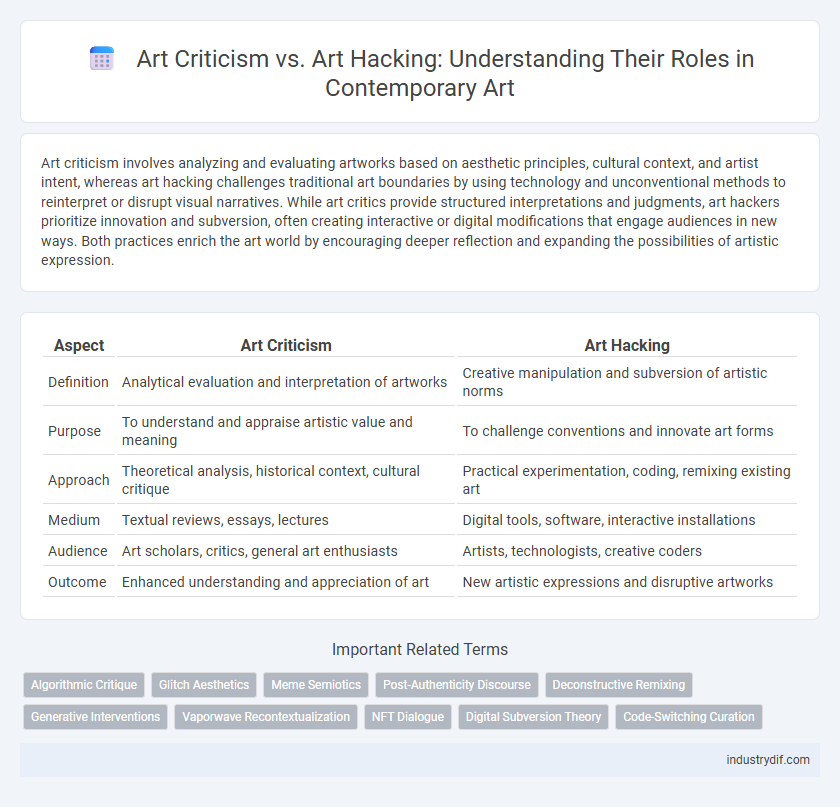
Art criticism involves analyzing and evaluating artworks based on aesthetic principles, cultural context, and artist intent, whereas art hacking challenges traditional art boundaries by using technology and unconventional methods to reinterpret or disrupt visual narratives. While art critics provide structured interpretations and judgments, art hackers prioritize innovation and subversion, often creating interactive or digital modifications that engage audiences in new ways. Both practices enrich the art world by encouraging deeper reflection and expanding the possibilities of artistic expression.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Art Criticism | Art Hacking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analytical evaluation and interpretation of artworks | Creative manipulation and subversion of artistic norms |
| Purpose | To understand and appraise artistic value and meaning | To challenge conventions and innovate art forms |
| Approach | Theoretical analysis, historical context, cultural critique | Practical experimentation, coding, remixing existing art |
| Medium | Textual reviews, essays, lectures | Digital tools, software, interactive installations |
| Audience | Art scholars, critics, general art enthusiasts | Artists, technologists, creative coders |
| Outcome | Enhanced understanding and appreciation of art | New artistic expressions and disruptive artworks |
Understanding Art Criticism: Definition and Scope
Art criticism involves analyzing and evaluating artworks to interpret meaning, assess technique, and place pieces within historical and cultural contexts. It encompasses diverse methods including formal analysis, contextual analysis, and expressive theories, aiming to deepen appreciation and understanding of art. This discipline guides audiences and creators by offering informed perspectives that shape the reception and value of artistic expressions.
Art Hacking Explained: Disrupting Creative Norms
Art hacking challenges traditional art criticism by disrupting established creative norms through innovative, technology-driven interventions that transform artistic expression. Utilizing digital tools and inventive methodologies, art hackers subvert conventional aesthetics and invite audience participation, creating dynamic, interactive experiences. This practice expands the boundaries of art, fostering experimental creativity and rethinking the relationship between artist, artwork, and viewer.
Historical Roots of Art Criticism
Art criticism traces its roots to ancient Greece, where philosophers like Plato and Aristotle analyzed aesthetics and artistic value, laying the foundation for systematic evaluation of art. During the Renaissance, art criticism evolved through the works of figures such as Giorgio Vasari, who documented artists' biographies and styles, influencing the criteria for artistic merit. This historical lineage contrasts with art hacking, a contemporary movement that disrupts traditional art norms by merging technology and experimental practices to challenge established critical frameworks.
The Evolution of Art Hacking in Contemporary Culture
Art hacking has evolved from a niche subculture into a mainstream form of creative expression that challenges traditional art criticism frameworks by blending technology, activism, and interactivity. Contemporary art hackers disrupt conventional gallery spaces and institutional narratives, fostering participatory experiences that critique societal norms and digital culture. This evolution highlights a shift towards democratized art-making processes, where the boundary between artist, critic, and audience increasingly blurs.
Key Methodologies: Critique vs. Intervention
Art criticism employs analytical methodologies emphasizing interpretation, contextual evaluation, and theoretical frameworks to assess artistic value and meaning. Art hacking adopts interventionist strategies, manipulating or repurposing artworks and systems to challenge conventional boundaries and provoke new dialogues. These divergent approaches highlight critique as reflective analysis, whereas intervention serves as active transformation within the art ecosystem.
