Wholesale offers bulk purchasing at significantly lower prices, ideal for businesses seeking large quantities of products with predictable inventory needs. Community group buying leverages collective purchasing power from local groups to unlock discounts typically unavailable to individual buyers, emphasizing social engagement and convenience. Both models reduce costs but differ in scale, buying structure, and customer interaction dynamics.
Table of Comparison
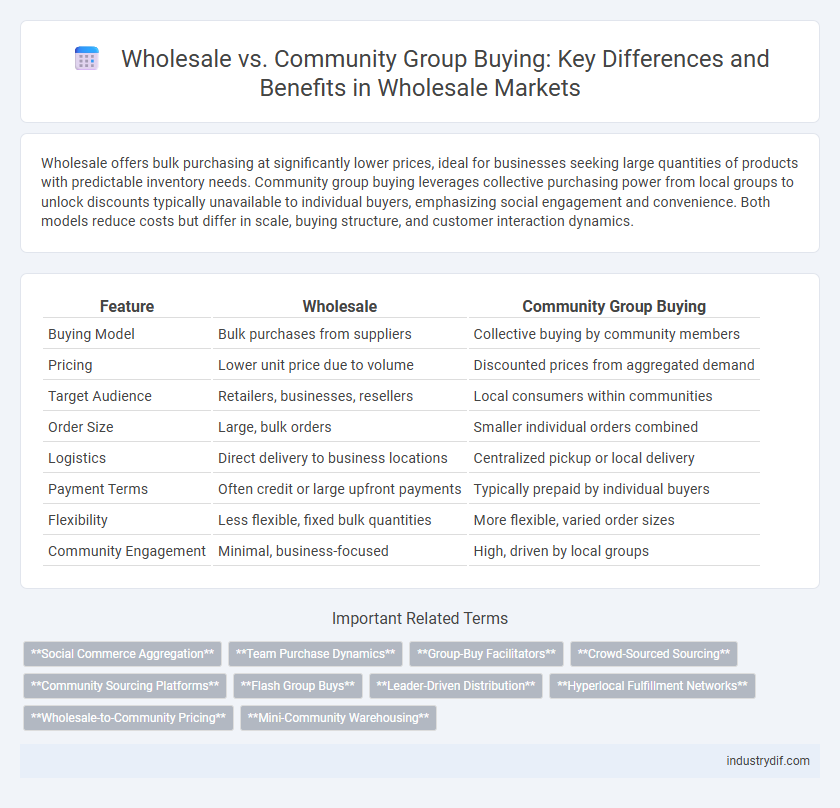
| Feature | Wholesale | Community Group Buying |
|---|---|---|
| Buying Model | Bulk purchases from suppliers | Collective buying by community members |
| Pricing | Lower unit price due to volume | Discounted prices from aggregated demand |
| Target Audience | Retailers, businesses, resellers | Local consumers within communities |
| Order Size | Large, bulk orders | Smaller individual orders combined |
| Logistics | Direct delivery to business locations | Centralized pickup or local delivery |
| Payment Terms | Often credit or large upfront payments | Typically prepaid by individual buyers |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, fixed bulk quantities | More flexible, varied order sizes |
| Community Engagement | Minimal, business-focused | High, driven by local groups |
Introduction to Wholesale and Community Group Buying
Wholesale involves purchasing large quantities of goods directly from manufacturers or distributors at discounted prices, enabling retailers or businesses to maximize profit margins through bulk sales. Community group buying organizes local consumers to collectively buy products in bulk, leveraging group volume to negotiate lower prices and reduce individual costs. Both models emphasize cost efficiency and bulk purchasing, but wholesale targets businesses, while community group buying focuses on end consumers collaborating within communities.
Key Differences Between Wholesale and Community Group Buying
Wholesale involves bulk purchasing directly from manufacturers or distributors, offering lower prices per unit through large-volume orders. Community group buying leverages collective buying power within local communities to negotiate discounts but typically requires smaller order volumes. Key differences include order scale, pricing structure, and distribution channels, with wholesale focusing on supply chain efficiency and community group buying emphasizing social collaboration.
How Wholesale Business Models Operate
Wholesale business models operate by purchasing large quantities of products directly from manufacturers or distributors at discounted rates, enabling retailers or businesses to buy in bulk at lower prices. This model emphasizes inventory management, supply chain efficiency, and volume sales to maximize profit margins. Unlike community group buying, wholesale transactions typically involve established businesses rather than individual consumers pooling demand.
The Community Group Buying Model Explained
The community group buying model leverages localized social networks to aggregate demand, enabling bulk purchasing at significantly lower prices compared to traditional wholesale channels. Consumers within a community coordinate orders through an organizer, who negotiates directly with suppliers to secure discounts and streamline distribution. This model enhances cost efficiency and fosters trust, differentiating it from conventional wholesale that operates on larger scale, often impersonal transactions.
Advantages of Wholesale for Retailers
Wholesale offers retailers significant advantages such as bulk purchasing discounts that enhance profit margins and reduce per-unit costs. Access to a wider variety of products through established suppliers ensures consistent inventory availability and faster replenishment cycles. Dedicated customer support from wholesalers helps retailers manage order logistics efficiently, minimizing delays and stockouts compared to community group buying models.
