Taxi services offer regulated fares and immediate street hails, ensuring consistent pricing and availability within specific zones. Ride-hailing platforms provide app-based booking, dynamic pricing, and a broader range of vehicle options, enhancing convenience and customer choice. Both modes play crucial roles in urban mobility by addressing different user preferences for reliability or flexibility.
Table of Comparison
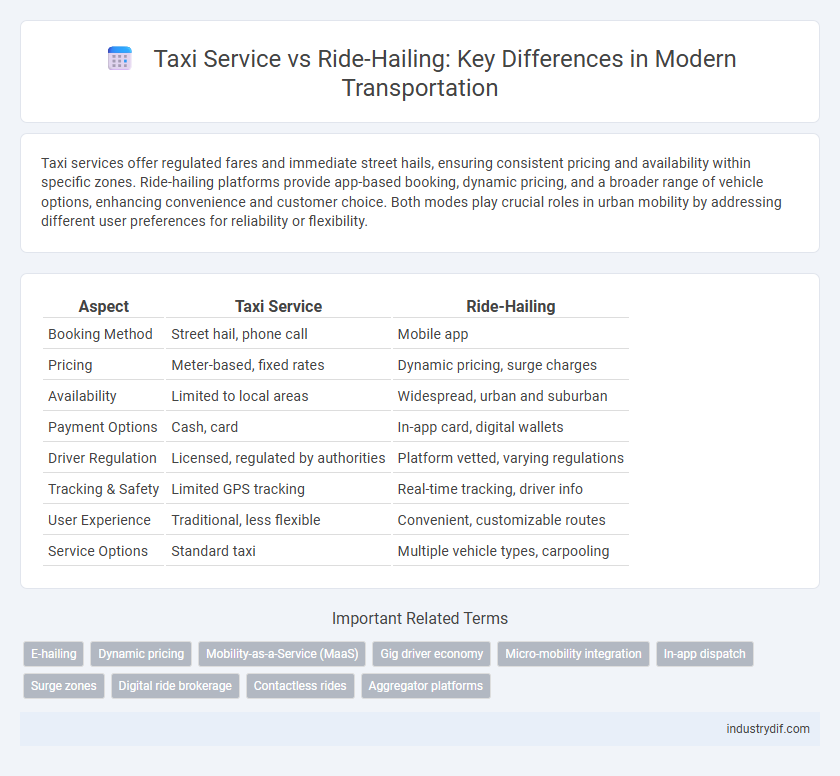
| Aspect | Taxi Service | Ride-Hailing |
|---|---|---|
| Booking Method | Street hail, phone call | Mobile app |
| Pricing | Meter-based, fixed rates | Dynamic pricing, surge charges |
| Availability | Limited to local areas | Widespread, urban and suburban |
| Payment Options | Cash, card | In-app card, digital wallets |
| Driver Regulation | Licensed, regulated by authorities | Platform vetted, varying regulations |
| Tracking & Safety | Limited GPS tracking | Real-time tracking, driver info |
| User Experience | Traditional, less flexible | Convenient, customizable routes |
| Service Options | Standard taxi | Multiple vehicle types, carpooling |
Overview of Taxi Services and Ride-Hailing
Taxi services operate through licensed drivers and regulated vehicles, offering street-hail or dispatch-based rides with standardized fare structures. Ride-hailing platforms use mobile apps to connect passengers with private drivers, featuring dynamic pricing and real-time tracking. Both services provide on-demand transportation but differ significantly in regulatory frameworks, payment methods, and customer experience.
History and Evolution of Urban Transportation
Taxi services originated in the early 17th century with horse-drawn carriages, evolving into motorized cabs by the late 19th century, establishing a regulated urban transportation network. Ride-hailing platforms emerged in the late 2000s with the advent of smartphones, leveraging GPS technology and app-based booking to disrupt traditional taxi industries worldwide. This digital transformation accelerated urban mobility by offering convenient, cashless, and dynamic pricing models, reshaping city transportation landscapes.
Licensing and Regulatory Differences
Taxi services typically require drivers and vehicles to obtain specific licenses and adhere to strict regulatory standards set by local transportation authorities, including fare controls and safety inspections. Ride-hailing companies operate under different frameworks, often classified as technology platforms rather than traditional transport providers, resulting in varied regulatory oversight that may relax vehicle requirements but enforce driver background checks and app-based fare transparency. These licensing and regulatory distinctions impact operational costs, insurance mandates, and consumer protections within urban mobility ecosystems.
Pricing Models and Fare Transparency
Taxi services typically operate on regulated fare structures with meter-based pricing that ensures consistent rates based on distance and time, offering clear fare transparency to passengers. Ride-hailing platforms use dynamic pricing models that can fluctuate based on demand, time, and location, often resulting in surge pricing that may reduce fare predictability. This contrast in pricing models highlights the trade-off between traditional taxi fare stability and the flexible, yet sometimes opaque, cost structure of ride-hailing services.
Booking Methods and User Experience
Taxi services primarily rely on traditional booking methods such as phone calls or street hailing, while ride-hailing platforms use mobile apps with GPS integration for instant booking. Ride-hailing apps offer real-time driver tracking, fare estimates, and digital payment options, enhancing user convenience and transparency. Taxi services may lack app-based features, potentially leading to longer wait times and less predictable pricing.
