Logistics encompasses the broad management of transporting goods over long distances, involving warehousing, inventory control, and route planning to optimize supply chains. Hyperlocal delivery focuses on the rapid transport of products within a confined geographic area, often completing orders within hours to meet immediate customer demands. While logistics prioritizes efficiency and scale, hyperlocal delivery emphasizes speed and convenience, catering to urban markets and time-sensitive needs.
Table of Comparison
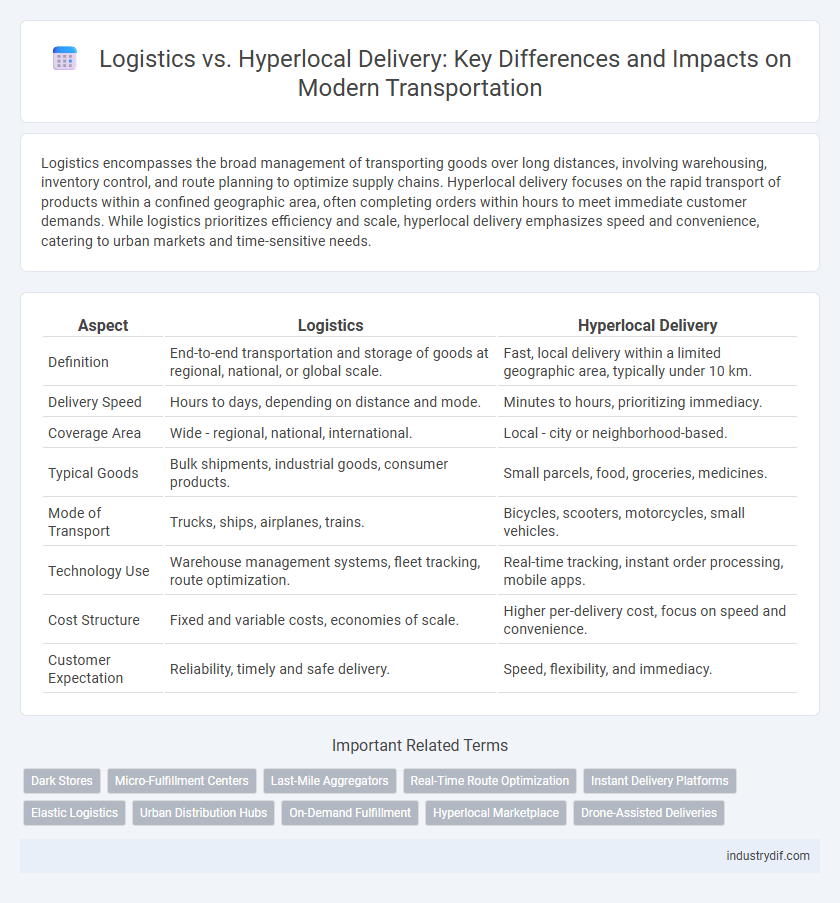
| Aspect | Logistics | Hyperlocal Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | End-to-end transportation and storage of goods at regional, national, or global scale. | Fast, local delivery within a limited geographic area, typically under 10 km. |
| Delivery Speed | Hours to days, depending on distance and mode. | Minutes to hours, prioritizing immediacy. |
| Coverage Area | Wide - regional, national, international. | Local - city or neighborhood-based. |
| Typical Goods | Bulk shipments, industrial goods, consumer products. | Small parcels, food, groceries, medicines. |
| Mode of Transport | Trucks, ships, airplanes, trains. | Bicycles, scooters, motorcycles, small vehicles. |
| Technology Use | Warehouse management systems, fleet tracking, route optimization. | Real-time tracking, instant order processing, mobile apps. |
| Cost Structure | Fixed and variable costs, economies of scale. | Higher per-delivery cost, focus on speed and convenience. |
| Customer Expectation | Reliability, timely and safe delivery. | Speed, flexibility, and immediacy. |
Understanding Logistics: Definition and Scope
Logistics encompasses the comprehensive management of the flow of goods, information, and resources from origin to consumption, involving transportation, warehousing, inventory control, and order fulfillment. It ensures efficient coordination across supply chains to optimize delivery timelines, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Hyperlocal delivery, a subset within this framework, focuses on rapid, last-mile distribution within confined geographic areas to meet immediate consumer demands.
