University degrees offer comprehensive theoretical knowledge and a broad educational foundation, essential for careers requiring deep subject mastery and research skills. Bootcamp certificates focus on practical, industry-relevant skills and fast-tracked learning, ideal for technology fields and rapid job market entry. Choosing between them depends on career goals, time availability, and the desired balance between academic depth and hands-on experience.
Table of Comparison
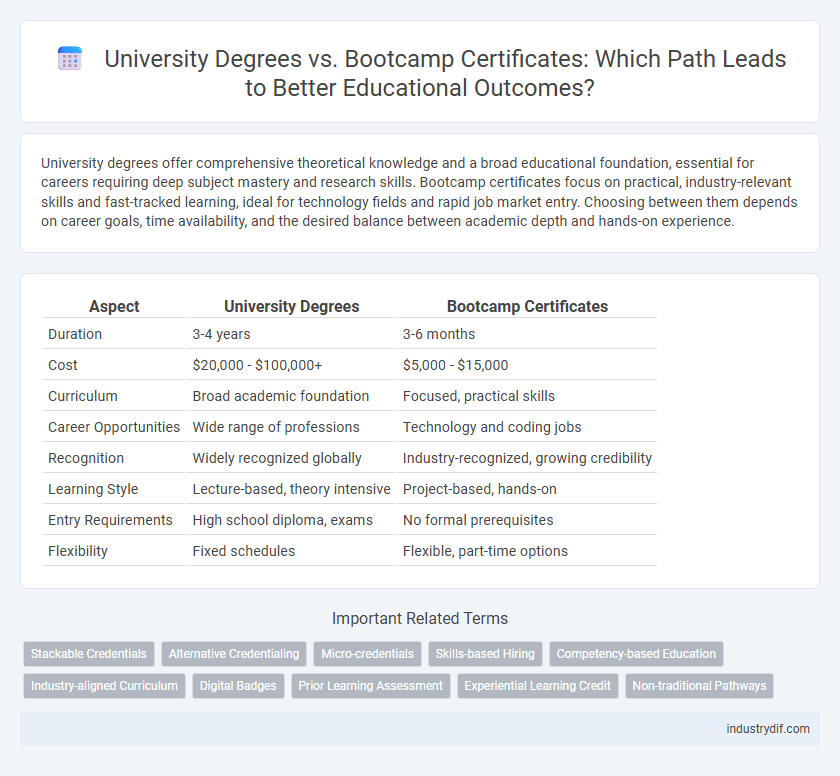
| Aspect | University Degrees | Bootcamp Certificates |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 3-4 years | 3-6 months |
| Cost | $20,000 - $100,000+ | $5,000 - $15,000 |
| Curriculum | Broad academic foundation | Focused, practical skills |
| Career Opportunities | Wide range of professions | Technology and coding jobs |
| Recognition | Widely recognized globally | Industry-recognized, growing credibility |
| Learning Style | Lecture-based, theory intensive | Project-based, hands-on |
| Entry Requirements | High school diploma, exams | No formal prerequisites |
| Flexibility | Fixed schedules | Flexible, part-time options |
Key Differences Between University Degrees and Bootcamp Certificates
University degrees provide comprehensive theoretical knowledge and critical thinking skills over several years, often including internships and research opportunities, while bootcamp certificates focus on practical, job-ready skills acquired in a shorter timeframe, typically a few months. Universities offer accredited programs recognized globally, supporting broader career paths and advanced education, whereas bootcamps emphasize specialized, hands-on training tailored to immediate industry demands, particularly in technology fields. Cost and flexibility differ significantly; university degrees involve substantial tuition fees and fixed schedules, while bootcamps are more affordable and often allow self-paced or intensive learning formats.
Curriculum Structure: Depth vs. Practicality
University degrees offer a comprehensive curriculum structure emphasizing theoretical depth, critical thinking, and foundational knowledge across multiple disciplines. Bootcamp certificates prioritize practicality, delivering intensive, skill-focused training designed to meet specific industry demands quickly. The choice between these paths depends on whether learners seek broad academic understanding or rapid acquisition of job-ready skills.
Time Investment: Duration and Flexibility
University degrees typically require a time investment of three to six years, demanding a fixed schedule and limited flexibility, whereas bootcamp certificates often span three to six months with intensive, flexible learning options tailored for working professionals. The extended duration of university programs offers comprehensive theoretical knowledge and in-depth specialization, contrasting with the fast-paced, skills-focused curriculum of bootcamps designed for rapid job market entry. Choosing between these options depends on prioritizing long-term academic credentials or accelerated practical skill acquisition within a shorter timeframe.
Cost Comparison: Tuition and Return on Investment
University degrees typically involve higher tuition fees averaging $20,000 to $50,000 annually, resulting in substantial student debt but often offering long-term career advancement and higher salary potential. Bootcamp certificates usually cost between $7,000 and $15,000 with shorter program durations, enabling quicker workforce entry and faster return on investment for tech and coding careers. Return on investment varies significantly by industry, degree prestige, and job market demand, with bootcamps providing a cost-effective alternative for skills-focused, high-demand professions.
Admissions Criteria: Entry Requirements
University degrees typically require high school diplomas, standardized test scores, and competitive GPAs for admissions, reflecting a rigorous entry process. Bootcamp certificates often have more accessible entry requirements, sometimes only needing a basic proficiency in relevant skills or a brief application assessment. This contrast highlights how universities prioritize academic preparation, while bootcamps focus on practical readiness and quick skill acquisition.
