Greywater recycling efficiently reuses wastewater from sinks, showers, and laundry for irrigation and flushing toilets, reducing freshwater demand and lowering utility costs. Blackwater upcycling treats sewage and organic waste through advanced processes like anaerobic digestion to generate biogas and nutrient-rich fertilizers, promoting sustainable energy and soil health. Comparing both, greywater recycling offers simpler systems for water conservation, while blackwater upcycling delivers broader environmental benefits by transforming waste into valuable resources.
Table of Comparison
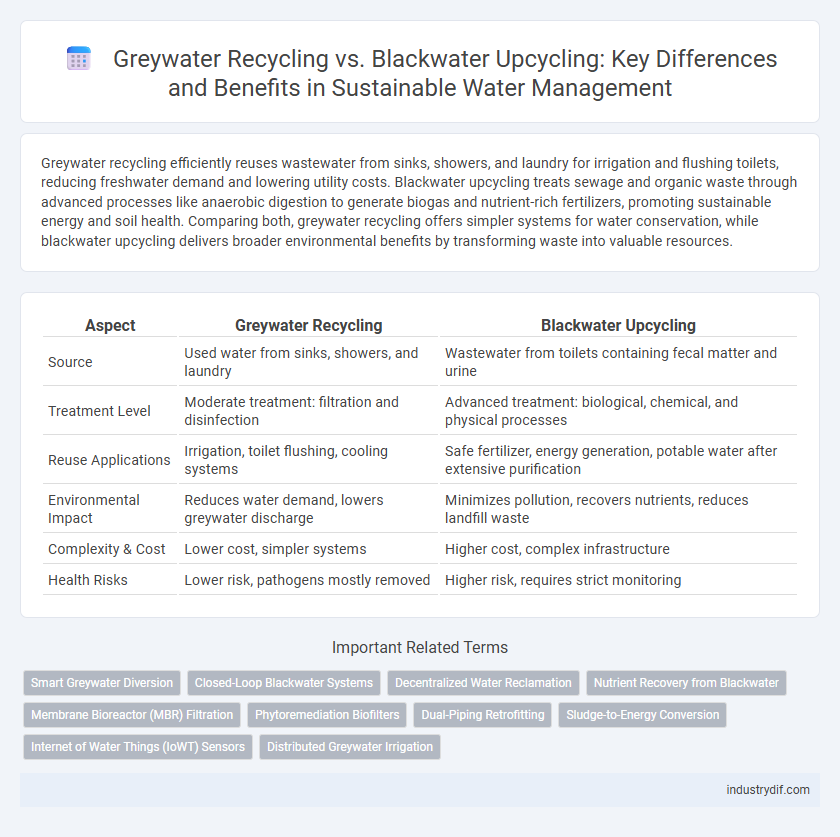
| Aspect | Greywater Recycling | Blackwater Upcycling |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Used water from sinks, showers, and laundry | Wastewater from toilets containing fecal matter and urine |
| Treatment Level | Moderate treatment: filtration and disinfection | Advanced treatment: biological, chemical, and physical processes |
| Reuse Applications | Irrigation, toilet flushing, cooling systems | Safe fertilizer, energy generation, potable water after extensive purification |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces water demand, lowers greywater discharge | Minimizes pollution, recovers nutrients, reduces landfill waste |
| Complexity & Cost | Lower cost, simpler systems | Higher cost, complex infrastructure |
| Health Risks | Lower risk, pathogens mostly removed | Higher risk, requires strict monitoring |
Understanding Greywater and Blackwater: Key Differences
Greywater recycling involves treating gently used water from sinks, showers, and laundry to be reused for irrigation and toilet flushing, significantly reducing overall water consumption. Blackwater upcycling, on the other hand, manages wastewater containing human waste and organic matter through advanced treatment processes that enable nutrient recovery and energy generation. Recognizing the key differences--greywater's lower contamination levels versus blackwater's higher pathogen load--is essential for implementing safe, effective water reuse systems.