What is Hyperlocal Delivery? Key Concepts
Hyperlocal delivery refers to the rapid transportation of goods within a limited geographic area, typically a city or neighborhood, often leveraging real-time data and local courier networks. Key concepts include speed, proximity, and convenience, with transactions usually fulfilled within hours to meet immediate consumer demands. This delivery model emphasizes last-mile efficiency, leveraging technology for route optimization and inventory management to ensure timely, on-demand service.
Core Differences: Logistics vs Hyperlocal Delivery
Logistics involves managing the entire supply chain, including warehousing, inventory management, and long-distance transportation, optimized for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Hyperlocal delivery emphasizes rapid, last-mile delivery within a limited geographic area, often under a few hours, prioritizing speed and immediacy for consumer convenience. The core difference lies in logistics' broad scope across regions versus hyperlocal delivery's focus on instant fulfillment within close proximity.
Technology’s Role in Modern Transportation
Advanced technology drives efficiency in logistics through real-time tracking, automated warehousing, and AI-powered route optimization, enhancing large-scale supply chain management. Hyperlocal delivery leverages mobile apps, GPS navigation, and instant communication platforms to ensure rapid, last-mile delivery within localized areas. Both sectors rely heavily on data analytics and IoT devices to improve accuracy, reduce costs, and increase customer satisfaction in modern transportation systems.
Speed and Efficiency: Comparative Analysis
Logistics involves the coordination of large-scale transportation networks to optimize the movement of goods over long distances, prioritizing efficiency through route planning and bulk shipments. Hyperlocal delivery focuses on ultra-fast, same-day or even hour-based delivery within a limited geographic area, leveraging proximity to enhance speed. The efficiency of logistics lies in its capacity to handle volume and cost-effectiveness, while hyperlocal delivery excels in rapid fulfillment and meeting immediate consumer demands.
Cost Structure: Logistics vs Hyperlocal Models
Logistics models typically involve higher fixed costs due to warehousing, inventory management, and long-distance transportation expenses, but benefit from economies of scale when handling large shipment volumes. Hyperlocal delivery focuses on minimizing variable costs by leveraging proximity to customers, using small fleets or gig workers for faster, on-demand service, which reduces last-mile delivery expenses. Understanding these cost structures helps businesses optimize supply chain strategies for efficiency and customer satisfaction in varying market demands.
Customer Experience in Both Systems
Logistics systems emphasize efficient warehouse management and bulk transportation, ensuring timely deliveries but often lacking personalized customer interaction. Hyperlocal delivery prioritizes fast, last-mile service within limited geographic areas, enhancing real-time tracking and customer satisfaction through immediate order fulfillment. Both models impact customer experience by balancing speed, reliability, and communication, with hyperlocal delivery driving higher engagement through localized service.
Scalability and Network Expansion
Logistics systems prioritize scalability through extensive network infrastructures, integrating warehouses and hubs to manage high-volume shipments efficiently across regions. Hyperlocal delivery emphasizes rapid, small-scale distribution within confined geographic areas, leveraging localized courier networks for real-time fulfillment. While logistics scales through centralized coordination and optimized routes, hyperlocal delivery expands networks by increasing fleet density and using dynamic routing algorithms for immediate customer demand.
Industry-Specific Use Cases and Examples
Logistics involves large-scale transportation management across regional or global supply chains, optimizing warehousing, inventory, and freight movement for industries like manufacturing and retail. Hyperlocal delivery targets last-mile distribution within a limited geographic area, critical for food delivery, e-commerce, and healthcare sectors requiring rapid, on-demand service. Industry-specific examples include automotive parts shipped via logistics networks for assembly lines, while grocery stores leverage hyperlocal delivery to meet immediate consumer needs.
