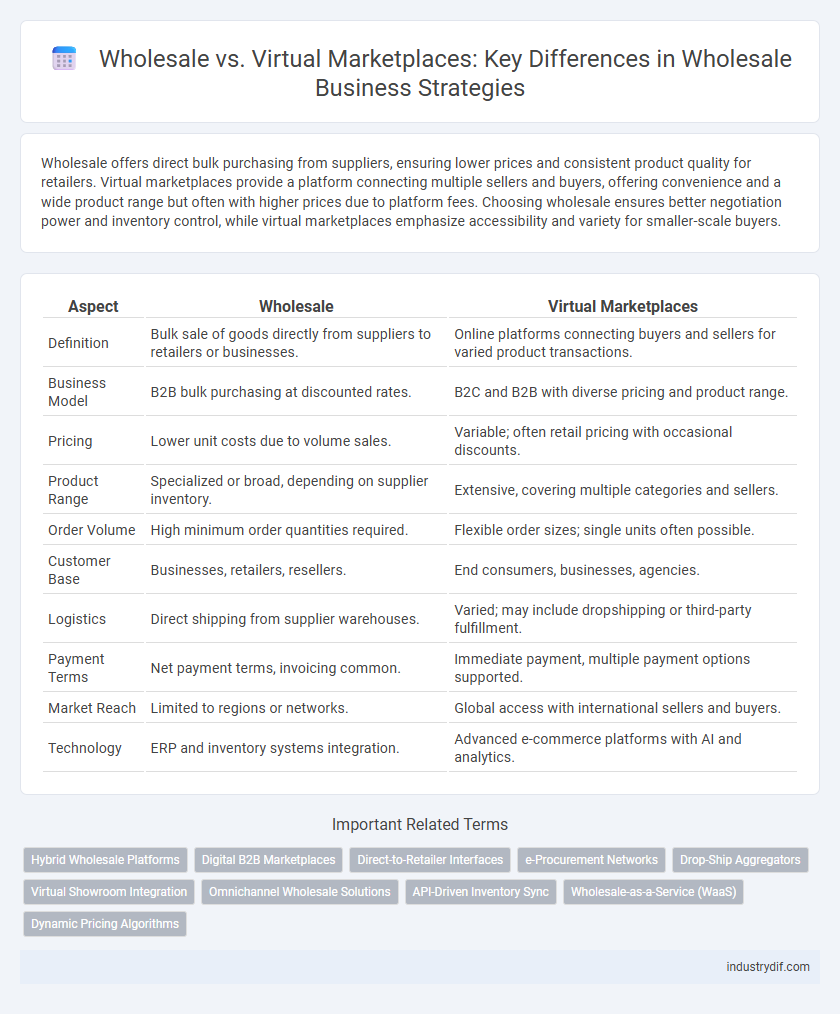
Wholesale offers direct bulk purchasing from suppliers, ensuring lower prices and consistent product quality for retailers. Virtual marketplaces provide a platform connecting multiple sellers and buyers, offering convenience and a wide product range but often with higher prices due to platform fees. Choosing wholesale ensures better negotiation power and inventory control, while virtual marketplaces emphasize accessibility and variety for smaller-scale buyers.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Wholesale | Virtual Marketplaces |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bulk sale of goods directly from suppliers to retailers or businesses. | Online platforms connecting buyers and sellers for varied product transactions. |
| Business Model | B2B bulk purchasing at discounted rates. | B2C and B2B with diverse pricing and product range. |
| Pricing | Lower unit costs due to volume sales. | Variable; often retail pricing with occasional discounts. |
| Product Range | Specialized or broad, depending on supplier inventory. | Extensive, covering multiple categories and sellers. |
| Order Volume | High minimum order quantities required. | Flexible order sizes; single units often possible. |
| Customer Base | Businesses, retailers, resellers. | End consumers, businesses, agencies. |
| Logistics | Direct shipping from supplier warehouses. | Varied; may include dropshipping or third-party fulfillment. |
| Payment Terms | Net payment terms, invoicing common. | Immediate payment, multiple payment options supported. |
| Market Reach | Limited to regions or networks. | Global access with international sellers and buyers. |
| Technology | ERP and inventory systems integration. | Advanced e-commerce platforms with AI and analytics. |
Defining Wholesale and Virtual Marketplaces
Wholesale involves the bulk purchase and sale of goods typically to retailers or other businesses, enabling large volume transactions at reduced prices. Virtual marketplaces are online platforms that connect multiple sellers with buyers, facilitating diverse product offerings without holding inventory. Wholesale emphasizes direct supplier-to-buyer relationships, while virtual marketplaces focus on digital interactions and wide product variety across various vendors.
