Dropshipping streamlines inventory management by allowing retailers to sell products without holding stock, relying on suppliers to fulfill orders directly to customers. Headless commerce separates the frontend presentation layer from the backend eCommerce functionality, offering greater flexibility in customizing user experiences and integrating multiple sales channels. Both models optimize wholesale operations but cater to different business needs: dropshipping minimizes overhead and inventory risk, while headless commerce enhances scalability and personalization.
Table of Comparison
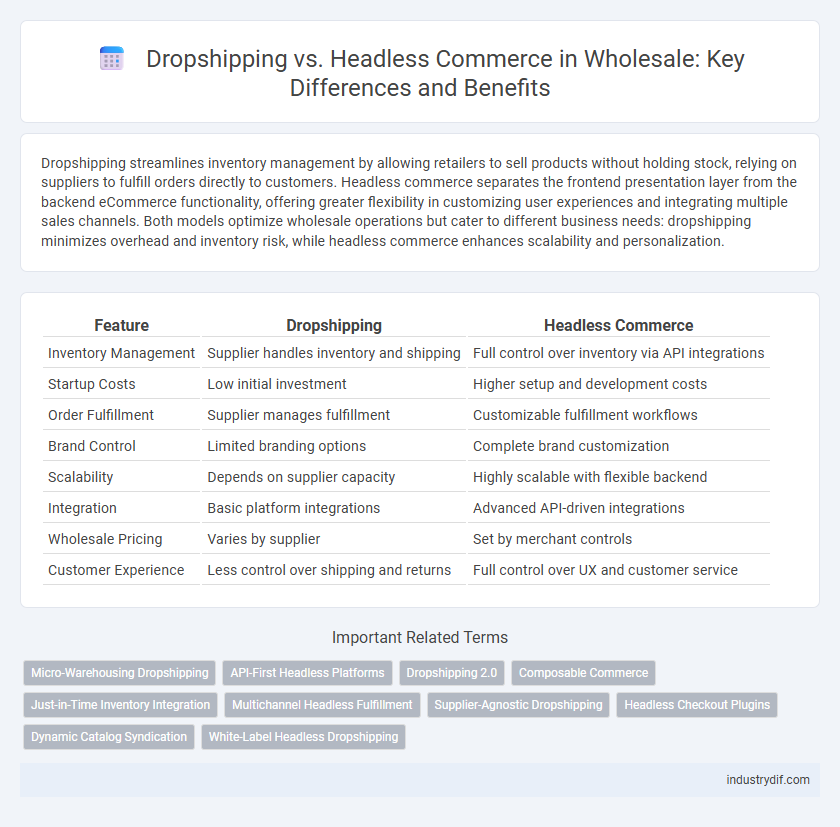
| Feature | Dropshipping | Headless Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Management | Supplier handles inventory and shipping | Full control over inventory via API integrations |
| Startup Costs | Low initial investment | Higher setup and development costs |
| Order Fulfillment | Supplier manages fulfillment | Customizable fulfillment workflows |
| Brand Control | Limited branding options | Complete brand customization |
| Scalability | Depends on supplier capacity | Highly scalable with flexible backend |
| Integration | Basic platform integrations | Advanced API-driven integrations |
| Wholesale Pricing | Varies by supplier | Set by merchant controls |
| Customer Experience | Less control over shipping and returns | Full control over UX and customer service |
Introduction to Dropshipping and Headless Commerce
Dropshipping is a wholesale fulfillment method where retailers sell products without holding inventory, relying on suppliers to ship directly to customers, reducing upfront costs and inventory risks. Headless commerce separates the frontend presentation layer from the backend e-commerce engine, enabling wholesale businesses to deliver customized, scalable shopping experiences across multiple channels. Combining dropshipping with headless commerce allows wholesalers to streamline operations while enhancing flexibility and front-end innovation, meeting diverse customer demands effectively.
