Waste segregation improves recycling efficiency by separating materials at the source, reducing contamination and lowering landfill waste. Smart bins enhance this process by using sensors and AI to automatically sort waste, providing real-time data for waste management optimization. Integrating both methods leads to a cleaner environment and more sustainable resource utilization.
Table of Comparison
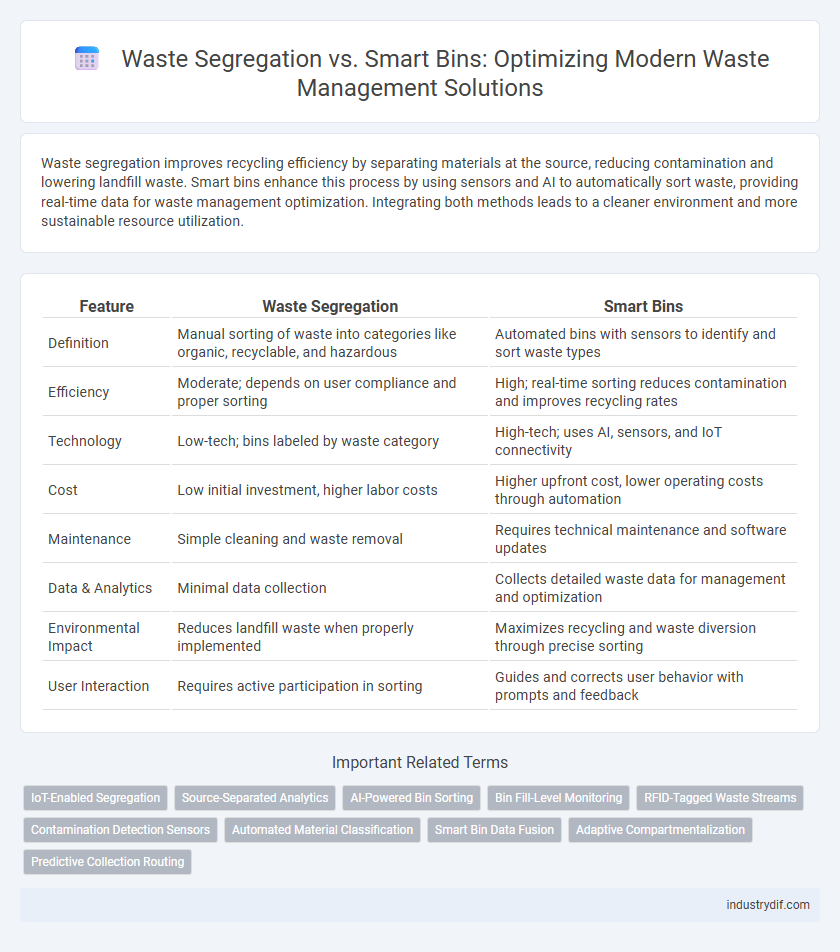
| Feature | Waste Segregation | Smart Bins |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manual sorting of waste into categories like organic, recyclable, and hazardous | Automated bins with sensors to identify and sort waste types |
| Efficiency | Moderate; depends on user compliance and proper sorting | High; real-time sorting reduces contamination and improves recycling rates |
| Technology | Low-tech; bins labeled by waste category | High-tech; uses AI, sensors, and IoT connectivity |
| Cost | Low initial investment, higher labor costs | Higher upfront cost, lower operating costs through automation |
| Maintenance | Simple cleaning and waste removal | Requires technical maintenance and software updates |
| Data & Analytics | Minimal data collection | Collects detailed waste data for management and optimization |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste when properly implemented | Maximizes recycling and waste diversion through precise sorting |
| User Interaction | Requires active participation in sorting | Guides and corrects user behavior with prompts and feedback |
Introduction to Waste Segregation and Smart Bins
Waste segregation involves separating waste into categories such as organic, recyclable, and hazardous materials to enhance recycling efficiency and reduce landfill burden. Smart bins use sensor technology to identify and sort waste automatically, improving accuracy and promoting proper disposal habits. Both methods aim to optimize waste management but differ significantly in implementation and technological integration.
Defining Waste Segregation: Principles and Importance
Waste segregation involves separating waste into distinct categories such as organic, recyclable, hazardous, and non-recyclable materials to enhance recycling efficiency and reduce landfill impact. This principle is crucial for preventing contamination, improving resource recovery rates, and minimizing environmental pollution. Implementing effective waste segregation can lead to significant cost savings in waste management and promote sustainability in urban and rural communities.
What are Smart Bins? Features and Technologies
Smart bins are advanced waste disposal units equipped with sensors and IoT technology to automatically detect, sort, and compact different types of waste, enhancing efficiency in waste management. Featuring real-time fill-level monitoring, RFID tagging, and data analytics, smart bins optimize collection routes and reduce operational costs. Integration with mobile apps and AI algorithms supports behavior-driven waste segregation, promoting sustainable practices and reducing contamination in recycling streams.
Manual Waste Segregation: Methods and Challenges
Manual waste segregation involves the physical sorting of recyclable, organic, and non-recyclable materials at the source, typically by individuals or waste workers. Common methods include color-coded bins, labeled containers, and community awareness programs to enhance segregation accuracy. Challenges encompass contamination risks, inconsistent compliance, labor intensity, and health hazards for workers handling unsegregated waste.
How Smart Bins Automate Waste Sorting
Smart bins utilize sensors and AI technology to automatically identify and sort waste into designated compartments, enhancing accuracy and efficiency compared to manual segregation. These bins reduce contamination by detecting recyclable, organic, and hazardous materials in real-time, optimizing waste processing streams. Integration with IoT systems enables smart bins to communicate fill levels and sorting data, streamlining collection schedules and reducing operational costs.
