Wholesale involves purchasing large quantities of goods directly from manufacturers or distributors to sell at a profit, enabling businesses to benefit from lower prices and bulk inventory. Peer-to-peer wholesale, in contrast, facilitates direct transactions between individual sellers and buyers without traditional intermediaries, promoting flexibility and personalized deals. This model leverages digital platforms to connect participants, often resulting in reduced costs and increased market reach.
Table of Comparison
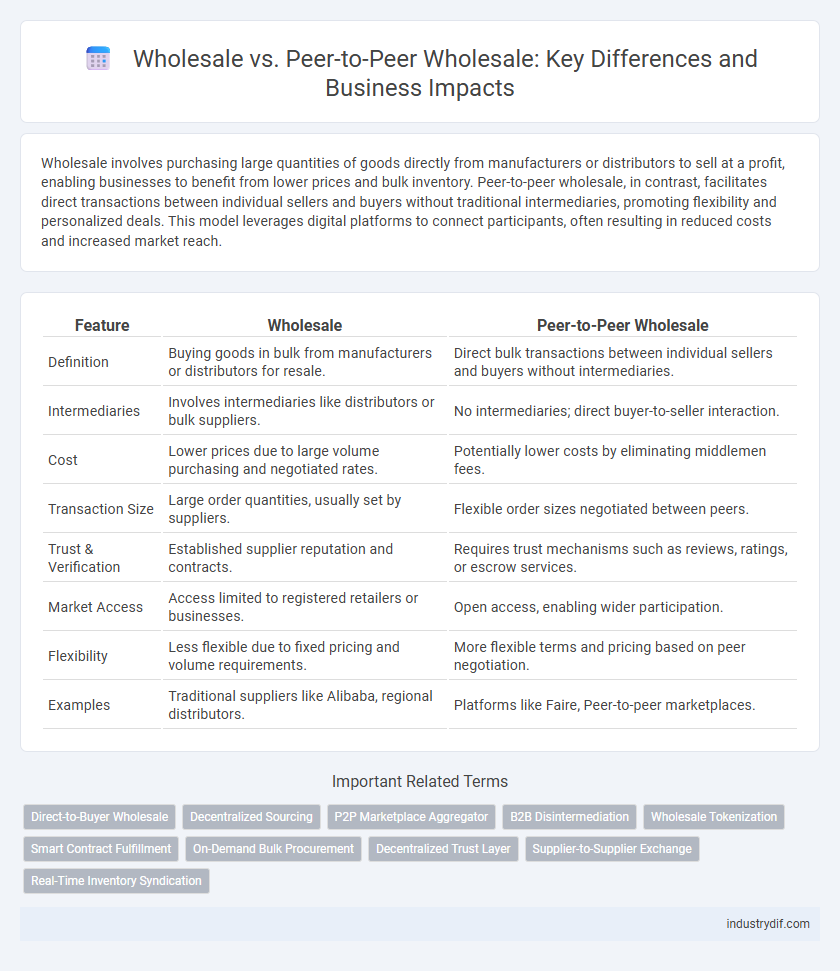
| Feature | Wholesale | Peer-to-Peer Wholesale |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying goods in bulk from manufacturers or distributors for resale. | Direct bulk transactions between individual sellers and buyers without intermediaries. |
| Intermediaries | Involves intermediaries like distributors or bulk suppliers. | No intermediaries; direct buyer-to-seller interaction. |
| Cost | Lower prices due to large volume purchasing and negotiated rates. | Potentially lower costs by eliminating middlemen fees. |
| Transaction Size | Large order quantities, usually set by suppliers. | Flexible order sizes negotiated between peers. |
| Trust & Verification | Established supplier reputation and contracts. | Requires trust mechanisms such as reviews, ratings, or escrow services. |
| Market Access | Access limited to registered retailers or businesses. | Open access, enabling wider participation. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible due to fixed pricing and volume requirements. | More flexible terms and pricing based on peer negotiation. |
| Examples | Traditional suppliers like Alibaba, regional distributors. | Platforms like Faire, Peer-to-peer marketplaces. |
Understanding Wholesale: Key Definitions
Wholesale involves purchasing large quantities of goods directly from manufacturers or distributors at discounted prices, enabling retailers to resell products at competitive rates. Peer-to-peer wholesale, by contrast, connects individual sellers and buyers directly without traditional intermediaries, often leveraging online platforms for increased flexibility. Understanding these key definitions clarifies the operational differences, pricing structures, and market dynamics inherent in each wholesale model.
