Supply chain management optimizes the flow of goods from manufacturers to consumers through multiple stages, ensuring efficiency and cost-effectiveness across long distances. Hyperlocal delivery emphasizes quick, last-mile transportation within a localized area, focusing on speed and convenience for immediate consumer needs. Both approaches leverage technology, but hyperlocal delivery relies heavily on real-time tracking and agile logistics to enhance customer satisfaction in urban environments.
Table of Comparison
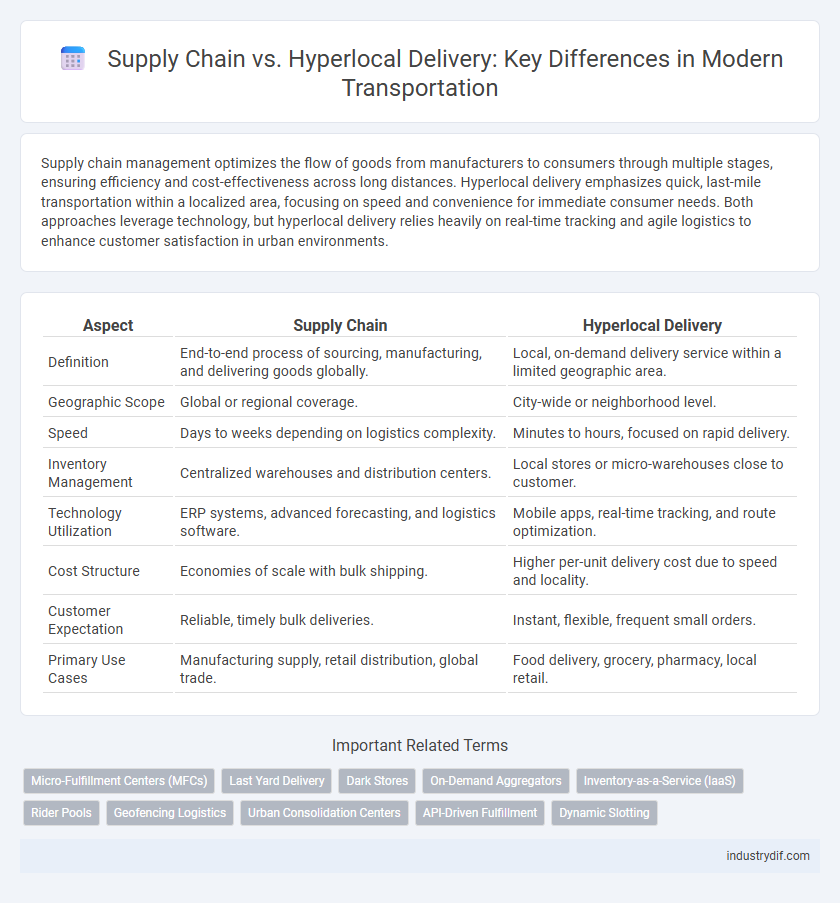
| Aspect | Supply Chain | Hyperlocal Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | End-to-end process of sourcing, manufacturing, and delivering goods globally. | Local, on-demand delivery service within a limited geographic area. |
| Geographic Scope | Global or regional coverage. | City-wide or neighborhood level. |
| Speed | Days to weeks depending on logistics complexity. | Minutes to hours, focused on rapid delivery. |
| Inventory Management | Centralized warehouses and distribution centers. | Local stores or micro-warehouses close to customer. |
| Technology Utilization | ERP systems, advanced forecasting, and logistics software. | Mobile apps, real-time tracking, and route optimization. |
| Cost Structure | Economies of scale with bulk shipping. | Higher per-unit delivery cost due to speed and locality. |
| Customer Expectation | Reliable, timely bulk deliveries. | Instant, flexible, frequent small orders. |
| Primary Use Cases | Manufacturing supply, retail distribution, global trade. | Food delivery, grocery, pharmacy, local retail. |
Understanding Supply Chain Logistics
Supply chain logistics involves the strategic coordination of procurement, transportation, warehousing, and inventory management to ensure seamless movement of goods from suppliers to end consumers. Unlike hyperlocal delivery, which emphasizes rapid, last-mile distribution within a limited geographic area, supply chain logistics optimizes global networks and multi-modal transportation to reduce costs and enhance efficiency. Advanced technologies like IoT, AI-driven analytics, and real-time tracking improve visibility and responsiveness across the supply chain, enabling better demand forecasting and inventory control.