Vehicle Standards and Maintenance
Taxi services often adhere to strict vehicle standards regulated by local transportation authorities, ensuring regular inspections and maintenance schedules to guarantee passenger safety and reliability. Ride-hailing companies typically require drivers to meet baseline vehicle requirements, but the variability in vehicle conditions can be higher due to less centralized oversight. Consistent maintenance in taxis contributes to better overall vehicle performance and passenger trust compared to the more diverse fleet of ride-hailing vehicles.
Driver Background Checks and Training
Taxi service drivers typically undergo rigorous background checks and standardized training mandated by local regulatory authorities to ensure passenger safety and service reliability. Ride-hailing companies implement their own background verification processes, often relying on digital screening methods and variable training programs that differ by platform and region. The disparity in driver vetting and training between traditional taxi services and ride-hailing platforms impacts overall service quality and passenger trust in urban transportation networks.
Payment Options and Digital Integration
Taxi services primarily accept traditional payment methods such as cash and credit cards, while many ride-hailing platforms offer integrated digital payment options including mobile wallets, app-based payments, and contactless transactions. Ride-hailing apps provide seamless digital integration by allowing users to book, pay, and rate drivers within a single interface, enhancing convenience and transparency. The extensive use of GPS tracking and digital receipts in ride-hailing creates a more streamlined and efficient payment experience compared to conventional taxi services.
Availability and Response Times
Taxi services typically offer consistent availability through established dispatch systems and street hailing, ensuring quick response times in urban areas. Ride-hailing platforms leverage GPS technology and extensive driver networks to provide rapid pickups, often exceeding traditional taxi response speeds during peak times. Both options strive to minimize wait times, but ride-hailing apps usually deliver more precise estimated arrival times due to real-time tracking.
Environmental Impact and Future Trends
Taxi services traditionally rely on fossil fuel vehicles, contributing to higher carbon emissions, whereas ride-hailing platforms often integrate electric and hybrid vehicles, promoting greener urban mobility. The future trends in transportation indicate a significant shift towards electrification, autonomous vehicles, and shared mobility models, which aim to reduce environmental impact and improve efficiency. Urban planners and policymakers increasingly support ride-hailing innovations that align with sustainability goals and reduce congestion compared to conventional taxi services.
Related Important Terms
E-hailing
E-hailing services leverage mobile apps to connect passengers with drivers, offering real-time tracking, cashless payments, and dynamic pricing, which enhances convenience and efficiency compared to traditional taxi services. The integration of GPS technology and ride-matching algorithms in e-hailing platforms reduces waiting times and optimizes route selection, contributing to improved urban mobility.
Dynamic pricing
Taxi services typically use fixed pricing structures regulated by city authorities, ensuring fare predictability for passengers, while ride-hailing platforms implement dynamic pricing algorithms that adjust fares based on real-time demand, traffic, and driver availability. Dynamic pricing in ride-hailing increases revenue efficiency during peak times but can lead to higher costs for consumers compared to traditional taxi rates.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS)
Taxi services provide traditional street-hail and pre-booked transportation, while ride-hailing platforms integrate real-time digital booking, payment, and dynamic routing within Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) ecosystems. MaaS enhances urban mobility by combining taxis, ride-hailing, public transit, and other transport modes into seamless, user-centric service bundles powered by integrated data and payment systems.
Gig driver economy
Taxi services operate under regulated fare structures and licensing, ensuring standardized pricing and driver accountability, whereas ride-hailing platforms leverage gig drivers who benefit from flexible schedules but face variable income and limited labor protections. The gig driver economy in ride-hailing has disrupted traditional taxi markets by offering dynamic pricing and app-based convenience, reshaping urban transportation dynamics.
Micro-mobility integration
Taxi services traditionally rely on street-hail and dispatch systems, limiting their integration with micro-mobility options such as e-scooters and bike-sharing. Ride-hailing platforms leverage app-based ecosystems to seamlessly combine taxis with micro-mobility solutions, enhancing first- and last-mile connectivity and reducing urban congestion.
In-app dispatch
In-app dispatch for ride-hailing services leverages GPS technology and dynamic routing algorithms to optimize driver allocation and reduce passenger wait times, enhancing overall efficiency compared to traditional taxi services that rely on radio or phone dispatch. This digital coordination enables seamless real-time tracking and payment integration, improving user experience and operational transparency.
Surge zones
Surge zones in ride-hailing platforms dynamically increase prices based on demand spikes, whereas traditional taxi services maintain fixed fare rates regardless of location-based demand fluctuations. This pricing model in ride-hailing maximizes driver availability during peak periods but can lead to higher costs for passengers in surge zones compared to standard taxi services.
Digital ride brokerage
Digital ride brokerage platforms revolutionize transportation by seamlessly connecting passengers with various taxi services and ride-hailing providers through integrated apps and algorithms. These platforms optimize route efficiency and fare comparison, enhancing user convenience and market competition within urban mobility ecosystems.
Contactless rides
Contactless rides in taxi services utilize traditional dispatch systems with added digital payment and app integration for minimal physical interaction. Ride-hailing platforms inherently support contactless experiences through in-app payment, driver tracking, and digital receipts, enhancing safety and convenience during trips.
Aggregator platforms
Aggregator platforms in ride-hailing services connect multiple taxi operators and independent drivers through a single app, offering real-time pricing, availability, and seamless booking options that traditional taxi services typically lack. These platforms use dynamic algorithms to optimize route efficiency and provide transparent fare estimates, enhancing convenience and competitive pricing over conventional taxi dispatch methods.
Taxi service vs ride-hailing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com