Shipping remains the dominant method for transporting large, heavy goods across long distances due to its cost-efficiency and established infrastructure. Drone delivery offers rapid, flexible solutions for small, time-sensitive packages within urban areas, reducing last-mile delivery times and traffic congestion. Integrating both methods optimizes supply chains by balancing speed, capacity, and cost-effectiveness in modern transportation networks.
Table of Comparison
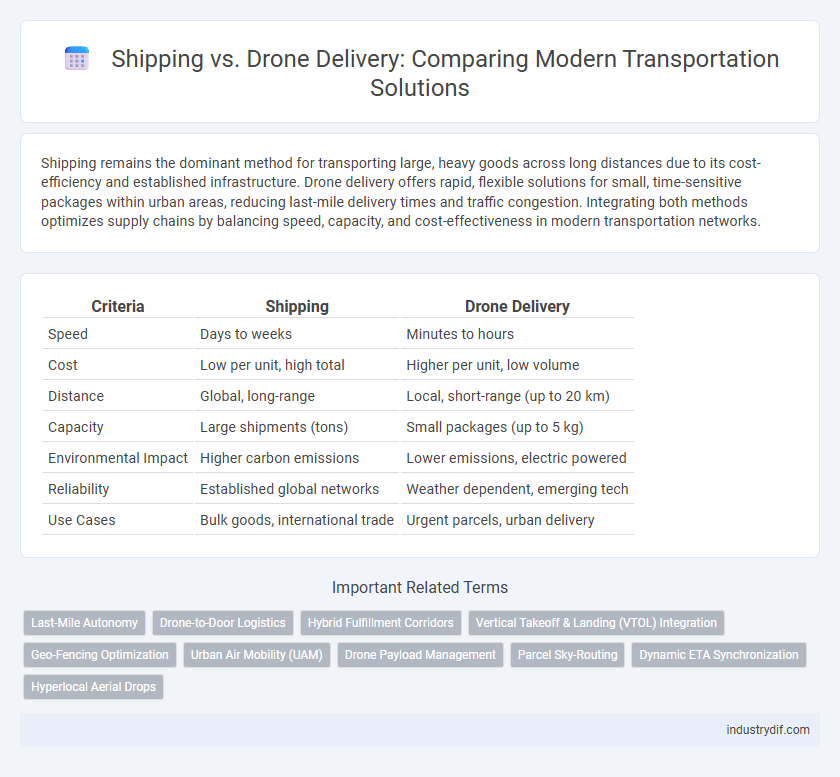
| Criteria | Shipping | Drone Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Days to weeks | Minutes to hours |
| Cost | Low per unit, high total | Higher per unit, low volume |
| Distance | Global, long-range | Local, short-range (up to 20 km) |
| Capacity | Large shipments (tons) | Small packages (up to 5 kg) |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon emissions | Lower emissions, electric powered |
| Reliability | Established global networks | Weather dependent, emerging tech |
| Use Cases | Bulk goods, international trade | Urgent parcels, urban delivery |
Overview of Shipping and Drone Delivery
Shipping primarily involves transporting goods via trucks, ships, or planes over long distances with established logistics networks supporting bulk cargo and international trade. Drone delivery utilizes unmanned aerial vehicles to quickly transport smaller packages over short distances, offering rapid last-mile delivery and reducing traffic congestion. Emerging drone technology enhances real-time tracking and environmentally friendly operations compared to traditional shipping methods.
Evolution of Transportation Methods
Shipping has long been the backbone of global transportation, efficiently moving large volumes of goods across continents via sea and land routes. Drone delivery represents a transformative evolution, offering rapid, last-mile logistics solutions with enhanced precision and reduced transit times in urban environments. Advances in autonomous flight technology and regulatory frameworks continue to accelerate the integration of drones alongside traditional shipping methods, shaping the future of transportation logistics.
Key Differences: Shipping vs Drone Delivery
Shipping typically involves transporting goods via trucks, ships, or airplanes over long distances, providing cost-effective solutions for bulk and heavy items. Drone delivery excels in rapid, last-mile transportation for lightweight packages within urban or remote areas, offering high precision and reduced delivery times. Key differences include scale, speed, cost, environmental impact, and regulatory challenges impacting the adoption of both methods.
Cost Comparison in Logistics
Shipping costs in logistics typically involve expenses related to fuel, labor, warehousing, and handling, making traditional shipping more cost-effective for large, heavy, or bulk shipments over long distances. Drone delivery offers lower last-mile delivery costs, reduced labor, and faster delivery times but is currently limited by payload capacity and regulatory restrictions, which can increase expenses for large-scale operations. Analyzing shipment size, distance, and frequency is crucial for determining whether shipping or drone delivery provides the best cost efficiency in a logistics strategy.
Speed and Efficiency in Delivery
Shipping typically offers larger capacity but slower delivery times, often ranging from several days to weeks depending on the distance and method. Drone delivery excels in rapid, last-mile logistics, reducing delivery times to under an hour for local shipments with enhanced route optimization. The efficiency of drone delivery is particularly beneficial for urgent, lightweight packages, while traditional shipping remains essential for bulk and international transport.
Environmental Impact Analysis
Shipping contributes significantly to global carbon emissions due to reliance on fossil fuels and large-scale fuel consumption by cargo ships. Drone delivery offers a lower carbon footprint through electric power and reduced fuel usage, though its impact varies with battery production and energy sources. Evaluating lifecycle emissions and scalability is essential to accurately compare the environmental benefits of shipping versus drone delivery.