Defining Hyperlocal Delivery
Hyperlocal delivery refers to the rapid distribution of goods within a confined geographic area, often focusing on same-day or even within-hours delivery to consumers. It leverages real-time data, advanced routing algorithms, and localized fulfillment centers to ensure expedited service and reduce transportation costs. Unlike traditional supply chain models that prioritize long-haul logistics and bulk shipments, hyperlocal delivery emphasizes speed, proximity, and customer convenience.
Key Differences Between Supply Chain and Hyperlocal Delivery
Supply chain management involves coordinating complex, multi-tier networks of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors to ensure efficient movement of goods over long distances. Hyperlocal delivery focuses on fast, last-mile delivery within a confined geographic area, often leveraging local inventory and real-time demand data for immediate fulfillment. Key differences include scale, delivery speed, inventory placement, and technology use, with supply chains emphasizing bulk transportation and hyperlocal prioritizing rapid, on-demand customer access.
Advantages of Traditional Supply Chains
Traditional supply chains offer extensive network integration that enables bulk transportation and economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs significantly. They provide robust inventory management and long-term supplier relationships, ensuring consistent product availability and quality control. The structured logistics and centralized warehousing systems enhance reliability and facilitate handling of large volumes across diverse geographic regions.
Benefits of Hyperlocal Delivery Models
Hyperlocal delivery models reduce transportation costs by minimizing delivery distances and enabling faster order fulfillment within localized areas. This approach enhances customer satisfaction through real-time tracking, increased delivery frequency, and greater flexibility in meeting urgent demands. Businesses benefit from improved inventory management and reduced carbon emissions due to shorter supply chain loops.
Technology’s Role in Modern Transportation
Advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and blockchain streamline supply chain management by enhancing transparency, enabling real-time tracking, and optimizing inventory and route planning. Hyperlocal delivery leverages GPS, mobile apps, and autonomous vehicles to ensure rapid, precise last-mile fulfillment within urban areas. Integration of these technologies fosters greater efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction in both supply chain logistics and hyperlocal transportation networks.
Impact on Last-Mile Delivery
Supply chain management focuses on optimizing the flow of goods from manufacturers to distribution centers, improving overall efficiency but often involves longer delivery times in last-mile logistics. Hyperlocal delivery emphasizes rapid, localized distribution within a limited geographic area, drastically reducing delivery time by leveraging local inventory and real-time order processing. The impact on last-mile delivery is significant, with hyperlocal models enhancing customer satisfaction through speed and flexibility, while traditional supply chains prioritize cost-efficiency and scale.
Cost Implications and Efficiencies
Supply chain logistics often involve higher fixed costs due to warehousing, inventory management, and long-haul transportation, impacting overall cost efficiency. Hyperlocal delivery reduces last-mile expenses by leveraging proximity to customers, enabling faster turnaround times and lower fuel consumption. Businesses optimizing hyperlocal delivery models can achieve significant cost savings while maintaining service quality through real-time demand forecasting and route optimization technologies.
Challenges Facing Each Model
Supply chain models grapple with complexities such as inventory management, long delivery lead times, and coordination across multiple stakeholders, often resulting in increased operational costs. Hyperlocal delivery faces challenges including last-mile logistics, fluctuating consumer demand, and the need for real-time tracking, which can strain small-scale distribution networks. Both models must address scalability and sustainability to meet evolving market expectations efficiently.
