Wholesale involves selling large quantities of products directly to retailers or businesses, often benefiting from bulk pricing and simplified supply chains. Embedded commerce integrates purchasing options directly within digital platforms, streamlining the customer journey by allowing transactions without redirecting to external websites. While wholesale emphasizes volume and distribution networks, embedded commerce prioritizes seamless customer experiences and instant purchasing capabilities.
Table of Comparison
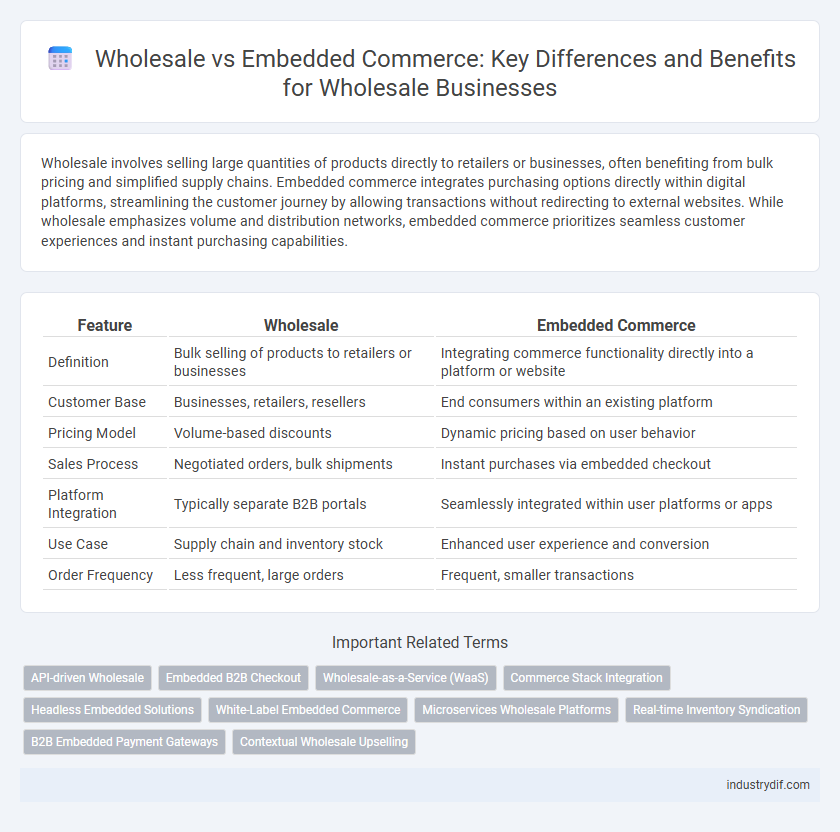
| Feature | Wholesale | Embedded Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bulk selling of products to retailers or businesses | Integrating commerce functionality directly into a platform or website |
| Customer Base | Businesses, retailers, resellers | End consumers within an existing platform |
| Pricing Model | Volume-based discounts | Dynamic pricing based on user behavior |
| Sales Process | Negotiated orders, bulk shipments | Instant purchases via embedded checkout |
| Platform Integration | Typically separate B2B portals | Seamlessly integrated within user platforms or apps |
| Use Case | Supply chain and inventory stock | Enhanced user experience and conversion |
| Order Frequency | Less frequent, large orders | Frequent, smaller transactions |
Understanding Wholesale: Definition and Key Features
Wholesale involves selling goods in large quantities directly to retailers, businesses, or professional users rather than individual consumers, offering bulk pricing and volume discounts. Key features include supply chain efficiency, inventory management, and scalable order processing systems designed to support large-scale transactions. Understanding wholesale requires recognizing its role as an essential intermediary that enables retailers to access products at competitive rates for resale.
What is Embedded Commerce? An Overview
Embedded commerce integrates purchasing capabilities directly into digital platforms, such as websites, apps, or social media, enabling seamless transactions without redirecting customers to separate e-commerce sites. In wholesale, embedded commerce streamlines the buying process for B2B clients by providing real-time inventory access, personalized pricing, and instant order placements within existing business tools. This approach enhances efficiency, reduces friction, and supports automated workflows critical to wholesale distribution and supply chain management.
Differences Between Wholesale and Embedded Commerce
Wholesale involves bulk purchasing and selling primarily to retailers or other businesses, emphasizing volume discounts and long-term contracts. Embedded commerce integrates purchasing functionalities directly within digital platforms or content, allowing end-users to buy products seamlessly without leaving the interface. Key differences lie in their target audience, sales process, and technological integration, with wholesale focusing on B2B transactions and embedded commerce enhancing B2C user experience.
Business Models: Wholesale vs Embedded Commerce
Wholesale business models involve purchasing large quantities of products at discounted rates to resell through various distribution channels, emphasizing volume sales and inventory management. Embedded commerce integrates buying options directly within digital platforms, streamlining the customer experience by enabling transactions without redirecting users to external sites. Both models differ in operational structure, with wholesale focusing on bulk supply chain efficiencies and embedded commerce prioritizing seamless, on-platform purchasing processes.
Technology Integration in Wholesale and Embedded Commerce
Technology integration in wholesale leverages advanced ERP systems, API connectivity, and AI-driven analytics to streamline supply chain management and improve order accuracy. Embedded commerce integrates purchasing capabilities directly within digital platforms using seamless APIs and SDKs, enabling real-time transactions without redirecting users. Both approaches prioritize automation and data synchronization but differ in deployment, with wholesale focusing on backend efficiencies and embedded commerce emphasizing front-end customer experience.
