Wholesale involves purchasing large quantities of products directly from manufacturers or distributors at reduced prices for resale, while ghost retail operates by selling products without holding inventory, relying on third-party suppliers to fulfill orders. Wholesale offers greater control over stock and pricing strategies, whereas ghost retail minimizes upfront costs and inventory risks. Choosing between the two depends on capital investment, risk tolerance, and operational preferences in the retail business model.
Table of Comparison
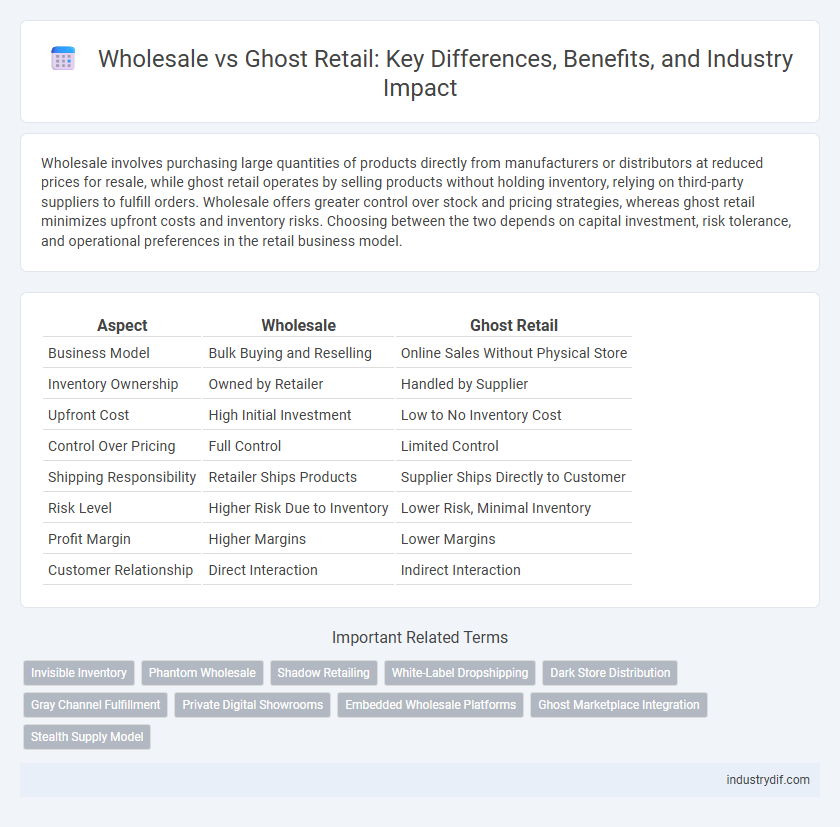
| Aspect | Wholesale | Ghost Retail |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Bulk Buying and Reselling | Online Sales Without Physical Store |
| Inventory Ownership | Owned by Retailer | Handled by Supplier |
| Upfront Cost | High Initial Investment | Low to No Inventory Cost |
| Control Over Pricing | Full Control | Limited Control |
| Shipping Responsibility | Retailer Ships Products | Supplier Ships Directly to Customer |
| Risk Level | Higher Risk Due to Inventory | Lower Risk, Minimal Inventory |
| Profit Margin | Higher Margins | Lower Margins |
| Customer Relationship | Direct Interaction | Indirect Interaction |
Understanding Wholesale: Definition and Core Concepts
Wholesale involves selling goods in large quantities directly to retailers or other businesses at a lower price per unit, facilitating supply chain efficiency and cost savings. It centers on bulk transactions that enable retailers to stock inventory without manufacturing products themselves. Understanding wholesale requires grasping core concepts such as economies of scale, distribution channels, and pricing strategies that differ from ghost retail models, which operate without physical storefronts.
What is Ghost Retail? Emerging Trends Explained
Ghost retail refers to a business model where products are sold online without holding physical inventory, relying on third-party suppliers for fulfillment. This trend leverages dropshipping and virtual storefronts, minimizing overhead costs and enabling rapid scalability. Emerging in response to rising e-commerce demands, ghost retail contrasts with traditional wholesale by eliminating upfront inventory investments and warehouse management.
Key Differences Between Wholesale and Ghost Retail
Wholesale involves purchasing products in bulk directly from manufacturers or distributors at lower prices for resale, allowing retailers to maintain inventory and manage physical stock. Ghost retail, also known as drop shipping, eliminates the need for inventory by forwarding customer orders directly to suppliers who ship products on behalf of the retailer, reducing upfront costs and storage requirements. Key differences include inventory ownership, upfront investment, and control over product handling, with wholesale providing more control and ghost retail offering a low-risk entry into retail markets.
Business Models: Wholesale vs Ghost Retail
Wholesale business models involve purchasing products in bulk directly from manufacturers or distributors at reduced prices, enabling retailers to stock physical inventory and manage in-store sales. Ghost retail operates without maintaining physical stock, relying on third-party suppliers to fulfill orders directly to customers, minimizing inventory risk and upfront costs. This model leverages digital platforms for storefronts, emphasizing dropshipping and agile supply chain management.
Supply Chain Dynamics in Wholesale and Ghost Retail
Wholesale involves direct bulk purchasing and distribution from manufacturers to retailers or businesses, streamlining supply chain dynamics with established inventory control and predictable demand forecasting. Ghost retail operates without physical storefronts, relying on third-party suppliers and drop shipping models, which introduce complexities in supply chain coordination and increased lead times. Supply chain efficiency in wholesale hinges on strong contractual relationships and inventory management, while ghost retail depends heavily on real-time data integration and flexible logistics to meet consumer demand.