Future Trends in Logistics and Hyperlocal Delivery
Future trends in logistics emphasize the integration of AI-driven automation and blockchain for enhanced transparency and efficiency across global supply chains. Hyperlocal delivery is rapidly evolving with the adoption of electric bikes, drones, and real-time data analytics to meet growing demand for instant, last-mile delivery solutions. Sustainable practices and smart city infrastructure are set to transform both logistics and hyperlocal delivery by reducing carbon footprints and optimizing route planning.
Related Important Terms
Dark Stores
Dark stores serve as crucial hubs in hyperlocal delivery, enabling rapid order fulfillment by storing inventory closer to consumers. Unlike traditional logistics centers that handle bulk, long-distance shipments, dark stores optimize last-mile delivery speed and efficiency within urban areas.
Micro-Fulfillment Centers
Micro-fulfillment centers optimize logistics by enabling rapid order processing and last-mile delivery in hyperlocal delivery networks, reducing transit times and lowering transportation costs. These compact facilities leverage automation and data-driven inventory management to enhance supply chain efficiency and meet increasing consumer demand for fast, localized delivery services.
Last-Mile Aggregators
Last-mile aggregators in logistics streamline the delivery process by consolidating multiple shipments to optimize routes and reduce costs, contrasting with hyperlocal delivery models that emphasize speed and proximity for immediate customer fulfillment. Leveraging real-time data and advanced route optimization algorithms, last-mile aggregators enhance efficiency across urban and suburban distributions, supporting scalable logistics networks.
Real-Time Route Optimization
Real-time route optimization in logistics enhances supply chain efficiency by dynamically adjusting routes based on traffic, weather, and delivery priorities. Hyperlocal delivery leverages this technology to ensure rapid, accurate shipments within confined urban areas, maximizing customer satisfaction and reducing operational costs.
Instant Delivery Platforms
Instant delivery platforms leverage hyperlocal delivery models to optimize last-mile logistics by minimizing delivery times and enhancing customer satisfaction. These platforms integrate real-time tracking, local inventory management, and AI-powered route optimization to achieve rapid fulfillment within urban areas.
Elastic Logistics
Elastic Logistics enhances supply chain efficiency by dynamically scaling resources in real-time to meet demand fluctuations, a key advantage over traditional logistics models. Unlike hyperlocal delivery which focuses on immediate, localized shipment within small geographic areas, Elastic Logistics integrates adaptive capacity management across broader networks, optimizing cost and speed for diverse delivery volumes.
Urban Distribution Hubs
Urban distribution hubs enhance logistics efficiency by consolidating shipments near high-demand areas, reducing last-mile delivery costs and transit times. Hyperlocal delivery relies on these strategically placed hubs to enable rapid, same-day service within dense urban environments, optimizing resource allocation and customer satisfaction.
On-Demand Fulfillment
Logistics encompasses managing the entire supply chain, including warehousing, inventory, and long-distance transportation, while hyperlocal delivery focuses on rapid, on-demand fulfillment within a limited geographic area, often leveraging technology for real-time order processing and route optimization. On-demand fulfillment in hyperlocal delivery minimizes delivery times and enhances customer satisfaction by utilizing local hubs and last-mile delivery solutions tailored for immediate order fulfillment.
Hyperlocal Marketplace
Hyperlocal marketplaces revolutionize last-mile logistics by connecting local businesses directly with nearby customers, enabling faster delivery times and reduced transportation costs compared to traditional logistics models. The emphasis on proximity-based inventory and real-time order fulfillment optimizes supply chain efficiency within constrained geographic areas.
Drone-Assisted Deliveries
Drone-assisted deliveries revolutionize logistics by enabling rapid, precise transport of goods within hyperlocal areas, significantly reducing last-mile delivery times and costs. Integrating drones into supply chain management enhances efficiency, minimizes traffic congestion, and supports real-time tracking for improved inventory control and customer satisfaction.
Logistics vs Hyperlocal Delivery Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com