The Science Behind Greywater Recycling
Greywater recycling involves treating and reusing water from sinks, showers, and laundry, using biological and physical filtration processes to remove contaminants like soap, oils, and organic matter. Advanced treatment methods, including membrane bioreactors and UV disinfection, enhance water quality to safe levels for irrigation or toilet flushing. Scientific analysis shows greywater systems reduce freshwater consumption by up to 50%, significantly conserving resources compared to blackwater upcycling, which requires more complex treatment due to higher pathogen loads.
How Blackwater Upcycling Works
Blackwater upcycling involves treating wastewater containing human waste and contaminants through advanced biological, chemical, and physical processes to remove pathogens and pollutants. This treatment enables the recovery of valuable resources such as nutrients, biogas, and purified water for reuse in agriculture or energy production. The integration of membrane filtration, anaerobic digestion, and nutrient recovery systems ensures efficient conversion of blackwater into sustainable outputs.
Environmental Impact: Greywater vs Blackwater Solutions
Greywater recycling significantly reduces freshwater consumption by treating and reusing water from sinks, showers, and laundry for irrigation or toilet flushing, minimizing wastewater discharge and conserving natural resources. Blackwater upcycling involves advanced treatment processes that transform sewage into reusable water and energy, effectively reducing pollution and lowering greenhouse gas emissions associated with wastewater management. Both solutions contribute to sustainable water management, but greywater recycling typically offers easier implementation with lower energy needs, while blackwater upcycling provides comprehensive environmental benefits through resource recovery.
Regulatory Standards for Water Reuse Systems
Regulatory standards for water reuse systems vary significantly between greywater recycling and blackwater upcycling, with greywater typically subject to less stringent regulations due to its lower pathogen content. Blackwater upcycling requires advanced treatment processes to meet health and safety criteria set by agencies such as the EPA and WHO, ensuring removal of harmful contaminants before reuse. Compliance with these standards is crucial for system design, operational monitoring, and safeguarding public health in both residential and industrial applications.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Implementing Greywater and Blackwater Technologies
Greywater recycling systems generally offer lower installation and maintenance costs compared to blackwater upcycling technologies, making them more accessible for residential use. Blackwater upcycling, despite higher initial expenses, provides greater long-term benefits by enabling advanced nutrient recovery and pathogen removal for agricultural and industrial applications. An effective cost-benefit analysis must consider factors like regulatory compliance, environmental impact, and potential revenue from resource recovery in each technology's lifecycle.
Residential and Commercial Applications
Greywater recycling in residential and commercial applications involves treating wastewater from sinks, showers, and laundry for reuse in irrigation and toilet flushing, significantly reducing freshwater demand. Blackwater upcycling takes a more advanced approach by processing sewage waste through anaerobic digestion or advanced filtration to recover nutrients and generate biogas, promoting energy-efficient waste management. Implementing these systems helps buildings achieve sustainability goals by conserving water resources and lowering environmental impact through innovative water reuse technologies.
Challenges in Greywater and Blackwater Treatment
Greywater recycling faces challenges such as the presence of household chemicals and organic matter that complicate effective treatment and increase the risk of microbial contamination. Blackwater upcycling is more complex due to high concentrations of pathogens, nutrients, and solids requiring advanced treatment processes like anaerobic digestion or membrane filtration. Both systems demand rigorous monitoring and management to prevent environmental pollution and ensure safe reuse.
Innovations in Water Upcycling Technologies
Innovations in water upcycling technologies have significantly advanced the efficiency of greywater recycling systems by integrating biological filtration and membrane bioreactors, enabling the safe reuse of household wastewater for irrigation and flushing. In contrast, blackwater upcycling technologies focus on nutrient recovery and energy generation through anaerobic digestion and electrochemical treatment, transforming sewage into biogas and reclaimed water with minimal environmental impact. These cutting-edge methods enhance water sustainability by reducing freshwater demand and mitigating pollution from domestic wastewater sources.
Future Trends in Sustainable Water Management
Greywater recycling technologies are advancing with smart filtration systems that enable safe reuse for irrigation and non-potable household purposes, significantly reducing freshwater demand. Blackwater upcycling is evolving through innovative anaerobic digestion and nutrient recovery methods, transforming wastewater into biogas and fertilizers, promoting circular economy principles. Future trends highlight integration of AI-driven monitoring and decentralized treatment systems, enhancing efficiency and scalability in sustainable water management.
