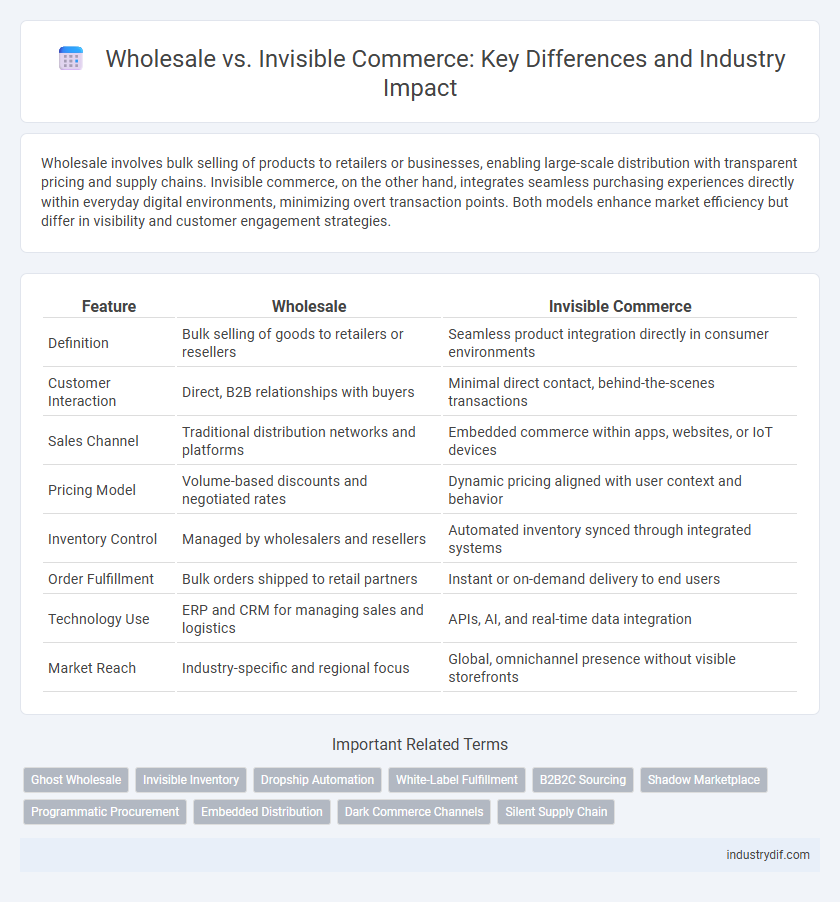
Wholesale involves bulk selling of products to retailers or businesses, enabling large-scale distribution with transparent pricing and supply chains. Invisible commerce, on the other hand, integrates seamless purchasing experiences directly within everyday digital environments, minimizing overt transaction points. Both models enhance market efficiency but differ in visibility and customer engagement strategies.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wholesale | Invisible Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bulk selling of goods to retailers or resellers | Seamless product integration directly in consumer environments |
| Customer Interaction | Direct, B2B relationships with buyers | Minimal direct contact, behind-the-scenes transactions |
| Sales Channel | Traditional distribution networks and platforms | Embedded commerce within apps, websites, or IoT devices |
| Pricing Model | Volume-based discounts and negotiated rates | Dynamic pricing aligned with user context and behavior |
| Inventory Control | Managed by wholesalers and resellers | Automated inventory synced through integrated systems |
| Order Fulfillment | Bulk orders shipped to retail partners | Instant or on-demand delivery to end users |
| Technology Use | ERP and CRM for managing sales and logistics | APIs, AI, and real-time data integration |
| Market Reach | Industry-specific and regional focus | Global, omnichannel presence without visible storefronts |
Understanding Wholesale: Definition and Key Features
Wholesale involves the sale of goods in large quantities, typically to retailers or businesses rather than direct consumers, enabling bulk purchasing and cost efficiency. Key features include bulk pricing, supply chain integration, and volume discounts, which drive profitability for both suppliers and resellers. Unlike Invisible Commerce, wholesale emphasizes transparent transactions and established business relationships instead of hidden or automated processes.
