized operations. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for bulk goods. | Scalable for urban demand fluctuations. |
Understanding Freight Logistics
Freight logistics involves managing the transportation of large volumes of goods over long distances using trucks, ships, or trains, emphasizing efficiency in supply chain coordination and cost reduction. Micro-fulfillment focuses on localized warehousing strategies to expedite last-mile delivery, often employing automated systems within urban centers to meet rapid consumer demand. Understanding freight logistics is crucial for integrating macro-level transport networks with micro-fulfillment operations to optimize inventory flow and delivery speed.
What Is Micro-Fulfillment?
Micro-fulfillment refers to a logistics strategy that utilizes small, localized warehouses or fulfillment centers to rapidly process and deliver goods, often situated within urban areas or near end customers. This approach contrasts with traditional freight systems that involve large-scale, centralized distribution hubs requiring longer transit times. Micro-fulfillment enhances speed, reduces transportation costs, and supports same-day or next-day deliveries, meeting the growing demand for quick order fulfillment in e-commerce and retail sectors.
Key Differences Between Freight and Micro-Fulfillment
Freight transportation involves the large-scale movement of goods over long distances using trucks, ships, or trains, focusing on bulk shipments and supply chain efficiency. Micro-fulfillment centers prioritize rapid, localized order processing and delivery, leveraging automation to handle small, high-frequency orders close to the end consumer. Key differences include scale, delivery speed, and technological integration, where freight emphasizes volume and cost-effectiveness, while micro-fulfillment targets speed and convenience in urban areas.
Advantages of Freight Solutions
Freight solutions offer substantial cost efficiency for transporting large volumes of goods over long distances, reducing per-unit shipping expenses significantly. They provide enhanced capacity and scalability, enabling businesses to handle bulk shipments and seasonal demand fluctuations with ease. Advanced freight logistics technologies ensure improved route optimization and real-time tracking, resulting in faster, more reliable deliveries compared to micro-fulfillment models.
Benefits of Micro-Fulfillment Centers
Micro-fulfillment centers significantly reduce last-mile delivery times by strategically locating inventory closer to urban consumers, enhancing speed and convenience in e-commerce fulfillment. These centers optimize space and labor costs through automation and streamlined processes, enabling efficient handling of smaller, frequent orders. Compared to traditional freight distribution, micro-fulfillment supports greater inventory flexibility and responsiveness, reducing shipping expenses and environmental impact.
Cost Considerations in Freight vs Micro-Fulfillment
Freight transportation often incurs higher costs due to fuel, labor, and infrastructure expenses associated with long-haul delivery and large shipment volumes. Micro-fulfillment centers reduce last-mile delivery costs by shortening shipping distances and increasing order processing efficiency, leading to lower fulfillment expenses. Companies must balance freight economies of scale against micro-fulfillment's agility and reduced delivery times to optimize overall cost structures.
Impact on Delivery Speed and Efficiency
Freight transportation involves bulk shipment over long distances, often resulting in longer delivery times but cost efficiency for large volumes. Micro-fulfillment centers, strategically located near urban areas, accelerate delivery speed by enabling rapid sorting and shipping of smaller, customer-specific orders. Integrating micro-fulfillment with traditional freight logistics enhances overall efficiency by balancing bulk transport economies with quick last-mile delivery.
Freight and Micro-Fulfillment in E-Commerce
Freight transportation plays a crucial role in e-commerce by enabling bulk shipments of goods from manufacturers to distribution centers, optimizing economies of scale and reducing per-unit shipping costs. Micro-fulfillment centers, strategically located near urban areas, enhance last-mile delivery efficiency by rapidly processing smaller orders and minimizing delivery times. Integrating freight solutions with micro-fulfillment systems supports seamless inventory flow and meets growing consumer demand for fast, reliable e-commerce delivery.