Benefits of Community Group Buying for Consumers
Community Group Buying offers consumers lower prices due to bulk purchasing power and reduced middleman costs. It enhances product accessibility by pooling demand within local communities, ensuring timely deliveries and fresher goods. This model fosters social trust and collaboration, providing personalized shopping experiences and increased customer satisfaction.
Pricing Structures: Wholesale vs Community Group Buying
Wholesale pricing structures typically involve bulk purchase discounts based on volume, allowing buyers to access lower per-unit costs through large orders. Community group buying leverages collective purchasing power where multiple buyers join to place a group order, resulting in negotiated lower prices often shared among members. While wholesale emphasizes scale and inventory commitments, community group buying focuses on social collaboration to achieve competitive pricing.
Supply Chain and Logistics Comparison
Wholesale relies on bulk purchasing and centralized distribution centers to streamline supply chains, ensuring rapid replenishment and lower per-unit transport costs. Community group buying leverages local networks and decentralized delivery points, reducing last-mile logistics complexity but often increasing coordination efforts and variability in supply consistency. Both models optimize supply efficiency differently, with wholesale emphasizing scale economies, while community group buying prioritizes localized demand fulfillment.
Buyer Requirements and Purchasing Power
Wholesale buyers typically require bulk quantities at lower prices to maximize margins, emphasizing consistent supply and long-term contracts. Community group buying leverages collective purchasing power by aggregating demand from multiple buyers, enabling access to discounted rates without the need for large individual orders. This model caters to smaller buyers seeking cost-efficiency while maintaining flexibility in purchase volume and frequency.
Future Trends in Wholesale and Community Group Buying
Future trends in wholesale include increased integration of digital platforms and AI-driven demand forecasting to optimize inventory management and reduce costs. Community group buying is projected to expand through mobile apps that leverage localized networks and social connections, enhancing personalized promotions and faster last-mile delivery. Both sectors are expected to adopt sustainable practices and blockchain technology for greater transparency and trust in supply chain operations.
Related Important Terms
Social Commerce Aggregation
Social commerce aggregation leverages community group buying by combining purchasing power within local networks, offering wholesalers enhanced market reach and personalized consumer engagement. This model contrasts traditional wholesale by prioritizing social interaction and collective buying decisions, driving efficiency and scalability through digital platforms.
Team Purchase Dynamics
Wholesale often relies on large volume orders from individual buyers, streamlining procurement through bulk pricing and supplier negotiations, whereas community group buying emphasizes collective ordering driven by local networks to leverage social trust and minimize costs. The team purchase dynamics in community group buying foster cooperative decision-making and shared benefits, contrasting with the transactional and efficiency-focused nature of traditional wholesale.
Group-Buy Facilitators
Group-buy facilitators streamline bulk purchasing by connecting wholesalers with community buyers, optimizing supply chains and reducing costs through aggregated demand. Their role enhances price negotiation leverage and inventory turnover for wholesalers, while offering community groups access to competitive pricing and diverse product selections.
Crowd-Sourced Sourcing
Wholesale leverages large-scale crowd-sourced sourcing to aggregate demand from multiple buyers, enabling bulk purchasing at lower costs and increased supplier negotiation power. Community group buying also utilizes crowd-sourced sourcing but focuses on localized groups to optimize delivery efficiency and foster direct consumer engagement within specific communities.
Community Sourcing Platforms
Community sourcing platforms in wholesale leverage localized consumer groups to aggregate demand, resulting in bulk purchasing power that drives down costs and enhances supply chain efficiency. These platforms outperform traditional wholesale models by fostering direct engagement between suppliers and community buyers, increasing transparency and enabling more responsive inventory management.
Flash Group Buys
Flash Group Buys in wholesale enable rapid, high-volume transactions by leveraging time-limited, exclusive offers that drive immediate demand and maximize supplier efficiency. This model outperforms traditional community group buying by creating urgency and streamlined bulk purchasing, optimizing supply chain responsiveness and inventory turnover.
Leader-Driven Distribution
Leader-driven distribution in wholesale emphasizes direct relationships between suppliers and key buyers, enabling streamlined bulk purchasing and efficient inventory management. Community group buying relies on influential local leaders to aggregate consumer demand, leveraging social networks to negotiate better prices and coordinate deliveries at scale.
Hyperlocal Fulfillment Networks
Hyperlocal fulfillment networks in wholesale optimize inventory distribution by leveraging proximity to customers, reducing delivery times and costs compared to traditional models. Community group buying intensifies this approach by pooling demand within neighborhoods, enabling bulk purchasing while maintaining fast, localized fulfillment.
Wholesale-to-Community Pricing
Wholesale-to-community pricing leverages bulk purchasing power to offer competitive rates that are significantly lower than traditional retail prices, enabling community groups to access goods at discounted rates without sacrificing quality. This pricing strategy bridges the gap between large-scale wholesale volumes and smaller community group demands, ensuring fair value and sustainable margins for both suppliers and buyers.
Mini-Community Warehousing
Mini-community warehousing integrates the efficiency of wholesale by consolidating bulk inventory within localized hubs, enabling faster distribution and reduced shipping costs. This approach enhances community group buying by offering immediate access to products in smaller quantities while maintaining wholesale pricing advantages.
Wholesale vs Community Group Buying Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com