What is Invisible Commerce? An Emerging Trend
Invisible commerce represents a rising trend where transactions occur seamlessly within digital environments, bypassing traditional storefronts and minimizing customer effort. Unlike conventional wholesale, which relies on bulk purchasing and direct distribution channels, invisible commerce integrates automated purchases through AI-powered platforms and IoT devices. This paradigm shift enhances supply chain efficiency by embedding buying processes into everyday digital interactions, reducing friction, and accelerating order fulfillment.
Comparing Supply Chains: Wholesale vs Invisible Commerce
Wholesale supply chains involve bulk purchasing from manufacturers to distribute products through established retail channels, optimizing inventory management and cost efficiency. Invisible commerce streamlines the supply chain by integrating directly with consumer platforms, minimizing intermediaries and enabling seamless real-time order fulfillment. This direct-to-consumer approach reduces lead times and enhances data-driven inventory adjustments compared to traditional wholesale distribution models.
Pricing Models: Wholesale Bulk vs Invisible Commerce Flexibility
Wholesale pricing models emphasize bulk discounts and fixed pricing structures designed for large volume purchases, optimizing cost efficiency for retailers and resellers. Invisible commerce offers flexible pricing strategies tailored to consumer behavior and dynamic market conditions, enabling personalized offers and real-time adjustments. This adaptability in invisible commerce allows businesses to maximize profit margins while maintaining competitive pricing in diverse sales environments.
Customer Relationships in Wholesale and Invisible Commerce
Wholesale prioritizes building long-term customer relationships through personalized interactions and bulk purchasing agreements, fostering trust and loyalty between suppliers and buyers. Invisible Commerce emphasizes seamless, automated transactions with minimal direct contact, relying on integrated technology to streamline purchasing and reduce friction. While wholesale thrives on strong relationship management, Invisible Commerce optimizes efficiency and scalability by minimizing human involvement in the buying process.
Technology’s Role in Wholesale and Invisible Commerce
Technology revolutionizes wholesale by enabling real-time inventory management, automated order processing, and seamless integration with supply chain systems, enhancing operational efficiency. Invisible commerce leverages AI, IoT, and advanced data analytics to create frictionless purchasing experiences, automating transactions without direct customer interaction. The fusion of ERP systems with machine learning algorithms in wholesale transforms traditional distribution channels, while invisible commerce benefits from cloud computing and API-driven platforms for scalable, adaptive trade environments.
Inventory Management: Traditional vs Invisible Commerce Approach
Wholesale inventory management relies on bulk purchasing, centralized warehousing, and visible stock levels to optimize supply chain efficiency and reduce costs. Invisible commerce leverages real-time data integration, decentralized inventory pools, and demand-driven fulfillment to minimize overstock and improve agility. This shift enables businesses to maintain optimal stock without physical inventory constraints, enhancing scalability and responsiveness in dynamic markets.
Market Reach: Expanding Through Wholesale vs Invisible Commerce
Wholesale expands market reach by enabling large-scale product distribution through established retail networks, increasing visibility and accessibility to diverse customer bases. Invisible commerce leverages seamless, behind-the-scenes transactions that integrate directly with consumer platforms, offering a more discreet but scalable method to access niche markets. Both approaches strategically enhance market penetration, with wholesale focusing on broad retail exposure and invisible commerce optimizing integration with digital ecosystems.
Benefits and Challenges: Wholesale vs Invisible Commerce
Wholesale offers established distribution networks and bulk pricing advantages, enabling businesses to scale inventory efficiently and reach wider markets. Invisible Commerce enhances customer experience through seamless, behind-the-scenes transactions, reducing friction and increasing conversion rates without overt sales interactions. Challenges in wholesale include high upfront costs and inventory management, while invisible commerce demands advanced technology integration and data privacy considerations.