Key Differences Between Dropshipping and Headless Commerce
Dropshipping enables wholesalers to sell products without holding inventory, relying on suppliers for order fulfillment, while headless commerce separates the front-end presentation layer from the e-commerce backend, offering greater customization and omnichannel flexibility. Dropshipping is inventory-light and cost-effective for testing product demand, whereas headless commerce supports complex integrations and scalable digital experiences essential for large wholesale operations. The key difference lies in infrastructure; dropshipping focuses on supply chain logistics, while headless commerce emphasizes front-end customization and seamless customer engagement.
Advantages of Dropshipping in Wholesale
Dropshipping in wholesale offers significant advantages such as reduced inventory costs and lower financial risk by eliminating the need to stock products upfront. This model enables wholesalers to quickly scale their product range and respond flexibly to market demand without investing in warehouse space or managing logistics. Faster market entry and streamlined order fulfillment processes make dropshipping an efficient solution for wholesale businesses aiming to optimize cash flow and operational efficiency.
Benefits of Headless Commerce for Wholesale Businesses
Headless commerce offers wholesale businesses enhanced flexibility by decoupling the front-end presentation layer from the back-end ecommerce functionality, enabling seamless integration with multiple sales channels and custom user experiences. This architecture improves scalability and performance, allowing wholesalers to handle large product catalogs and high transaction volumes efficiently. Additionally, headless commerce supports rapid innovation and easier adaptation to market changes, driving competitive advantage in the wholesale sector.
Technology Stack: Dropshipping vs Headless Commerce
Dropshipping relies on a simplified technology stack integrating e-commerce platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce with supplier APIs for real-time inventory and order management, minimizing upfront infrastructure costs. Headless commerce leverages decoupled front-end frameworks such as React or Vue.js combined with robust backend commerce engines like Magento or CommerceTools, offering greater customization and scalability for complex wholesale operations. The choice between dropshipping and headless commerce technology stacks depends on the need for speed and flexibility versus deep integration and control in wholesale environments.
Scalability and Flexibility in Wholesale Operations
Dropshipping offers scalable inventory management by eliminating the need for upfront stock investment, enabling wholesale businesses to quickly expand product offerings without warehousing constraints. Headless commerce enhances flexibility through decoupled front-end and back-end systems, allowing wholesalers to customize user experiences and integrate multiple sales channels seamlessly. Combining dropshipping with headless commerce architectures optimizes scalability and operational agility for large-scale wholesale distribution networks.
Order Fulfillment and Inventory Management Comparison
Dropshipping streamlines order fulfillment by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, eliminating the need for inventory storage and reducing overhead costs. Headless commerce offers greater control over inventory management by decoupling the front-end and back-end systems, enabling seamless integration with multiple warehouses and real-time stock updates. Wholesale businesses benefit from dropshipping's reduced risk and headless commerce's scalable inventory solutions to optimize supply chain efficiency.
Integration Capabilities with Wholesale Platforms
Dropshipping offers seamless integration with major wholesale platforms through API connections, enabling automated order fulfillment and inventory synchronization. Headless commerce provides flexible integration via customizable APIs, allowing businesses to connect multiple wholesale channels and tailor user experiences. Both solutions enhance scalability, but headless commerce excels in adapting to complex wholesale workflows and diverse platform architectures.
Cost Structure: Dropshipping vs Headless Commerce
Dropshipping minimizes upfront inventory costs by eliminating the need for warehousing, relying on third-party suppliers to ship products directly to customers, which reduces fixed expenses but involves higher per-unit fees. Headless commerce demands a more significant initial investment in custom development and infrastructure, generating ongoing costs associated with managing separate front-end and back-end systems, yet offers greater control over user experience and scalability. Businesses must weigh dropshipping's lower barrier to entry against headless commerce's advanced customization capabilities and potential for long-term cost efficiency.
Which Model is Best for Future-Proofing Wholesale Businesses?
