Cargo shipping relies on established maritime routes and large vessels to transport vast quantities of goods cost-effectively over long distances, making it ideal for bulk shipments and international trade. Hyperloop freight, leveraging magnetic levitation and vacuum tubes, promises ultra-fast transit times and reduced environmental impact by drastically cutting travel duration between logistics hubs. While cargo shipping excels in capacity and global coverage, hyperloop freight offers a revolutionary alternative for time-sensitive deliveries and inland cargo movement.
Table of Comparison
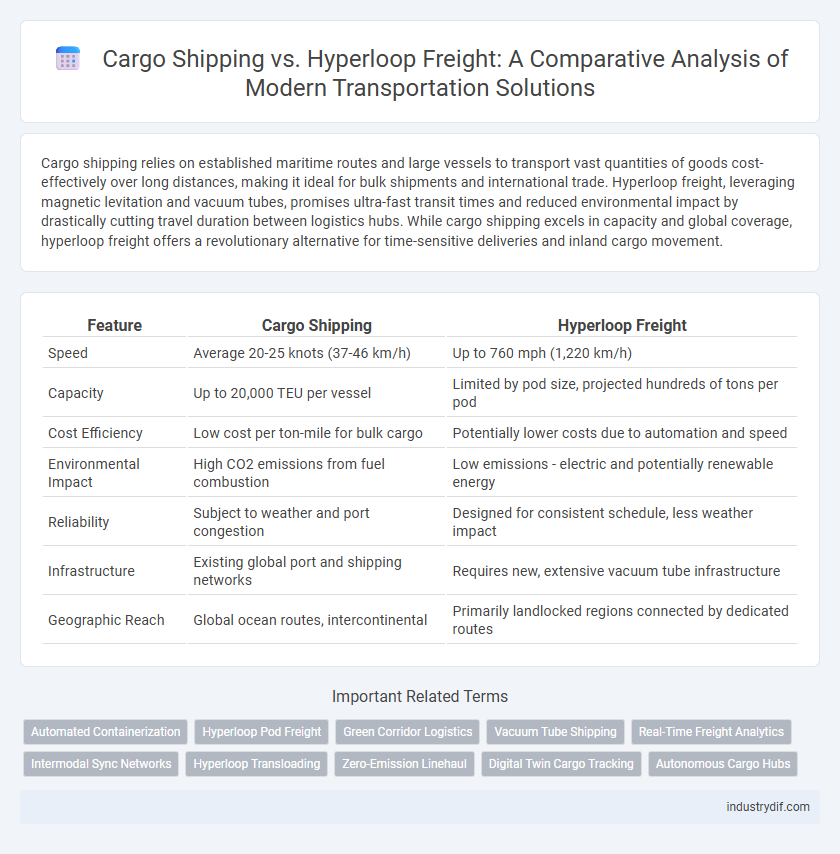
| Feature | Cargo Shipping | Hyperloop Freight |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Average 20-25 knots (37-46 km/h) | Up to 760 mph (1,220 km/h) |
| Capacity | Up to 20,000 TEU per vessel | Limited by pod size, projected hundreds of tons per pod |
| Cost Efficiency | Low cost per ton-mile for bulk cargo | Potentially lower costs due to automation and speed |
| Environmental Impact | High CO2 emissions from fuel combustion | Low emissions - electric and potentially renewable energy |
| Reliability | Subject to weather and port congestion | Designed for consistent schedule, less weather impact |
| Infrastructure | Existing global port and shipping networks | Requires new, extensive vacuum tube infrastructure |
| Geographic Reach | Global ocean routes, intercontinental | Primarily landlocked regions connected by dedicated routes |
Overview of Cargo Shipping and Hyperloop Freight
Cargo shipping relies on traditional maritime vessels and trucks, handling vast volumes of goods globally with established infrastructure and relatively low shipping costs. Hyperloop freight, an emerging technology, offers rapid, energy-efficient transit through low-pressure tubes, significantly reducing delivery times and minimizing environmental impact. The comparison highlights cargo shipping's global reach and capacity against hyperloop freight's potential for speed and sustainability in freight transportation.