Related Important Terms
Smart Greywater Diversion
Smart greywater diversion systems optimize water conservation by redirecting lightly used water from baths, sinks, and washing machines to irrigation or toilet flushing, reducing reliance on potable water supplies. Unlike blackwater upcycling, which requires complex treatment for sewage reuse, greywater recycling harnesses lower-contaminant wastewater with simpler filtration and disinfection processes, enhancing sustainability and lowering operational costs.
Closed-Loop Blackwater Systems
Closed-loop blackwater systems effectively treat and recycle wastewater from toilets and kitchen sinks, enabling nutrient recovery and reducing environmental pollution compared to conventional greywater recycling, which primarily reuses water from showers and laundry. These advanced upcycling technologies convert blackwater into safe, reusable water and fertilizer, supporting sustainable water management and agricultural practices.
Decentralized Water Reclamation
Decentralized water reclamation systems enhance urban sustainability by enabling efficient greywater recycling, which repurposes relatively clean household wastewater for non-potable uses, reducing the demand on freshwater resources. Blackwater upcycling involves advanced onsite treatment technologies that convert highly contaminated wastewater into reusable water and energy, offering a closed-loop solution for waste management and resource recovery in residential and commercial settings.
Nutrient Recovery from Blackwater
Blackwater upcycling enables efficient nutrient recovery by extracting essential elements like nitrogen and phosphorus from human waste, transforming pollutants into valuable fertilizers that support sustainable agriculture. Unlike greywater recycling, which primarily treats lightly contaminated water for reuse, blackwater treatment focuses on optimizing nutrient extraction to close the nutrient loop and reduce environmental impact.
Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Filtration
Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) filtration offers advanced treatment for both greywater recycling and blackwater upcycling by combining biological degradation with membrane separation, effectively removing organic contaminants and pathogens. This technology enhances water reuse potential by producing high-quality effluent suitable for irrigation, industrial processes, or potable applications while minimizing environmental impact.
Phytoremediation Biofilters
Phytoremediation biofilters harness aquatic plants like water hyacinth and reed beds to naturally treat greywater by removing nutrients, heavy metals, and pathogens, making it safe for reuse in irrigation and flushing. Blackwater upcycling through advanced phytoremediation involves complex biofilters that degrade organic pollutants and pharmaceuticals, converting sewage into nutrient-rich fertilizer, thereby closing the water and nutrient cycle sustainably.
Dual-Piping Retrofitting
Dual-piping retrofitting enables the efficient separation and management of greywater and blackwater, facilitating greywater recycling for non-potable uses and blackwater upcycling through advanced treatment processes. This infrastructure upgrade reduces freshwater consumption by reusing greywater for irrigation and flushing, while enabling blackwater transformation into biogas and nutrient-rich fertilizers, promoting sustainable water and waste management.
Sludge-to-Energy Conversion
Greywater recycling reduces wastewater volume by treating lightly contaminated water from sinks and showers for reuse, while blackwater upcycling involves converting highly polluted sewage sludge through anaerobic digestion or thermal processes into biogas for energy recovery. Sludge-to-energy conversion enhances sustainability by simultaneously addressing waste management and renewable energy production, significantly lowering methane emissions from untreated blackwater sludge.
Internet of Water Things (IoWT) Sensors
Greywater recycling systems integrated with Internet of Water Things (IoWT) sensors enable real-time monitoring of water quality and flow rates, enhancing system efficiency and reducing contamination risks. Blackwater upcycling, leveraging IoWT sensor networks, facilitates advanced treatment processes by precisely tracking chemical composition and microbial activity, promoting sustainable wastewater reuse.
Distributed Greywater Irrigation
Distributed greywater irrigation systems efficiently recycle household wastewater from sinks, showers, and laundry to irrigate landscapes, reducing freshwater demand and lowering sewage discharge. Unlike blackwater upcycling, which requires extensive treatment due to high pathogen levels, greywater recycling provides a sustainable, lower-risk method for water conservation in urban and residential environments.
Greywater Recycling vs Blackwater Upcycling Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com