Impact on Environmental Sustainability
Waste segregation enhances environmental sustainability by enabling efficient recycling and reducing landfill waste, conserving natural resources and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Smart bins complement segregation by using sensors and data analytics to optimize waste collection routes, minimize overflow, and promote proper disposal behavior. Together, these approaches reduce pollution, improve resource recovery, and support circular economy goals.
Cost Analysis: Traditional vs. Smart Waste Management
Traditional waste segregation involves manual sorting that incurs higher labor costs and often leads to inefficiencies, whereas smart bins reduce operational expenses through automated sorting and real-time monitoring. Smart waste management systems optimize collection routes, significantly lowering fuel consumption and maintenance expenses associated with conventional methods. Although initial investment in smart bins is higher, the long-term cost savings from enhanced efficiency and reduced landfill fees provide a favorable return on investment.
User Engagement and Behavioral Change
Waste segregation encourages users to consciously separate recyclables, compostables, and landfill items, fostering long-term behavioral change through active participation. Smart bins enhance user engagement by providing real-time feedback and incentives, making waste disposal more interactive and intuitive. Combining waste segregation practices with smart bin technology significantly improves recycling rates and enhances environmental responsibility among communities.
Integration with Smart City Initiatives
Waste segregation enhances recycling efficiency by categorizing waste into organic, recyclable, and hazardous materials, aligning with urban sustainability goals. Smart bins equipped with sensors and IoT technology monitor real-time waste levels, optimize collection routes, and reduce operational costs in smart city frameworks. Integrating smart bins with waste segregation programs supports data-driven decision-making, improves resource management, and contributes to cleaner, more efficient urban environments.
Future Trends in Waste Management Technologies
Future trends in waste management technologies emphasize advanced waste segregation systems integrated with smart bins equipped with IoT sensors and AI algorithms to optimize sorting accuracy and efficiency. Smart bins enable real-time monitoring of waste levels, contamination detection, and automated categorization, reducing the burden on manual segregation processes and improving recycling rates. The integration of machine learning and data analytics drives predictive waste collection schedules, supporting sustainable urban waste management and minimizing environmental impact.
Related Important Terms
IoT-Enabled Segregation
IoT-enabled smart bins enhance waste segregation by using sensors and real-time data analytics to identify, sort, and optimize the disposal of recyclables, organics, and landfill waste with higher accuracy. These intelligent systems reduce contamination rates, improve collection efficiency, and support sustainable urban waste management practices through automated monitoring and adaptive routing.
Source-Separated Analytics
Source-separated analytics enhance waste segregation efficiency by providing precise data on waste composition and volume at the origin, enabling tailored recycling and disposal strategies. Smart bins equipped with sensors and IoT technology facilitate real-time monitoring and reporting, optimizing waste management through data-driven decisions that reduce contamination and increase resource recovery.
AI-Powered Bin Sorting
AI-powered bin sorting enhances waste segregation by using advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms to accurately identify and separate recyclables, organic matter, and non-recyclables in real time, significantly reducing contamination rates. Smart bins equipped with AI improve recycling efficiency and collection logistics by automatically categorizing waste, optimizing sorting processes, and enabling data-driven waste management decisions.
Bin Fill-Level Monitoring
Waste segregation enhances recycling efficiency by separating materials at the source, reducing contamination and improving resource recovery rates. Smart bins equipped with fill-level monitoring sensors optimize collection routes and schedules, minimizing overflow issues and operational costs while promoting sustainable waste management practices.
RFID-Tagged Waste Streams
RFID-tagged waste streams enhance waste segregation by enabling precise tracking and categorization of materials, improving recycling rates and reducing contamination. Smart bins integrated with RFID technology facilitate automated sorting and real-time monitoring, optimizing collection routes and operational efficiency in waste management systems.
Contamination Detection Sensors
Waste segregation improves recycling efficiency by separating materials at the source, reducing contamination in waste streams, whereas smart bins equipped with contamination detection sensors utilize advanced technologies like infrared and AI to identify and alert for improper disposal in real-time. These sensors enhance sorting accuracy, minimize cross-contamination, and optimize waste management operations through data-driven insights.
Automated Material Classification
Automated material classification in waste segregation utilizes smart bins equipped with sensors and AI technology to accurately identify and separate recyclables, organic waste, and hazardous materials, enhancing sorting efficiency and reducing contamination rates. This technology streamlines the waste management process by minimizing human error and optimizing recycling streams, leading to improved resource recovery and lower environmental impact.
Smart Bin Data Fusion
Smart bin data fusion integrates sensor inputs such as fill level, waste type, and environmental conditions to optimize waste segregation efficiency and collection routes. This advanced technology reduces contamination rates and operational costs by enabling real-time, data-driven decisions for dynamic waste management systems.
Adaptive Compartmentalization
Adaptive compartmentalization in waste segmentation enhances efficiency by dynamically adjusting bin compartments based on real-time waste composition data, reducing contamination and increasing recycling rates. Smart bins equipped with sensors and AI-driven sorting mechanisms enable precise separation of organic, recyclable, and hazardous waste, optimizing waste management processes and promoting sustainability.
Predictive Collection Routing
Waste segregation enhances recycling efficiency by separating materials at the source, while smart bins equipped with sensors optimize predictive collection routing through real-time fill-level data and AI algorithms, reducing operational costs and minimizing environmental impact. Integrating smart bins with waste segregation systems enables dynamic route planning, leading to faster collection times and improved resource allocation.
Waste Segregation vs Smart Bins Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com