Courier services specialize in fast, secure transportation of parcels, often handling individual or small shipments directly from sender to recipient. Last-mile delivery focuses on the final step of the supply chain, ensuring packages reach the end customer efficiently, especially in urban and densely populated areas. Optimizing last-mile delivery reduces costs and enhances customer satisfaction by improving speed and accuracy.
Table of Comparison
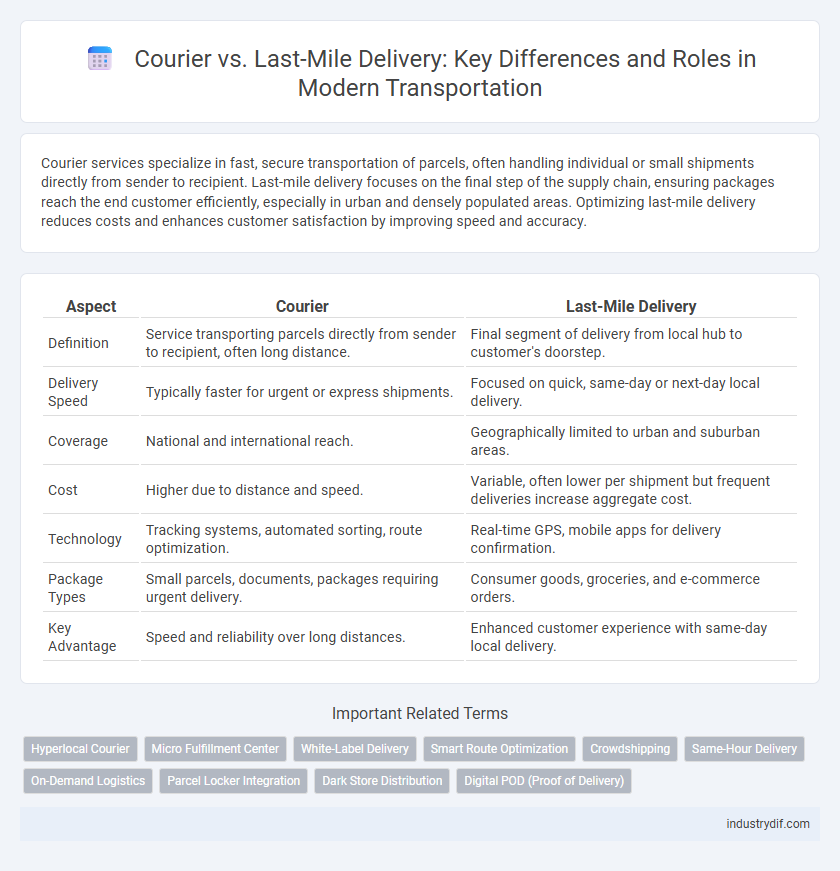
| Aspect | Courier | Last-Mile Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Service transporting parcels directly from sender to recipient, often long distance. | Final segment of delivery from local hub to customer's doorstep. |
| Delivery Speed | Typically faster for urgent or express shipments. | Focused on quick, same-day or next-day local delivery. |
| Coverage | National and international reach. | Geographically limited to urban and suburban areas. |
| Cost | Higher due to distance and speed. | Variable, often lower per shipment but frequent deliveries increase aggregate cost. |
| Technology | Tracking systems, automated sorting, route optimization. | Real-time GPS, mobile apps for delivery confirmation. |
| Package Types | Small parcels, documents, packages requiring urgent delivery. | Consumer goods, groceries, and e-commerce orders. |
| Key Advantage | Speed and reliability over long distances. | Enhanced customer experience with same-day local delivery. |
Defining Courier Services vs Last-Mile Delivery
Courier services involve the direct, secure transport of parcels or documents from sender to recipient, often offering expedited and personalized delivery options. Last-mile delivery refers to the final step in the distribution process, where goods are transported from a local hub to the end customer, focusing on speed and efficiency in densely populated urban areas. Both services prioritize timely delivery but differ in scale, scope, and operational complexities.
Key Differences Between Courier and Last-Mile Delivery
Courier services typically handle the direct, often time-sensitive transportation of small parcels or documents between two points, prioritizing speed and reliability over long distances. Last-mile delivery focuses specifically on the final leg of the shipping process, ensuring packages reach the customer's doorstep efficiently, often within urban or suburban settings. Key differences include courier services managing point-to-point deliveries with potential multiple stops, while last-mile delivery optimizes route planning and fulfillment logistics to minimize transit time in densely populated areas.
Service Speed: Courier vs Last-Mile Delivery
Courier services prioritize speed by offering direct, often same-day or express delivery tailored for urgent shipments, minimizing transit times through dedicated routes and fewer stops. Last-mile delivery focuses on efficiently navigating the final segment to the recipient, balancing speed with route optimization to handle multiple deliveries within tight time windows. Service speed in courier solutions typically surpasses last-mile delivery due to limited intermediate handling and quicker dispatch processes.
Coverage Areas: Urban, Suburban, and Rural Reach
Courier services typically emphasize rapid delivery within urban and suburban areas, leveraging dense networks to ensure speed and reliability. Last-mile delivery solutions extend coverage to a broader range of environments, including challenging rural regions, by optimizing route planning and using adaptive transportation methods. This strategic differentiation enhances accessibility and customer satisfaction across diverse geographic locations.