Influential Figures in Art Criticism and Hacking
Influential figures in art criticism include Clement Greenberg, whose formalist approach shaped modernist art discourse, and John Berger, known for his socio-political readings of visual culture. In contrast, art hacking pioneers like Eduardo Kac, who integrates biotechnology with digital art, and Zach Blas, who critiques power structures through interactive installations, challenge traditional art paradigms. These figures exemplify divergent methodologies: criticism analyzes and interprets artworks, while hacking redefines artistic boundaries through innovative technological interventions.
Ethical Considerations in Art Judgement and Manipulation
Ethical considerations in art criticism emphasize fairness, respect for the artist's intent, and cultural sensitivity to avoid misrepresentation or bias in judgment. In contrast, art hacking challenges traditional boundaries by manipulating artworks or systems, raising concerns about authenticity, intellectual property rights, and the potential for cultural appropriation. Balancing these ethical dimensions requires transparent dialogue about the impact of critique and intervention on artistic integrity and audience perception.
Technology’s Role in Shaping Criticism and Hacking
Technology revolutionizes art criticism by enabling real-time, data-driven analysis and interactive digital platforms that expand accessibility and audience engagement. In contrast, art hacking leverages coding, software manipulation, and experimental digital tools to subvert traditional art boundaries and create disruptive, innovative works. Both fields intersect at the convergence of creativity and technology, redefining how art is interpreted, produced, and consumed in contemporary culture.
Impact on Artists and the Art Market
Art criticism shapes the art market by influencing public perception and gallery representation, often determining an artist's commercial success and reputation through expert reviews and academic discourse. In contrast, art hacking disrupts traditional market dynamics by introducing unauthorized alterations or reinterpretations that challenge ownership and originality, potentially destabilizing established value systems. Both practices impact artists differently: art criticism can enhance career legitimacy, while art hacking may provoke controversy, encouraging reconsideration of artistic boundaries and market norms.
Future Trends: Where Criticism Meets Hacking
Art criticism is evolving through integration with digital tools, enabling real-time analysis and interactive audience engagement. Art hacking disrupts traditional boundaries by leveraging technology to remix, reinterpret, and democratize creative expression. Future trends show a convergence where critical theory and technological innovation fuse, fostering immersive, participatory art experiences that challenge conventional interpretation.
Related Important Terms
Algorithmic Critique
Algorithmic critique in art hacking leverages computational methods and data analysis to dissect and reinterpret artworks, challenging traditional art criticism's reliance on subjective human judgment and theoretical frameworks. This approach enables a dynamic exploration of artistic meaning, exposing patterns and biases through machine learning and digital tools that unveil new dimensions of cultural expression.
Glitch Aesthetics
Glitch aesthetics emphasize the beauty found in digital errors and system failures, challenging traditional art criticism by celebrating imperfection and unpredictability. Art hacking subverts conventional artistic norms through technological manipulation, fostering a critical dialogue that blurs boundaries between creation and malfunction within contemporary digital art.
Meme Semiotics
Art criticism dissects the symbolic language and cultural context behind traditional artworks, while art hacking employs meme semiotics to subvert and remix visual codes for provocative social commentary. Meme semiotics reveals how shared symbols evolve rapidly in digital spaces, transforming art consumption into participatory, dynamic critique rather than static interpretation.
Post-Authenticity Discourse
Art criticism in the post-authenticity discourse interrogates conventional notions of originality and authorship by deconstructing established aesthetic values, while art hacking disrupts traditional artistic boundaries through subversive appropriation and digital manipulation techniques. This paradigm shift highlights the tension between institutional validation and grassroots innovation, emphasizing the fluidity of meaning and the destabilization of canonical art narratives.
Deconstructive Remixing
Deconstructive remixing in art criticism dissects traditional narratives to expose underlying assumptions and cultural biases, revealing new interpretations. In contrast, art hacking employs this technique to subvert original works, repurposing elements for innovative, often disruptive, creative expressions.
Generative Interventions
Art criticism evaluates generative interventions by analyzing their conceptual depth, aesthetic innovation, and cultural commentary within the context of contemporary art discourse. Art hacking leverages generative technologies to disrupt traditional art creation processes, enabling dynamic, algorithm-driven expressions that challenge conventional boundaries and redefine authorship.
Vaporwave Recontextualization
Art criticism traditionally analyzes and interprets artworks through established aesthetic and cultural frameworks, while art hacking subverts these norms by recontextualizing Vaporwave's retro-futuristic visuals and consumerist symbols to challenge mainstream art narratives. Vaporwave recontextualization in art hacking deconstructs digital nostalgia and hypercapitalism, transforming familiar imagery into a critique of contemporary culture's commodification and media saturation.
NFT Dialogue
Art criticism traditionally dissects aesthetics, cultural significance, and artist intent, while art hacking challenges conventions by employing NFTs to disrupt ownership and value frameworks. This evolving NFT dialogue merges critical analysis with innovative digital practices, reshaping contemporary art discourse.
Digital Subversion Theory
Art Criticism traditionally evaluates aesthetic and cultural value, while Art Hacking employs Digital Subversion Theory to disrupt conventional digital art platforms and challenge proprietary constraints through unauthorized intervention. This practice exposes systemic biases and redefines authorship by leveraging technology to create participatory, politically charged artworks that question surveillance and control in digital environments.
Code-Switching Curation
Art criticism traditionally evaluates aesthetic and cultural value, while art hacking challenges conventional boundaries through code-switching curation that blends diverse linguistic and artistic codes. This innovative approach disrupts normative narratives by integrating multiple cultural languages within digital and physical art spaces, fostering dynamic reinterpretations and expanded audience engagement.
Art Criticism vs Art Hacking Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com