What is Peer-to-Peer Wholesale?
Peer-to-peer wholesale is a decentralized business model where manufacturers or suppliers sell products directly to retailers or buyers without intermediaries, optimizing cost efficiency and supply chain transparency. Unlike traditional wholesale, which relies on distributors or wholesalers to manage inventory and logistics, peer-to-peer wholesale leverages digital platforms to connect sellers and buyers directly. This model enhances pricing competitiveness and accelerates transaction speed in bulk purchasing markets.
Traditional Wholesale vs Peer-to-Peer Wholesale: Core Differences
Traditional wholesale involves bulk purchasing from manufacturers or distributors, where intermediaries manage storage, logistics, and sales to retailers. Peer-to-peer wholesale, in contrast, connects buyers and sellers directly, leveraging digital platforms to streamline transactions, reduce costs, and enhance transparency. Core differences include the degree of intermediaries, operational efficiency, and scalability, with peer-to-peer models emphasizing decentralized networks and real-time market responsiveness.
Supply Chain Structures: Centralized vs Decentralized
Wholesale supply chain structures are predominantly centralized, where a single entity manages inventory, procurement, and distribution to ensure consistency and efficiency across large volumes. Peer-to-peer wholesale adopts a decentralized model, enabling direct transactions between suppliers and buyers, which enhances flexibility and reduces intermediary costs. Centralized systems benefit from streamlined logistics and bulk purchasing power, while decentralized networks leverage real-time information sharing and localized supply chain responsiveness.
Pricing Models in Wholesale and Peer-to-Peer Wholesale
Wholesale pricing models typically involve bulk purchase discounts, fixed price tiers, and minimum order quantities to optimize cost-efficiency for large buyers. Peer-to-peer wholesale leverages dynamic pricing, where prices fluctuate based on supply, demand, and direct negotiations between parties to ensure competitive and real-time rates. Understanding these differences enables businesses to select pricing strategies aligned with their operational scale and market responsiveness.
Inventory Management: Bulk Orders vs On-Demand Sourcing
Wholesale relies on bulk orders to maintain large inventory levels, enabling cost savings through economies of scale and consistent product availability. Peer-to-peer wholesale utilizes on-demand sourcing, minimizing inventory holding costs and increasing flexibility by matching supply directly with demand. Efficient inventory management in wholesale hinges on balancing bulk stock levels, while peer-to-peer models emphasize real-time sourcing to reduce excess inventory risk.
Technology’s Role in Modern Wholesale Channels
Technology revolutionizes modern wholesale channels by enabling seamless integration between wholesalers and retailers through automated inventory management and real-time data analytics. Peer-to-peer wholesale leverages decentralized platforms to connect businesses directly, reducing intermediaries and enhancing transaction transparency. Advanced technologies such as blockchain and AI streamline supply chain operations, optimize pricing strategies, and improve communication efficiency across both traditional and peer-to-peer wholesale networks.
Benefits of Peer-to-Peer Wholesale for Small Businesses
Peer-to-peer wholesale enables small businesses to access diverse product ranges directly from other businesses, reducing reliance on traditional distributors and lowering procurement costs. This model fosters stronger business relationships and increases flexibility in order quantities and delivery schedules, which is critical for managing cash flow and inventory effectively. Enhanced transparency and direct negotiations empower small businesses to secure better pricing and customized terms, driving competitiveness in the wholesale market.