Technology Integration in Courier and Last-Mile Delivery
Technology integration in courier and last-mile delivery enhances efficiency through real-time tracking systems, automated route optimization, and AI-driven logistics management. Couriers leverage GPS and mobile apps for seamless package handoffs, while last-mile delivery employs drones, autonomous vehicles, and smart lockers to expedite final parcel distribution. Advanced analytics and IoT devices enable data-driven decision-making, reducing delivery times and improving customer satisfaction in both sectors.
Cost Structures: Courier vs Last-Mile Delivery
Courier services typically involve higher fixed costs due to centralized sorting facilities and long-distance transportation, while last-mile delivery incurs variable costs driven by factors such as route density, delivery speed, and customer location. Last-mile delivery often experiences increased expenses from labor-intensive processes and fuel consumption in urban congestion zones. Optimizing last-mile logistics through route optimization and local micro-fulfillment centers can significantly reduce operational costs compared to traditional courier models.
Impact on Customer Experience
Couriers provide personalized, often same-day delivery services ensuring direct handoff, which enhances reliability and customer satisfaction. Last-mile delivery focuses on optimizing the final leg logistics through technology and route efficiency, reducing delivery times and improving real-time tracking for consumers. Both methods significantly influence customer experience by balancing speed, convenience, and transparency in the delivery process.
Challenges in Courier and Last-Mile Delivery
Courier services face challenges including limited tracking visibility, high operational costs, and strict delivery time windows, which affect efficiency and customer satisfaction. Last-mile delivery struggles with urban congestion, failed delivery attempts, and the need for scalable, flexible logistics solutions to meet increasing consumer demand. Both sectors require advanced technology integration and optimized route planning to overcome these obstacles and ensure timely, cost-effective service.
Sustainability Practices in Both Delivery Models
Courier services often prioritize sustainability through optimized route planning and the use of electric vehicles to reduce carbon emissions. Last-mile delivery focuses on minimizing environmental impact by consolidating shipments, employing bike couriers, and leveraging local distribution hubs to decrease fuel consumption. Both models increasingly adopt eco-friendly packaging and digital tracking to enhance efficiency and reduce their overall carbon footprint.
Future Trends in Courier and Last-Mile Delivery
Future trends in courier and last-mile delivery include the integration of autonomous vehicles and drones to enhance speed and efficiency. Advanced AI-driven route optimization and real-time tracking systems are expected to reduce delivery times and improve customer experience. Sustainable delivery practices, such as electric vehicles and carbon-neutral options, are becoming increasingly important to meet environmental goals.
Related Important Terms
Hyperlocal Courier
Hyperlocal courier services specialize in rapid, small-scale deliveries within a confined geographic area, boosting efficiency and customer satisfaction by minimizing transit time and enhancing real-time tracking. Unlike traditional last-mile delivery that covers broader regions and multiple drop-offs, hyperlocal couriers prioritize instant parcel movement, catering primarily to urgent, same-day demands in urban settings.
Micro Fulfillment Center
Micro fulfillment centers enhance last-mile delivery efficiency by strategically positioning inventory closer to consumers, reducing transit time and operational costs compared to traditional courier services that often rely on centralized warehouses. Leveraging automation and real-time data, these centers enable rapid order processing and precise route optimization, crucial for meeting the growing demand for faster, localized delivery solutions.
White-Label Delivery
White-label delivery services enable businesses to offer last-mile delivery under their own brand, enhancing customer loyalty and seamless experience without managing logistics directly. Unlike traditional couriers, white-label solutions provide customizable delivery options that integrate with e-commerce platforms, optimizing efficiency and brand visibility in last-mile transportation.
Smart Route Optimization
Smart route optimization in courier services significantly enhances delivery speed and efficiency by leveraging real-time traffic data and predictive analytics. Last-mile delivery benefits from these technologies by reducing fuel consumption and improving customer satisfaction through precise, timely drop-offs.
Crowdshipping
Crowdshipping leverages everyday travelers to perform last-mile delivery, offering a flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional courier services that typically rely on dedicated professional fleets. This model enhances urban logistics by reducing delivery times and carbon emissions while increasing parcel traceability and customer convenience.
Same-Hour Delivery
Same-hour delivery in courier services emphasizes rapid, point-to-point parcel transport, ensuring packages reach recipients within 60 minutes of dispatch, optimizing urban logistics efficiency. Last-mile delivery focuses on streamlined routing and real-time tracking to minimize delays and enhance customer satisfaction during the critical final leg of the supply chain.
On-Demand Logistics
On-demand logistics in transportation emphasizes rapid, flexible courier services that prioritize speed and real-time tracking for immediate parcel delivery. Last-mile delivery focuses on the critical final step from distribution hubs to end customers, optimizing route efficiency and customer experience through advanced algorithms and urban delivery solutions.
Parcel Locker Integration
Parcel locker integration enhances last-mile delivery efficiency by allowing secure, contactless parcel drop-offs and pickups, reducing failed delivery attempts and operational costs. Couriers benefit from streamlined routes and flexible delivery windows, improving customer satisfaction and optimizing resource allocation in urban logistics.
Dark Store Distribution
Dark store distribution enhances last-mile delivery efficiency by leveraging localized inventory hubs to reduce delivery times and costs compared to traditional courier services. This model optimizes urban logistics by providing on-demand fulfillment directly from dark stores, streamlining the supply chain for rapid customer service.
Digital POD (Proof of Delivery)
Digital Proof of Delivery (POD) enhances both courier and last-mile delivery services by providing real-time confirmation of package receipt through electronic signatures, photos, and GPS timestamps. This technology reduces disputes, improves supply chain transparency, and accelerates payment processing in urban and rural delivery networks.
Courier vs Last-Mile Delivery Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com