Pricing Strategies: Wholesale vs Ghost Retail
Wholesale pricing strategies emphasize bulk discounts and lower per-unit costs to attract large-volume buyers, maximizing sales through reduced margins. Ghost retail pricing leverages dynamic, market-responsive adjustments and minimal overhead to offer competitive prices directly to consumers without physical storefront expenses. Both models optimize pricing to balance profitability with market reach, but wholesale depends on volume-driven economies while ghost retail benefits from agile, demand-based pricing.
Pros and Cons: Wholesale Compared to Ghost Retail
Wholesale offers bulk purchasing advantages with lower per-unit costs and established supplier relationships, enabling higher profit margins and inventory control; however, it requires significant upfront investment and storage capacity. Ghost retail minimizes inventory risk and startup costs by selling products without holding stock, leveraging dropshipping methods, but it often results in lower profit margins and less control over shipping and product quality. Choosing between wholesale and ghost retail depends on balancing capital availability, risk tolerance, and desired control over the supply chain.
Technology’s Impact on Wholesale and Ghost Retail
Technology revolutionizes wholesale and ghost retail by enhancing supply chain efficiency through real-time data analytics and automated inventory management systems. Advanced AI-driven forecasting tools optimize demand prediction, reducing overstock and stockouts in both models. Blockchain integration increases transparency and security in transactions, fostering trust between suppliers and ghost retailers.
Market Opportunities in Wholesale and Ghost Retail
Wholesale offers extensive market opportunities by enabling bulk purchasing at reduced costs, facilitating larger profit margins for retailers and manufacturers. Ghost retail capitalizes on e-commerce trends through virtual storefronts that minimize overhead expenses and target niche markets with personalized product offerings. Both models drive efficient inventory turnover but differ in scalability and customer engagement strategies, presenting diverse growth potentials within supply chain ecosystems.
Future Outlook: Wholesale vs Ghost Retail
Wholesale is expected to maintain steady growth as brands prioritize bulk purchasing to optimize supply chains and reduce costs. Ghost retail, characterized by virtual storefronts without physical inventory, is rapidly expanding due to e-commerce advancements and consumer demand for convenience. Future market trends indicate a hybrid model blending wholesale efficiency with ghost retail's digital agility will dominate, reshaping traditional distribution channels.
Related Important Terms
Invisible Inventory
Wholesale involves selling products in bulk to retailers or businesses, allowing physical inventory to be stocked and managed directly. Ghost retail operates on invisible inventory models, where sellers list products they do not physically hold, relying on suppliers to ship items directly to customers.
Phantom Wholesale
Phantom Wholesale operates as a hybrid model blending traditional wholesale efficiency with the anonymity of ghost retail, enabling brands to distribute products in bulk without direct customer interaction. This approach reduces overhead costs and streamlines inventory management while maintaining brand presence across multiple sales channels.
Shadow Retailing
Shadow retailing, a subset of ghost retail, involves wholesalers supplying products to unauthorized sellers who operate outside official distribution channels, undermining brand control and pricing strategies. This underground market disrupts traditional wholesale relationships by circumventing established retail systems and creating challenges in inventory tracking and product authenticity verification.
White-Label Dropshipping
White-label dropshipping in wholesale enables businesses to sell products under their own brand without holding inventory, contrasting with ghost retail where sellers list items without brand differentiation or direct supplier control. This method enhances brand identity and customer trust while streamlining supply chain management and reducing upfront investment risks.
Dark Store Distribution
Wholesale leverages bulk inventory management and direct supplier relationships to optimize cost efficiency, while ghost retail employs dark store distribution to fulfill online orders rapidly without traditional storefronts. Dark store distribution enhances last-mile delivery speed and inventory turnover by operating localized warehouses exclusively for e-commerce fulfillment in wholesale and ghost retail models.
Gray Channel Fulfillment
Wholesale leverages bulk purchasing and direct supplier relationships to ensure consistent inventory flow, while ghost retail operates through unauthorized channels that exploit gray market fulfillment, risking brand reputation and product authenticity. Gray channel fulfillment bypasses official distribution routes, often resulting in lost revenue for wholesalers and increased consumer confusion due to unregulated product sourcing.
Private Digital Showrooms
Wholesale leverages bulk purchasing and distribution through established retail channels, while ghost retail utilizes private digital showrooms to create exclusive, brand-controlled shopping experiences without physical storefronts. Private digital showrooms enable wholesalers to showcase curated product selections directly to target buyers, enhancing personalization and reducing inventory costs.
Embedded Wholesale Platforms
Embedded wholesale platforms streamline supply chain management by integrating directly with retailers' systems, enabling real-time inventory updates and automated order processing. This contrasts with ghost retail models that rely on third-party marketplaces, often lacking seamless data synchronization and limiting scalability for wholesale suppliers.
Ghost Marketplace Integration
Ghost retail integrates seamlessly with wholesale operations by enabling businesses to list products on multiple online marketplaces without holding physical inventory, optimizing supply chain efficiency. This model leverages real-time data synchronization and automated order fulfillment systems to reduce overhead and expand market reach compared to traditional wholesale methods.
Stealth Supply Model
Wholesale involves bulk purchasing from manufacturers to resell through established channels, leveraging transparent supply chains and consistent inventory management. The Stealth Supply Model in ghost retail bypasses traditional visibility by sourcing products covertly, allowing sellers to test markets without revealing suppliers or inventory origins.
Wholesale vs Ghost Retail Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com