Wholesale operations primarily involve bulk purchasing and distribution of goods, emphasizing cost efficiency and large-scale transaction volumes. Circular supply chains prioritize sustainability by reusing, refurbishing, and recycling materials to minimize waste and environmental impact. Integrating circular principles into wholesale can reduce resource consumption and foster a more resilient, eco-friendly distribution network.
Table of Comparison
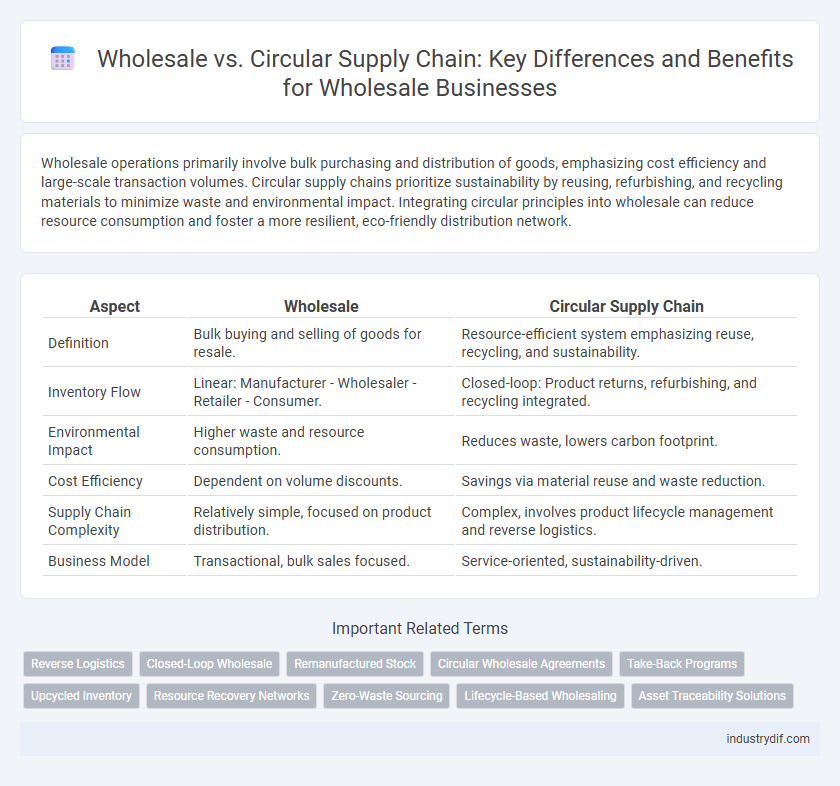
| Aspect | Wholesale | Circular Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bulk buying and selling of goods for resale. | Resource-efficient system emphasizing reuse, recycling, and sustainability. |
| Inventory Flow | Linear: Manufacturer - Wholesaler - Retailer - Consumer. | Closed-loop: Product returns, refurbishing, and recycling integrated. |
| Environmental Impact | Higher waste and resource consumption. | Reduces waste, lowers carbon footprint. |
| Cost Efficiency | Dependent on volume discounts. | Savings via material reuse and waste reduction. |
| Supply Chain Complexity | Relatively simple, focused on product distribution. | Complex, involves product lifecycle management and reverse logistics. |
| Business Model | Transactional, bulk sales focused. | Service-oriented, sustainability-driven. |
Understanding Wholesale Supply Chains
Wholesale supply chains involve the bulk purchase and distribution of goods from manufacturers to retailers or other businesses, emphasizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness. These supply chains prioritize inventory management, demand forecasting, and bulk logistics to ensure product availability at competitive prices. Unlike circular supply chains, which focus on reuse and sustainability, wholesale supply chains primarily concentrate on maximizing throughput and minimizing costs in the traditional linear flow of goods.
Key Features of Circular Supply Chains
Circular supply chains emphasize resource efficiency by prioritizing product reuse, refurbishment, and recycling to minimize waste generation and environmental impact. They integrate closed-loop processes that enable continuous material cycling, extending product lifecycles and reducing the reliance on virgin raw materials. Key features include reverse logistics, sustainable sourcing, and collaboration across stakeholders to optimize material flow and promote a regenerative economy.
Comparative Overview: Wholesale vs Circular Models
Wholesale models primarily operate through linear supply chains focused on bulk purchasing and mass distribution, aiming for economies of scale and market reach. Circular supply chains emphasize resource efficiency by integrating product reuse, recycling, and remanufacturing processes to minimize waste and promote sustainability. While wholesale prioritizes cost-effectiveness and volume-driven growth, circular models innovate around environmental responsibility and long-term resource preservation.
Environmental Impact of Wholesale vs Circular Supply Chains
Wholesale supply chains typically generate significant environmental impact due to linear resource use, resulting in increased waste and higher carbon emissions throughout product distribution. Circular supply chains minimize environmental footprint by promoting resource efficiency, reuse, and recycling, significantly reducing landfill contributions and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. The shift from wholesale to circular models supports sustainable production and consumption, aligning with global environmental goals.
Economic Benefits: Wholesale vs Circular Approaches
Wholesale supply chains optimize cost efficiency by leveraging bulk purchasing and streamlined logistics, driving significant reductions in unit expenses. Circular supply chains enhance economic benefits through resource recovery, waste minimization, and product lifecycle extension, which reduce raw material costs and foster sustainable revenue streams. Businesses integrating circular approaches within wholesale models achieve improved profitability by combining cost savings with environmental incentives and customer loyalty.