Common Challenges in Peer-to-Peer Wholesale
Peer-to-peer wholesale often faces challenges such as inconsistent product quality, lack of standardized pricing, and difficulties in ensuring reliable logistics compared to traditional wholesale models. Trust and verification issues arise due to the absence of centralized oversight, leading to potential disputes and payment delays. Limited scalability and regulatory compliance complexities further hinder the efficiency and growth of peer-to-peer wholesale networks.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Wholesale and Peer-to-Peer Platforms
Wholesale is rapidly evolving with the integration of advanced technologies such as blockchain and AI, which enhance transparency, efficiency, and trust in supply chains. Peer-to-peer wholesale platforms are gaining traction by enabling direct transactions between manufacturers and retailers, reducing intermediaries and lowering costs. Future trends indicate a hybrid model combining traditional wholesale infrastructure with peer-to-peer technology to optimize scalability and flexibility in global trade.
Related Important Terms
Direct-to-Buyer Wholesale
Direct-to-buyer wholesale enables manufacturers to bypass intermediaries and sell products in bulk directly to retailers or businesses, enhancing pricing transparency and reducing supply chain costs. This model contrasts with peer-to-peer wholesale, which relies on platforms connecting multiple buyers and sellers, often introducing additional layers that can affect negotiation flexibility and lead times.
Decentralized Sourcing
Decentralized sourcing in peer-to-peer wholesale enables direct transactions between buyers and sellers, reducing reliance on traditional intermediaries common in conventional wholesale models. This approach enhances transparency, increases supply chain efficiency, and fosters competitive pricing by leveraging distributed networks for product distribution.
P2P Marketplace Aggregator
Wholesale involves bulk transactions between manufacturers and retailers, streamlining supply chains with centralized distribution. Peer-to-peer Wholesale Marketplace Aggregators facilitate direct connections between buyers and sellers, enhancing market transparency and reducing intermediaries for more competitive pricing and faster transactions.
B2B Disintermediation
Wholesale involves traditional B2B transactions where intermediaries facilitate bulk product distribution between manufacturers and retailers, whereas Peer-to-Peer Wholesale enables direct interactions between businesses, reducing the need for middlemen. This shift towards B2B disintermediation enhances supply chain efficiency, lowers costs, and fosters transparent pricing, revolutionizing wholesale market dynamics.
Wholesale Tokenization
Wholesale tokenization transforms traditional large-scale transactions by digitizing assets into secure, tradeable tokens, enhancing liquidity and transparency in bulk trade operations. Peer-to-peer wholesale leverages this technology to enable direct asset exchanges between parties, reducing intermediaries and transaction costs while increasing market efficiency.
Smart Contract Fulfillment
Wholesale transactions typically involve centralized suppliers and distributors managing inventory and payment processes, while Peer-to-Peer Wholesale leverages blockchain technology to enable direct interactions between buyers and sellers. Smart Contract Fulfillment automates contract execution and payment release, reducing intermediaries, enhancing transparency, and minimizing disputes in Peer-to-Peer Wholesale networks.
On-Demand Bulk Procurement
On-demand bulk procurement in wholesale enables businesses to purchase large quantities of products quickly, leveraging established supply chains for consistent inventory management. Peer-to-peer wholesale, by contrast, facilitates direct transactions between buyers and sellers, enhancing flexibility and reducing intermediaries but may lack the reliability and scale of traditional wholesale channels.
Decentralized Trust Layer
Wholesale relies on centralized trust mechanisms where transactions are verified and managed by a single authority, creating potential bottlenecks and risks of fraud. Peer-to-peer wholesale leverages a decentralized trust layer, using blockchain technology to enable transparent, secure, and direct transactions between parties without intermediaries.
Supplier-to-Supplier Exchange
Wholesale traditionally involves centralized supplier-to-buyer transactions, whereas peer-to-peer wholesale emphasizes direct supplier-to-supplier exchanges, enhancing inventory flexibility and reducing lead times. This supplier-to-supplier model optimizes supply chain efficiency by enabling bulk resource sharing and real-time demand responsiveness within wholesale networks.
Real-Time Inventory Syndication
Wholesale relies on centralized inventory systems that update stock levels periodically, which can lead to delays in order fulfillment and inaccuracies in product availability. Peer-to-peer wholesale leverages real-time inventory syndication, enabling instant synchronization of stock data across all participants, reducing stockouts and improving supply chain efficiency.
Wholesale vs Peer-to-Peer Wholesale Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com