Future Trends in Transportation Logistics
Supply chain logistics is rapidly evolving with the integration of AI-driven analytics and blockchain technology, enhancing transparency and efficiency in long-distance freight management. Hyperlocal delivery is poised to expand through autonomous vehicles and drone technology, enabling faster, last-mile connections within urban environments. Future transportation logistics will increasingly blend these approaches, leveraging IoT-enabled tracking and sustainable electric fleets to meet rising consumer expectations for speed and reliability.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs)
Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs) drastically enhance hyperlocal delivery efficiency by enabling rapid order fulfillment within urban areas, reducing last-mile delivery times compared to traditional supply chain models. These compact, technologically advanced facilities integrate automation and localized inventory management to support real-time demand, optimizing logistics for e-commerce and grocery sectors.
Last Yard Delivery
Last yard delivery optimizes supply chain efficiency by minimizing transit time from local hubs to customer doorsteps, integrating real-time tracking and route optimization technologies. Hyperlocal delivery enhances this process with ultra-fast, on-demand services within a limited geographic area, reducing delivery costs and carbon footprint while improving customer satisfaction.
Dark Stores
Dark stores revolutionize hyperlocal delivery by serving as strategically located micro-fulfillment centers that optimize last-mile logistics and reduce delivery times within urban supply chains. Their integration within supply chain frameworks enhances inventory management efficiency, enabling faster order processing and improved customer satisfaction in densely populated areas.
On-Demand Aggregators
On-demand aggregators in transportation optimize hyperlocal delivery by connecting multiple suppliers with consumers in real-time, enhancing speed and efficiency compared to traditional supply chain models that rely on bulk shipments and longer lead times. These platforms leverage data analytics and GPS technology to dynamically route deliveries within local areas, reducing operational costs and improving customer satisfaction through faster fulfillment.
Inventory-as-a-Service (IaaS)
Supply Chain solutions leverage centralized warehouses and complex logistics networks to manage Inventory-as-a-Service (IaaS), optimizing stock levels across multiple locations to reduce costs and improve fulfillment efficiency. Hyperlocal Delivery utilizes decentralized inventory pools located closer to end consumers, enabling rapid order processing and same-day delivery through real-time inventory visibility and agile replenishment strategies.
Rider Pools
Rider pools in supply chain logistics typically consist of specialized drivers managing long-haul routes and bulk shipments, optimizing fleet utilization across wide geographic areas. In contrast, hyperlocal delivery leverages smaller, flexible rider pools operating within constrained urban zones to ensure rapid, on-demand service and enhanced last-mile efficiency.
Geofencing Logistics
Geofencing logistics enhances hyperlocal delivery by creating virtual boundaries that enable real-time tracking, efficient route optimization, and seamless last-mile fulfillment within confined geographic areas. Unlike traditional supply chain models that span broader regions, geofencing in hyperlocal delivery reduces transit times and operational costs by triggering automatic dispatch and inventory updates based on precise location data.
Urban Consolidation Centers
Urban Consolidation Centers (UCCs) streamline last-mile logistics by consolidating shipments from multiple suppliers to optimize delivery routes, significantly reducing traffic congestion and emissions in dense urban areas. Unlike traditional supply chain models that rely on broader distribution networks, UCCs support hyperlocal delivery by enabling faster, more efficient parcel sorting and dispatch within city limits.
API-Driven Fulfillment
API-driven fulfillment revolutionizes supply chain management by enabling seamless integration between inventory systems and hyperlocal delivery networks, ensuring real-time visibility and faster order processing. This technology optimizes last-mile delivery efficiency by dynamically routing shipments through localized hubs, reducing transit times and operational costs.
Dynamic Slotting
Dynamic slotting in transportation streamlines supply chain operations by optimizing delivery windows based on real-time demand, inventory levels, and traffic conditions, reducing delays and enhancing efficiency. Hyperlocal delivery leverages dynamic slotting to enable faster, more precise time slots within localized areas, improving customer satisfaction and operational agility.
Supply Chain vs Hyperlocal Delivery Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com