Supply Chain Management: Comparing Approaches
Wholesale supply chain management emphasizes bulk inventory handling, centralized warehousing, and distributor networks to optimize large-scale product flow. Embedded commerce integrates real-time order processing directly within digital platforms, enabling seamless supplier-to-customer interactions and streamlined inventory updates. Comparing approaches reveals wholesale prioritizes operational efficiency through aggregation, while embedded commerce focuses on agility and enhanced connectivity across the supply chain.
Payment and Transaction Processes
Wholesale payment and transaction processes typically involve bulk order management, purchase orders, and negotiated payment terms such as net 30 or net 60, ensuring tailored financial workflows for B2B clients. Embedded commerce integrates seamless payment gateways directly within digital platforms, enabling instant transactions, automated invoicing, and real-time payment tracking for enhanced operational efficiency. Wholesale systems prioritize flexible credit arrangements and batch processing, while embedded commerce focuses on frictionless checkout experiences and secure, API-driven payment solutions.
Customer Experience: B2B vs B2B2C
Wholesale commerce typically centers on B2B transactions where businesses prioritize bulk ordering, pricing transparency, and efficient reordering processes to enhance customer experience. Embedded commerce integrates directly into B2B2C platforms, offering seamless purchasing options that cater to both the business and the end consumer, improving personalization and convenience. This integration enables wholesalers to maintain strong B2B relationships while providing retailers and end customers with streamlined access to products and services.
Scalability and Growth Potential
Wholesale offers extensive scalability through bulk order processing and established supply chain networks, enabling businesses to quickly expand inventory and reach larger markets. Embedded commerce integrates seamless purchasing within digital platforms, providing personalized shopping experiences and real-time analytics that drive targeted growth. Combining wholesale's large-scale distribution with embedded commerce's customer-centric technology maximizes growth potential by optimizing both operational efficiency and engagement.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Wholesale relies on bulk purchasing and traditional distribution channels to maximize profit margins and streamline inventory management. Embedded commerce integrates purchasing directly into digital platforms, enhancing customer experience and enabling real-time transactions. Selecting the right model depends on factors like target audience, sales volume, and desired level of integration with existing systems.
Related Important Terms
API-driven Wholesale
API-driven wholesale enables seamless integration of product catalogs, pricing, and inventory management directly into buyer systems, streamlining order processing and reducing manual errors. Compared to embedded commerce, API-driven wholesale offers greater flexibility and scalability for B2B transactions by facilitating real-time data exchange and automated workflows.
Embedded B2B Checkout
Embedded B2B checkout streamlines wholesale transactions by integrating purchasing directly within digital platforms, reducing friction and accelerating order fulfillment. This approach enhances customer experience and operational efficiency compared to traditional wholesale models that rely on separate ordering systems.
Wholesale-as-a-Service (WaaS)
Wholesale-as-a-Service (WaaS) revolutionizes traditional wholesale by offering scalable APIs that integrate seamlessly with embedded commerce platforms, enabling businesses to streamline supply chains and enhance B2B transactions. This model leverages cloud infrastructure and real-time data analytics to optimize inventory management, pricing strategies, and order fulfillment, driving operational efficiency and accelerating market responsiveness.
Commerce Stack Integration
Wholesale commerce relies on robust commerce stack integration to streamline supply chain management, inventory synchronization, and bulk order processing, enabling seamless B2B transactions at scale. Embedded commerce integrates directly within platforms for enhanced user experience but often requires tailored APIs and middleware to connect with existing wholesale systems and maintain efficient operational workflows.
Headless Embedded Solutions
Headless embedded solutions in wholesale enable seamless integration of commerce functionalities directly into enterprise systems, enhancing flexibility and customization compared to traditional wholesale platforms. These solutions allow wholesale businesses to deliver personalized purchasing experiences across multiple channels without compromising back-end operations or scalability.
White-Label Embedded Commerce
White-label embedded commerce enables wholesalers to seamlessly integrate customizable e-commerce solutions into their platforms, enhancing brand consistency and customer experience without the complexity of building from scratch. This approach contrasts with traditional wholesale models by offering scalable, turnkey digital storefronts that accelerate market entry and enable real-time inventory and pricing synchronization.
Microservices Wholesale Platforms
Microservices wholesale platforms offer scalable, modular solutions that enhance flexibility and integration capabilities compared to traditional embedded commerce systems. These platforms enable wholesalers to efficiently manage complex product catalogs, streamline order processing, and customize workflows to meet diverse B2B requirements.
Real-time Inventory Syndication
Real-time inventory syndication in wholesale allows seamless synchronization of stock levels across multiple sales channels, reducing overselling risks and improving order fulfillment accuracy. Embedded commerce integrates purchasing capabilities directly within content platforms, but lacks the robust inventory updates essential for efficient wholesale operations.
B2B Embedded Payment Gateways
Wholesale businesses benefit from B2B embedded payment gateways by streamlining transactions within existing platforms, reducing friction and enhancing purchase efficiency. These embedded solutions integrate payment processing directly into wholesale digital channels, improving cash flow management and enabling seamless B2B commerce experiences.
Contextual Wholesale Upselling
Contextual wholesale upselling leverages real-time data and buyer behavior to present relevant product recommendations within the wholesale purchasing process, significantly enhancing order value and customer satisfaction. Embedded commerce integrates wholesale transactions directly into existing digital platforms, reducing friction and streamlining purchasing but requires advanced customization to fully capitalize on upselling opportunities.
Wholesale vs Embedded Commerce Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com