Environmental Implications
Freight transportation significantly impacts the environment through high carbon emissions and energy consumption due to long-haul trucking and shipping. Micro-fulfillment centers reduce the carbon footprint by shortening delivery distances and optimizing last-mile logistics with localized inventory. Implementing micro-fulfillment solutions can drastically lower transportation-related greenhouse gas emissions, supporting sustainable supply chain practices.
Future Trends in Freight and Micro-Fulfillment
Future trends in freight emphasize automation, real-time tracking, and sustainable practices to enhance efficiency and reduce carbon footprints. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage advanced robotics and AI-driven inventory management to speed up last-mile delivery and meet growing e-commerce demand. Integration of digital platforms and smart logistics solutions will drive seamless coordination between freight operations and micro-fulfillment networks.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Freight Networks
Micro-freight networks optimize last-mile delivery by leveraging localized, smaller-scale distribution hubs to reduce transit times and costs, enhancing efficiency in urban logistics. These networks support micro-fulfillment centers by enabling rapid redistribution of goods, addressing the growing demand for faster deliveries and reducing dependency on large, centralized warehouses.
Urban Micro-Hubs
Urban micro-hubs optimize last-mile delivery by integrating micro-fulfillment centers with freight operations, reducing transit times and transportation costs in densely populated areas. These hubs leverage data analytics and real-time tracking to streamline inventory management and enhance delivery efficiency within urban logistics networks.
Nano Distribution Centers
Nano distribution centers represent a breakthrough in freight logistics by enabling ultra-localized micro-fulfillment that significantly reduces delivery times and transportation costs. These compact hubs streamline last-mile freight operations through advanced automation and strategic placement, optimizing urban supply chains and minimizing carbon emissions.
Last-Mile Consolidation
Last-mile consolidation in transportation optimizes freight delivery by combining multiple small shipments into a single route, reducing costs and carbon emissions. Micro-fulfillment centers strategically located near urban areas enable faster, more efficient last-mile distribution, bridging the gap between large freight shipments and customer demand.
Hyperlocal Fulfillment
Hyperlocal fulfillment leverages micro-fulfillment centers strategically located near urban hubs to expedite last-mile delivery, significantly reducing transit times and transportation costs compared to traditional freight methods. This approach enhances supply chain efficiency by minimizing large-scale freight reliance, optimizing inventory distribution, and meeting increasing consumer demand for rapid delivery in densely populated areas.
Freight Deconsolidation
Freight deconsolidation streamlines supply chains by breaking down large shipments into smaller, manageable loads for faster delivery in micro-fulfillment centers. This process reduces transportation costs, improves inventory accuracy, and enhances last-mile delivery efficiency in urban logistics.
Autonomous Micro-Delivery
Autonomous micro-delivery leverages robotics and AI to efficiently transport small parcels within urban environments, reducing reliance on traditional freight systems that handle bulk shipments over longer distances. This innovation enhances last-mile delivery speed and accuracy by utilizing compact, self-driving vehicles optimized for dense city logistics.
Cross-Docking Nodes
Cross-docking nodes serve as critical intersections in freight logistics, enabling the rapid transfer of goods between inbound and outbound transportation without long-term storage. In micro-fulfillment, these nodes optimize last-mile delivery efficiency by integrating smaller, localized inventory hubs within the broader freight network.
Dynamic Freight Allocation
Dynamic freight allocation enhances transportation efficiency by optimizing load distribution based on real-time demand, reducing costs and transit times in both freight and micro-fulfillment operations. Integrating AI-driven algorithms enables precise matching of shipments to available carriers, increasing supply chain agility and improving last-mile delivery performance.
Dark Store Logistics
Dark store logistics optimize micro-fulfillment by enabling rapid order processing and last-mile delivery within urban areas, contrasting with traditional freight systems that emphasize bulk transportation over longer distances. Leveraging localized inventory hubs, dark stores reduce delivery times and increase supply chain efficiency by minimizing the need for extensive freight movements.
Freight vs Micro-Fulfillment Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com