Key Differences Between Wholesale and Virtual Marketplaces
Wholesale involves bulk purchasing directly from manufacturers or distributors, offering lower prices per unit and control over inventory management. Virtual marketplaces act as online platforms connecting multiple sellers with buyers, providing diverse product selections but with less control over product sourcing and pricing. Key differences include inventory ownership, pricing strategies, and the level of direct supplier interaction.
How Wholesale Works in the Digital Age
Wholesale in the digital age leverages advanced e-commerce platforms and data analytics to streamline bulk purchasing and inventory management. Businesses benefit from automated order processing, real-time pricing updates, and direct communication channels with suppliers, enhancing efficiency and scalability. Digital tools enable wholesalers to expand market reach and optimize supply chains, reducing costs and delivery times.
Benefits of Traditional Wholesale for Businesses
Traditional wholesale offers businesses direct access to bulk inventory with consistent quality control and lower per-unit costs, enabling predictable supply chain management. It facilitates stronger supplier relationships and negotiation power, which can lead to favorable credit terms and customized product offerings. Businesses benefit from immediate product availability and reduced dependency on third-party platforms, enhancing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Advantages of Virtual Marketplaces for Sellers and Buyers
Virtual marketplaces offer sellers extensive reach to global audiences and lower overhead costs compared to traditional wholesale channels. Buyers benefit from a wide product selection, transparent pricing, and convenient access to real-time reviews and ratings. Enhanced data analytics in virtual marketplaces enable sellers to optimize inventory and personalize buyer experiences, driving increased sales efficiency.
Cost Comparison: Wholesale vs Virtual Marketplace Fees
Wholesale typically involves lower per-unit costs due to bulk purchasing but requires higher upfront investment and storage expenses, impacting overall profitability. Virtual marketplaces charge listing fees, transaction commissions ranging from 5% to 15%, and sometimes subscription costs, which can accumulate and reduce margins on smaller volume sales. Businesses must analyze total cost structures, including fees and inventory holding costs, to determine the most cost-effective channel for their products.
Supply Chain Management in Wholesale versus Online Marketplaces
Wholesale supply chain management emphasizes streamlined inventory control, bulk order processing, and direct supplier relationships to ensure timely product availability and cost efficiency. Virtual marketplaces rely heavily on real-time data analytics, third-party logistics integration, and decentralized supplier networks to manage diverse product sourcing and rapid order fulfillment. Effective supply chain strategies in wholesale prioritize volume consolidation and demand forecasting, while online marketplaces focus on agility and scalability to accommodate fluctuating consumer demands.
Customer Acquisition Strategies in Both Models
Wholesale relies heavily on direct relationships and long-term contracts to acquire customers, leveraging volume discounts and personalized service to secure large buyers. Virtual marketplaces emphasize digital marketing, data analytics, and user experience optimization to attract diverse buyers through online channels. Both models require strategic adaptations, with wholesale focusing on trust and bulk purchasing, while virtual marketplaces prioritize scalability and broad market reach.
Scalability and Growth Potential: Wholesale vs Virtual Marketplaces
Wholesale offers significant scalability through bulk transactions and long-term contracts, enabling businesses to manage large inventories efficiently and expand production capacity. Virtual marketplaces provide rapid growth potential by connecting sellers to a global audience with minimal overhead and dynamic pricing models. Scalability in wholesale depends on supplier relationships and logistics, while virtual marketplaces leverage advanced technology platforms for exponential market reach and consumer data insights.