Challenges in Adopting Circular Supply Chains
Wholesale businesses face significant challenges in adopting circular supply chains due to the complexity of integrating reuse, recycling, and refurbishing processes within traditional distribution models. High upfront costs, lack of standardized infrastructure, and limited supplier collaboration hinder seamless transition to circular practices. Additionally, tracking product lifecycle data and managing reverse logistics present operational difficulties that require advanced technological solutions.
Technology’s Role in Wholesale and Circular Supply Chains
Technology plays a crucial role in optimizing both wholesale and circular supply chains by enabling real-time data analytics, inventory management, and demand forecasting. In wholesale, advanced ERP systems and AI-driven platforms enhance order processing efficiency and reduce excess stock, while in circular supply chains, technologies like IoT and blockchain facilitate tracking product lifecycle, ensuring sustainable resource use and efficient reverse logistics. Integration of digital tools accelerates transparency, reduces waste, and supports sustainable practices crucial for circular economy models.
Sustainability Metrics in Supply Chain Management
Wholesale supply chains typically emphasize volume efficiency and cost reduction, often leading to increased resource consumption and waste generation. Circular supply chains prioritize sustainability metrics such as material recovery rates, carbon footprint reduction, and waste minimization to close the loop and promote resource regeneration. Integrating circular principles within wholesale operations enhances environmental performance by tracking metrics like lifecycle emissions, reuse percentages, and end-of-life product recovery.
Case Studies: Transitioning from Wholesale to Circular
Case studies reveal that transitioning from wholesale to a circular supply chain significantly reduces waste while improving resource efficiency, with companies reporting up to 40% cost savings in materials. Businesses adopting circular models integrate product take-back programs and remanufacturing processes, resulting in extended product lifecycles and enhanced customer loyalty. Embracing circular supply chain strategies drives sustainability goals and creates new revenue streams by turning returned goods into valuable secondary products.
Future Trends: Wholesale and Circular Supply Chain Integration
Future trends in wholesale emphasize the integration of circular supply chain models to enhance sustainability and reduce waste. Embracing closed-loop systems, wholesalers optimize inventory management and product lifecycle extension, driving resource efficiency and cost savings. Advances in digital technologies enable real-time tracking and transparency, supporting seamless collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers in circular networks.
Related Important Terms
Reverse Logistics
Wholesale reverse logistics involves managing product returns, refurbishments, and recycling to minimize losses and maximize resale value, aligning with the principles of a circular supply chain that emphasizes sustainability and resource efficiency. Incorporating circular supply chain strategies into wholesale reverse logistics reduces waste and operational costs while promoting environmental responsibility through continuous product lifecycle management.
Closed-Loop Wholesale
Closed-loop wholesale integrates circular supply chain principles by emphasizing product reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling within wholesale distribution, minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency. This model transforms traditional wholesale by creating continuous value flows, reducing environmental impact, and supporting sustainable inventory management.
Remanufactured Stock
Wholesale channels often source remanufactured stock to reduce costs and minimize waste, integrating circular supply chain principles that emphasize product life extension and resource efficiency. This approach enhances sustainability by prioritizing the reuse of components while maintaining competitive pricing and inventory turnover in wholesale markets.
Circular Wholesale Agreements
Circular wholesale agreements prioritize sustainability by enabling the return, reuse, and recycling of products within the supply chain, reducing waste and resource consumption. These agreements integrate circular economy principles into traditional wholesale operations, fostering long-term partnerships that support environmental responsibility and cost efficiency.
Take-Back Programs
Take-back programs in wholesale enhance circular supply chains by facilitating the return and reuse of products, reducing waste and promoting sustainable resource management. These initiatives enable wholesalers to close the loop by reclaiming inventory, minimizing environmental impact, and supporting product lifecycle extension.
Upcycled Inventory
Upcycled inventory in wholesale transforms surplus or unsold products into valuable stock, reducing waste and lowering procurement costs. Integrating circular supply chain principles enhances sustainability by promoting resource efficiency and extending product life cycles within wholesale operations.
Resource Recovery Networks
Wholesale systems traditionally emphasize bulk procurement and distribution efficiency, whereas Circular Supply Chains prioritize resource recovery networks to minimize waste and maximize material reuse. Resource recovery networks integrate collection, sorting, and recycling processes that enable circular supply chains to close the loop, driving sustainability across wholesale operations.
Zero-Waste Sourcing
Wholesale models often struggle with excess inventory waste, while circular supply chains prioritize zero-waste sourcing by reclaiming and repurposing materials throughout the product lifecycle. Integrating circular supply chain strategies enables wholesalers to minimize environmental impact and optimize resource efficiency through closed-loop sourcing and product recovery systems.
Lifecycle-Based Wholesaling
Lifecycle-based wholesaling enhances inventory efficiency by integrating circular supply chain principles, emphasizing product reuse, refurbishment, and recycling to extend asset value. This approach reduces waste and costs while promoting sustainable sourcing and distribution strategies in wholesale operations.
Asset Traceability Solutions
Wholesale operations benefit from asset traceability solutions by enabling real-time tracking of inventory throughout the supply chain, reducing losses and improving stock accuracy. In contrast, circular supply chains leverage these traceability systems to enhance resource reutilization, monitor product lifecycle, and support sustainable asset recovery processes.
Wholesale vs Circular Supply Chain Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com