Career Outcomes: Employability and Advancement
University degrees often provide a comprehensive theoretical foundation and recognized credentials valued by employers, enhancing long-term career advancement and higher salary potential. Bootcamp certificates focus on practical, job-ready skills tailored for rapid entry into tech roles, increasing employability for specific positions with less time and financial investment. Employers seeking candidates for specialized, skill-intensive jobs may prefer bootcamp graduates for immediate job performance, while those targeting leadership or research roles typically prioritize university degree holders.
Industry Relevance and Skill Alignment
University degrees offer comprehensive theoretical knowledge and a broad academic foundation, which can be essential for roles requiring deep subject matter expertise or research capabilities. Bootcamp certificates focus on practical, industry-relevant skills and rapid skill acquisition, aligning closely with current technology trends and employer demands in fields like software development and data science. Employers increasingly value bootcamp graduates for their hands-on experience and ability to adapt quickly to evolving job requirements, while degrees remain important for positions emphasizing analytical thinking and advanced education.
Networking and Professional Development Opportunities
University degrees offer extensive networking opportunities through alumni associations, career fairs, and academic conferences, fostering long-term professional relationships and industry connections. Bootcamp certificates provide focused networking via industry partnerships, mentorship programs, and direct access to hiring managers, enabling rapid entry into tech communities. Both paths support professional development but differ in depth and duration of engagement with potential employers and peers.
Recognition and Accreditation in the Job Market
University degrees typically hold widespread recognition and formal accreditation from established educational authorities, making them highly valued by employers across various industries. Bootcamp certificates, while increasingly accepted, often lack standardized accreditation and may be viewed as less comprehensive, depending on the employer's familiarity with the program. Hiring managers tend to prioritize degrees for roles requiring deep theoretical knowledge, whereas bootcamp credentials are favored for practical, skill-specific positions in fast-evolving tech sectors.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
University degrees typically offer comprehensive theoretical knowledge and recognized accreditation that can open doors to a wide range of careers, while bootcamp certificates emphasize practical skills and faster entry into the job market. Key factors to consider include your career goals, timeline, financial investment, and preferred learning style, as university programs usually require several years and higher costs compared to intensive bootcamps. Researching industry demand, potential salary outcomes, and employer preferences in your desired field helps determine which educational path aligns best with your professional aspirations.
Related Important Terms
Stackable Credentials
Stackable credentials enable learners to combine university degrees and bootcamp certificates, enhancing skill sets with targeted, industry-relevant knowledge. This modular approach increases employability by allowing continuous education and flexible career advancement in rapidly evolving job markets.
Alternative Credentialing
University degrees offer comprehensive theoretical knowledge and widely recognized credentials, while bootcamp certificates provide focused, practical skills tailored to industry demands. Alternative credentialing through bootcamps accelerates workforce entry and addresses skill gaps, appealing to learners seeking flexible, cost-effective education paths.
Micro-credentials
Micro-credentials offer targeted skill validation that complements traditional university degrees by providing industry-relevant competencies in a shorter timeframe. These focused credentials enhance employability by demonstrating specific expertise, making them vital in the evolving education landscape.
Skills-based Hiring
Skills-based hiring increasingly favors practical experience and proven competencies, making bootcamp certificates a viable alternative to traditional university degrees for employers prioritizing job-ready abilities. Bootcamps emphasize hands-on projects and up-to-date technical training, aligning closely with industry demands and accelerating workforce entry compared to multi-year academic programs.
Competency-based Education
Competency-based education emphasizes mastery of specific skills and real-world application, making bootcamp certificates highly effective for targeted, practical training in tech and emerging fields. University degrees offer a broader theoretical foundation and critical thinking development, providing a comprehensive knowledge base that supports long-term career growth and adaptability.
Industry-aligned Curriculum
University degrees often provide a comprehensive, theory-based education that covers foundational principles across diverse fields, while bootcamp certificates concentrate on hands-on skills with industry-aligned curricula designed to meet current job market demands. Bootcamps typically emphasize practical experience and up-to-date technologies, enabling faster entry into specialized roles in technology and business sectors, whereas university programs offer broader academic knowledge and research opportunities supporting long-term career growth.
Digital Badges
Digital badges offer a flexible and verifiable alternative to traditional university degrees and bootcamp certificates by showcasing specific skills and achievements through blockchain technology and metadata. Universities increasingly incorporate these digital badges to complement degree programs, while bootcamps use them to validate practical skills, enhancing employability in the tech industry.
Prior Learning Assessment
Prior Learning Assessment (PLA) evaluates competencies acquired through work experience, bootcamps, or informal education, enabling students to translate practical skills into academic credits toward university degrees. This process enhances educational pathways by bridging the gap between traditional university degrees and bootcamp certificates, promoting flexible and competency-based credentialing.
Experiential Learning Credit
University degrees often incorporate Experiential Learning Credit (ELC) that recognizes internships, co-ops, and real-world projects for academic credit, providing students with formal acknowledgment of practical skills. Bootcamp certificates emphasize intensive hands-on training and projects but typically do not offer accredited ELC, limiting their academic credit transferability compared to traditional degrees.
Non-traditional Pathways
Non-traditional pathways such as bootcamp certificates offer accelerated, skill-focused training compared to traditional university degrees, often leading to faster entry into tech careers. Employers increasingly recognize bootcamp certifications for their practical, project-based learning, making them a viable alternative for career changers and professionals seeking rapid upskilling.
University Degrees vs Bootcamp Certificates Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com