Historical Evolution of Freight Transportation
Cargo shipping has traditionally relied on maritime vessels and trucks, evolving over centuries to optimize long-distance and bulk freight transport with innovations like containerization. The Hyperloop freight concept, emerging in the 21st century, promises to revolutionize freight transportation by enabling near-supersonic speeds using magnetic levitation in low-pressure tubes. This shift marks a technological leap from conventional shipping methods, aiming to reduce transit times drastically while improving energy efficiency and sustainability in freight logistics.
Technology Behind Traditional Cargo Shipping
Traditional cargo shipping relies on established maritime technology including large container ships equipped with GPS navigation, radar systems, and automated loading cranes to efficiently transport goods across global waterways. These vessels utilize diesel engines optimized for fuel efficiency across long distances, supported by sophisticated logistics software managing inventory and route planning. Despite slower speeds compared to emerging technologies, this system offers scalable capacity and extensive global infrastructure connectivity.
Hyperloop Freight: Concept and Development
Hyperloop Freight represents a transformative innovation in cargo shipping, utilizing near-vacuum tubes to achieve speeds up to 700 miles per hour, drastically reducing delivery times compared to traditional freight transport. The concept leverages magnetic levitation and low-pressure environments to minimize air resistance and energy consumption, promising higher efficiency and lower environmental impact. Development efforts by companies like Virgin Hyperloop include successful prototype tests and plans for commercial routes aiming to revolutionize the logistics industry by enabling ultra-fast, reliable freight transportation.
Speed and Transit Time Comparison
Cargo shipping typically involves transit times ranging from several days to weeks depending on distance and route efficiency, with ocean freight averaging 20-40 days for intercontinental deliveries. Hyperloop freight promises significantly reduced transit times, potentially cutting delivery from days to under an hour for distances up to 1,000 kilometers due to its near-vacuum, high-speed pod travel exceeding 600 mph. This drastic speed advantage positions Hyperloop freight as a revolutionary alternative to traditional shipping methods, especially for time-sensitive cargo.
Cost Analysis: Cargo Shipping vs Hyperloop Freight
Cargo shipping incurs lower operational costs due to established infrastructure and economies of scale, with average expenses ranging from $0.02 to $0.05 per ton-mile. Hyperloop freight, while promising ultra-fast delivery, currently faces high capital expenditure and maintenance costs, estimated to exceed $0.10 per ton-mile in early deployment phases. Cost analysis reveals cargo shipping as more cost-efficient for bulk, long-distance transport, whereas hyperloop freight targets premium, time-sensitive shipments despite higher per-unit costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cargo shipping contributes significantly to global CO2 emissions, accounting for nearly 3% of worldwide greenhouse gas output, primarily due to heavy fuel oil consumption. Hyperloop freight promises a more sustainable alternative by utilizing electric propulsion and magnetic levitation, drastically reducing carbon emissions and energy consumption compared to traditional maritime transport. Transitioning to hyperloop technology could enhance supply chain sustainability while minimizing environmental degradation associated with conventional cargo shipping.
Capacity and Scalability in Global Trade
Cargo shipping currently dominates global trade with the ability to transport vast quantities of goods, often exceeding 20,000 TEUs per vessel, supporting extensive scalability across international markets. Hyperloop freight offers a revolutionary approach with high-speed transit potential and modular pod designs that can scale operations rapidly for on-demand shipments, though it remains limited by current infrastructure and volume capacity compared to maritime vessels. Integrating hyperloop technology could enhance last-mile delivery efficiency and complement ocean freight, optimizing overall supply chain capacity and scalability in global commerce.
Safety and Reliability Factors
Cargo shipping has established safety protocols and extensive regulatory oversight, leading to a reliable record in transporting goods over long distances, though it faces risks from weather disruptions and port congestions. Hyperloop freight promises enhanced reliability through its controlled environment and automated technology, reducing human error and external hazards that traditional cargo shipping faces. Safety measures in hyperloop systems include airtight tubes and real-time monitoring, potentially offering a more secure and consistent freight transport method compared to maritime cargo shipping.