Choosing the Right Model: Factors to Consider for Your Business
Wholesale offers direct bulk purchasing with lower costs and greater control over inventory and pricing, ideal for businesses seeking consistent supply and long-term partnerships. Virtual marketplaces provide broader reach and access to diverse customer bases but often involve higher fees and less control over branding and customer data. Factors such as target audience, operational capacity, margin goals, and scalability should guide businesses in choosing between wholesale and virtual marketplace models.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Wholesale Platforms
Hybrid wholesale platforms combine traditional wholesale operations with virtual marketplace features, enabling businesses to access a broader network of suppliers and buyers while maintaining control over pricing and inventory. These platforms optimize supply chain efficiency by integrating real-time data analytics and seamless transactions, bridging the gap between physical wholesale distribution and digital marketplace convenience.
Digital B2B Marketplaces
Digital B2B marketplaces streamline wholesale transactions by connecting manufacturers, distributors, and retailers on a single platform, enabling real-time inventory updates and optimized supply chain management. These marketplaces reduce overhead costs and enhance market reach compared to traditional wholesale methods, facilitating faster procurement and bulk order processing with integrated payment and logistics solutions.
Direct-to-Retailer Interfaces
Wholesale emphasizes direct-to-retailer interfaces that streamline supply chain efficiency by eliminating intermediaries, enabling better pricing control and faster inventory turnover. Virtual marketplaces connect multiple buyers and sellers on digital platforms, but direct wholesale channels foster stronger brand-to-retailer relationships and customized order fulfillment.
e-Procurement Networks
Wholesale leverages e-Procurement Networks to streamline large-scale B2B transactions by connecting suppliers and buyers through integrated digital platforms that enhance negotiation efficiency and inventory management. Virtual Marketplaces, while broad in scope, often cater to a wider range of buyers and sellers but lack the specialized procurement workflows and contract management features essential for wholesale operations.
Drop-Ship Aggregators
Drop-ship aggregators streamline wholesale by consolidating multiple suppliers into a single platform, enabling retailers to access vast product inventories without holding stock. Unlike traditional wholesale, virtual marketplaces leverage drop-ship models to reduce overhead, improve scalability, and accelerate order fulfillment through seamless supplier integration.
Virtual Showroom Integration
Virtual showroom integration enhances wholesale operations by providing immersive, interactive product displays that streamline buyer decision-making and reduce the need for physical inventory samples. This technology enables wholesalers to expand their reach globally, facilitate personalized customer experiences, and improve order accuracy through real-time virtual demonstrations and detailed product information.
Omnichannel Wholesale Solutions
Omnichannel wholesale solutions integrate physical and virtual marketplaces, enabling seamless inventory management, real-time order processing, and unified customer experiences across multiple sales channels. These solutions optimize supply chain efficiency and enhance client engagement by providing wholesalers with synchronized digital platforms alongside traditional wholesale operations.
API-Driven Inventory Sync
API-driven inventory sync enables wholesalers to maintain real-time stock accuracy across multiple sales channels, reducing overselling and stockouts. Virtual marketplaces rely heavily on these integrations to provide seamless product availability updates, enhancing buyer trust and operational efficiency.
Wholesale-as-a-Service (WaaS)
Wholesale-as-a-Service (WaaS) revolutionizes traditional wholesale models by integrating cloud-based platforms that streamline inventory management, order processing, and real-time data analytics, enabling businesses to scale efficiently without the limitations of physical marketplaces. Unlike virtual marketplaces that aggregate multiple sellers, WaaS offers a tailored, scalable infrastructure designed specifically to optimize wholesale operations with enhanced automation and direct supplier-to-buyer connectivity.
Dynamic Pricing Algorithms
Dynamic pricing algorithms in wholesale enable real-time price adjustments based on supply, demand, and competitor pricing, ensuring optimal margins and inventory turnover. Virtual marketplaces leverage these algorithms to offer personalized pricing, enhancing buyer engagement and driving higher sales velocity in competitive environments.
Wholesale vs Virtual Marketplaces Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com