Choosing the Right Model: Factors to Consider for Businesses
Choosing the right model between wholesale and invisible commerce depends on factors like target market reach, inventory management, and customer engagement strategies. Wholesale offers bulk sales and predictable revenue, ideal for businesses prioritizing large volume distribution and brand control. Invisible commerce suits companies seeking seamless, integrated purchasing experiences through digital platforms, emphasizing convenience and data-driven personalization.
Related Important Terms
Ghost Wholesale
Ghost Wholesale revolutionizes traditional wholesale by enabling suppliers to sell products directly through third-party e-commerce platforms without managing physical storefronts or inventory displays. This seamless integration reduces overhead costs and expands market reach while maintaining complete control over branding and product pricing.
Invisible Inventory
Invisible inventory in invisible commerce allows wholesalers to optimize stock visibility and reduce holding costs by leveraging real-time data integration and on-demand fulfillment models. This approach contrasts with traditional wholesale, where physical inventory is maintained and managed, often leading to increased storage expenses and slower response times to market demand fluctuations.
Dropship Automation
Wholesale offers bulk inventory control and volume discounts, while invisible commerce prioritizes seamless, automated dropship operations with minimal stock handling. Dropship automation streamlines order fulfillment by integrating supplier systems directly with e-commerce platforms, reducing overhead and enabling real-time inventory updates.
White-Label Fulfillment
Wholesale involves bulk purchasing and distribution of products under established brand names, while Invisible Commerce emphasizes seamless, behind-the-scenes white-label fulfillment that allows retailers to offer products without brand exposure. White-label fulfillment in Invisible Commerce streamlines order processing, inventory management, and shipping, enabling businesses to expand product offerings without handling manufacturing or branding complexities.
B2B2C Sourcing
Wholesale involves bulk purchasing and distributing goods primarily from manufacturers to retailers, enabling businesses to manage inventory and pricing efficiently. Invisible Commerce in B2B2C sourcing streamlines supply chain operations through automated integration and data-driven insights, enhancing transparency and reducing friction between suppliers, distributors, and end consumers.
Shadow Marketplace
Shadow marketplaces represent a hidden layer of commerce operating parallel to traditional wholesale channels, leveraging invisible commerce strategies to bypass standard regulations and detection. These platforms facilitate discreet transactions that often evade formal supply chain visibility, impacting pricing transparency and market control within wholesale industries.
Programmatic Procurement
Programmatic procurement enhances wholesale operations by automating purchase decisions through real-time data integration, optimizing inventory management and pricing strategies. Unlike invisible commerce, which prioritizes seamless consumer experiences, programmatic procurement focuses on efficiency and scalability within wholesale supply chains.
Embedded Distribution
Wholesale leverages embedded distribution by seamlessly integrating products into third-party platforms, enabling efficient bulk sales without direct consumer interaction. Invisible commerce transforms traditional wholesale channels by embedding purchasing options within everyday digital experiences, optimizing supply chain transparency and reducing transactional friction.
Dark Commerce Channels
Dark Commerce Channels operate within Wholesale by facilitating transactions through untraceable or less transparent platforms, significantly impacting supply chain visibility and compliance monitoring. Unlike traditional Wholesale, these channels exploit digital anonymity to bypass standard distribution controls, creating challenges in inventory tracking and regulatory adherence.
Silent Supply Chain
Wholesale relies on transparent supply chain operations with visible inventory flows and direct supplier relationships, whereas invisible commerce leverages a silent supply chain characterized by discreet, automated transactions and seamless integration between suppliers and retailers. The silent supply chain enhances efficiency by minimizing manual intervention, reducing lead times, and enabling real-time data sharing across wholesale networks, resulting in optimized inventory management and faster order fulfillment.
Wholesale vs Invisible Commerce Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com