Future Prospects: Adoption and Disruption in Freight Logistics
Cargo shipping remains the backbone of global freight logistics with extensive infrastructure supporting vast quantities of goods across oceans, while hyperloop freight promises revolutionary speed and efficiency by transporting cargo through near-vacuum tubes at speeds exceeding 600 mph. The future adoption of hyperloop systems could disrupt traditional shipping by drastically reducing transit times, lowering emissions, and enabling just-in-time delivery for industrial supply chains. Investment from major logistics firms and government partnerships is accelerating hyperloop pilot projects, signaling a transformative shift poised to redefine global freight transportation.
Related Important Terms
Automated Containerization
Automated containerization in cargo shipping enhances efficiency by enabling seamless loading, unloading, and tracking of containers through robotic systems and IoT integration. Hyperloop freight leverages automated containerization to achieve ultra-fast transit times, using magnetic levitation and vacuum tubes to transport standardized containers with minimal human intervention.
Hyperloop Pod Freight
Hyperloop pod freight offers significantly faster transit times compared to traditional cargo shipping, reducing delivery from days or weeks to mere hours by using low-pressure tubes and magnetic levitation technology. This innovative transport method also enhances energy efficiency and reduces carbon emissions, positioning it as a sustainable alternative for high-speed freight logistics.
Green Corridor Logistics
Cargo shipping remains a dominant method for global freight transport, emitting significant greenhouse gases due to fuel consumption, whereas hyperloop freight offers a low-emission alternative by utilizing electric propulsion and vacuum-sealed tubes to reduce air resistance. Green corridor logistics prioritize sustainability by integrating hyperloop technology to minimize carbon footprints and optimize energy efficiency across supply chains.
Vacuum Tube Shipping
Vacuum tube shipping, a core technology behind hyperloop freight, offers unprecedented speed and energy efficiency compared to traditional cargo shipping by drastically reducing air resistance through near-vacuum conditions. This innovation enables cargo to be transported at speeds exceeding 600 mph, significantly cutting delivery times and operational costs while minimizing environmental impact.
Real-Time Freight Analytics
Cargo shipping relies heavily on traditional tracking systems that provide limited real-time freight analytics, often causing delays in identifying shipment issues. Hyperloop freight incorporates advanced sensor networks and AI-driven platforms, offering precise, real-time data on cargo location, condition, and transit efficiency to optimize supply chain decisions.
Intermodal Sync Networks
Cargo shipping relies on established intermodal sync networks integrating maritime, rail, and trucking to optimize global freight logistics, emphasizing efficiency in large-scale container transport. Hyperloop freight promises to revolutionize intermodal networks by enabling ultra-fast, energy-efficient transit, minimizing transfer times, and enhancing synchronization between cargo hubs.
Hyperloop Transloading
Hyperloop transloading streamlines cargo transfer by reducing handling times and minimizing damage risks compared to traditional cargo shipping methods. This ultrafast, energy-efficient system integrates seamlessly with existing supply chains, enhancing freight throughput and lowering overall operational costs.
Zero-Emission Linehaul
Zero-emission linehaul in cargo shipping faces challenges due to reliance on diesel-powered trucks, whereas hyperloop freight offers a sustainable alternative by utilizing magnetic levitation and electric propulsion to eliminate greenhouse gas emissions. The hyperloop's potential for rapid, energy-efficient transport over long distances could revolutionize freight logistics by drastically reducing carbon footprints compared to traditional diesel linehaul systems.
Digital Twin Cargo Tracking
Digital twin cargo tracking in hyperloop freight offers real-time, highly accurate monitoring of shipment conditions and locations, significantly reducing delays and losses compared to traditional cargo shipping methods. This advanced digital integration enhances predictive maintenance, optimizes route planning, and increases overall supply chain transparency in transportation logistics.
Autonomous Cargo Hubs
Autonomous cargo hubs streamline cargo shipping by integrating automated sorting, loading, and unloading systems, significantly reducing turnaround times and labor costs. Hyperloop freight leverages these hubs to provide rapid, energy-efficient transport, enhancing supply chain speed and reliability compared to traditional cargo shipping methods.
Cargo Shipping vs Hyperloop Freight Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com