Scalability and Practical Use Cases
Shipping methods offer high scalability for large volume and long-distance deliveries, efficiently supporting industries like e-commerce and international trade. Drone delivery excels in quick, last-mile logistics with practical use cases in healthcare, emergency supplies, and urban package distribution, though current scalability is limited by battery life and regulatory constraints. Integrating drones with existing shipping networks can enhance overall delivery efficiency, especially in densely populated or hard-to-reach areas.
Regulatory and Safety Challenges
Shipping faces extensive regulatory frameworks governing vessel operations, cargo handling, and international maritime laws, ensuring safety but often causing delays. Drone delivery encounters evolving regulatory challenges related to airspace restrictions, privacy concerns, and certification requirements for unmanned aerial vehicles. Safety protocols for drones focus on collision avoidance, secure payload handling, and mitigating risks in densely populated areas, demanding robust technological and legal oversight.
Technological Innovations Driving Change
Advancements in autonomous navigation systems and AI-powered route optimization have significantly enhanced both shipping and drone delivery efficiency. Shipping leverages innovations in container tracking and automated port operations, reducing transit times and costs on a global scale. Drone delivery integrates cutting-edge battery technology and real-time data processing, enabling faster, last-mile deliveries in urban and remote areas.
Future Trends in Transportation Industry
Shipping and drone delivery are revolutionizing the transportation industry by enhancing efficiency and reducing carbon emissions. Autonomous drones offer rapid, last-mile delivery solutions for urban areas, while shipping continues to evolve with smart vessels and eco-friendly fuels to support global trade. Integration of AI, IoT, and sustainable technologies drives future trends, enabling real-time tracking, optimized routes, and reduced environmental impact in transportation logistics.
Related Important Terms
Last-Mile Autonomy
Last-mile autonomy in shipping leverages automated ground vehicles and drones to enhance delivery speed and reduce human labor costs. Drone delivery offers significant advantages in reaching remote or congested urban areas quickly, minimizing traffic delays and expanding service coverage beyond traditional shipping routes.
Drone-to-Door Logistics
Drone-to-door logistics revolutionizes last-mile shipping by drastically reducing delivery times and minimizing dependence on traditional transportation infrastructures, enabling faster, more efficient parcel distribution directly to consumers. This innovation leverages autonomous flight technology and real-time routing algorithms to optimize delivery paths, significantly cutting costs and carbon emissions compared to conventional truck and ship freight methods.
Hybrid Fulfillment Corridors
Hybrid fulfillment corridors integrate traditional shipping methods with drone delivery systems to optimize last-mile logistics, reducing delivery times by up to 50% and cutting carbon emissions significantly. These corridors leverage centralized distribution hubs where shipments transition from cargo vessels or trucks to drones, enabling efficient, flexible, and scalable parcel distribution in densely populated or hard-to-reach areas.
Vertical Takeoff & Landing (VTOL) Integration
Vertical Takeoff & Landing (VTOL) integration in drone delivery revolutionizes last-mile logistics by enabling precise, rapid, and flexible parcel transport without the need for extensive infrastructure. Compared to traditional shipping, VTOL drones reduce delivery time and operational costs while minimizing environmental impact through electric propulsion and optimized flight paths.
Geo-Fencing Optimization
Geo-fencing optimization in shipping leverages GPS and RFID technologies to define precise delivery zones, minimizing route deviations and enhancing fleet management efficiency. Drone delivery systems utilize geo-fencing to ensure safe flight paths and regulatory compliance, reducing the risk of airspace violations while optimizing last-mile parcel distribution.
Urban Air Mobility (UAM)
Urban Air Mobility (UAM) leverages drone delivery to address last-mile logistics challenges by enabling faster, congestion-free transport of goods compared to traditional shipping methods. Advanced drone technology integrates seamlessly with smart city infrastructure, optimizing route efficiency and reducing delivery times in densely populated urban areas.
Drone Payload Management
Drone payload management optimizes load capacity through advanced weight distribution algorithms and sensor integration, enabling precise delivery of packages up to several kilograms while maintaining flight stability. Compared to traditional shipping, drones reduce transit time and enhance last-mile delivery efficiency by dynamically adjusting payload configurations based on real-time environmental data and flight conditions.
Parcel Sky-Routing
Parcel Sky-Routing revolutionizes shipping by leveraging drone delivery to enhance last-mile logistics, significantly reducing transit time and operational costs for parcels under 5 kg. This technology optimizes aerial pathways through real-time data analytics, improving route efficiency and enabling rapid, eco-friendly delivery in urban areas.
Dynamic ETA Synchronization
Dynamic ETA synchronization in shipping leverages real-time tracking, enabling precise updates for cargo transit times across global supply chains. Drone delivery enhances this capability by integrating GPS data with AI algorithms to provide instant, adaptive estimated arrival times for last-mile delivery, reducing uncertainty and improving customer satisfaction.
Hyperlocal Aerial Drops
Hyperlocal aerial drops via drones enhance shipping efficiency by significantly reducing delivery times within urban and suburban areas, leveraging GPS-guided navigation for precise parcel placement. This method minimizes last-mile logistics challenges and lowers carbon emissions compared to traditional ground transportation.
Shipping vs Drone Delivery Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com