Dropshipping offers low upfront investment and flexible inventory management, making it ideal for testing new markets in wholesale, while headless commerce provides robust customization and seamless omnichannel experiences essential for scaling and future-proofing complex wholesale operations. Wholesale businesses aiming for long-term growth benefit from headless commerce's decoupled architecture, enabling rapid integration with emerging technologies and personalized customer journeys. Optimizing supply chain efficiency and enhancing digital storefront agility are critical factors when choosing between these models for sustainable wholesale success.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Warehousing Dropshipping
Micro-warehousing dropshipping enhances wholesale efficiency by strategically positioning small inventory hubs near key markets, reducing delivery times and shipping costs compared to traditional headless commerce models. This approach streamlines order fulfillment, supports real-time inventory management, and scales seamlessly to meet fluctuating demand in wholesale distribution.
API-First Headless Platforms
API-first headless commerce platforms enable seamless integration and customization for wholesalers, offering direct control over backend systems and frontend experiences without relying on dropshipping intermediaries. This approach streamlines inventory management, accelerates product updates, and enhances scalability compared to traditional dropshipping models that often limit real-time data synchronization and brand consistency.
Dropshipping 2.0
Dropshipping 2.0 revolutionizes wholesale by integrating advanced inventory automation, real-time supplier data, and seamless order fulfillment, enhancing scalability and reducing stock risks compared to traditional dropshipping. This model leverages AI-driven analytics and direct supplier partnerships to optimize pricing strategies and improve delivery speed, setting new standards for efficiency in wholesale ecommerce.
Composable Commerce
Dropshipping eliminates inventory management by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, while headless commerce separates the front-end presentation layer from the back-end commerce engine, offering greater flexibility in user experience customization. Composable commerce leverages modular APIs and microservices, enabling businesses to integrate dropshipping and headless commerce components seamlessly for scalable, agile wholesale operations.
Just-in-Time Inventory Integration
Dropshipping enables wholesalers to implement just-in-time inventory integration by directly fulfilling customer orders from suppliers, reducing overhead and minimizing stock risks. Headless commerce supports agile, customizable supply chain management through API-driven platforms, allowing seamless synchronization of real-time inventory data across multiple channels.
Multichannel Headless Fulfillment
Multichannel headless fulfillment in wholesale leverages APIs to integrate various sales channels with backend inventory systems, enabling real-time stock updates and streamlined order processing without the constraints of traditional e-commerce platforms. Dropshipping depends on third-party suppliers for inventory management and shipping, often resulting in slower fulfillment and less control compared to the agile, scalable headless commerce model optimized for wholesale multichannel distribution.
Supplier-Agnostic Dropshipping
Supplier-agnostic dropshipping enables wholesalers to seamlessly integrate multiple suppliers without being locked into a single inventory source, optimizing product variety and fulfillment efficiency. Headless commerce offers customizable front-end experiences but often requires specific backend integrations, making supplier flexibility more limited compared to the freedom found in supplier-agnostic dropshipping models.
Headless Checkout Plugins
Headless checkout plugins enhance wholesale e-commerce by decoupling the front-end and back-end systems, enabling seamless integration with multiple platforms and faster, customizable checkout experiences. These plugins improve scalability and flexibility in dropshipping and wholesale models by streamlining complex inventory and order management processes without compromising user experience.
Dynamic Catalog Syndication
Dropshipping leverages dynamic catalog syndication to automatically update product availability and pricing in real-time across multiple sales channels, enhancing inventory accuracy without holding stock. Headless commerce utilizes dynamic catalog syndication to decouple front-end presentation from back-end inventory systems, enabling seamless content delivery and rapid updates across diverse customer touchpoints in wholesale environments.
White-Label Headless Dropshipping
White-label headless dropshipping combines the flexibility of headless commerce with the customization of white-label branding, allowing wholesalers to offer tailored e-commerce experiences without managing inventory or fulfillment. This model optimizes scalability and brand control, leveraging APIs for seamless integration across multiple platforms while minimizing operational overhead.
Dropshipping vs Headless Commerce Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com