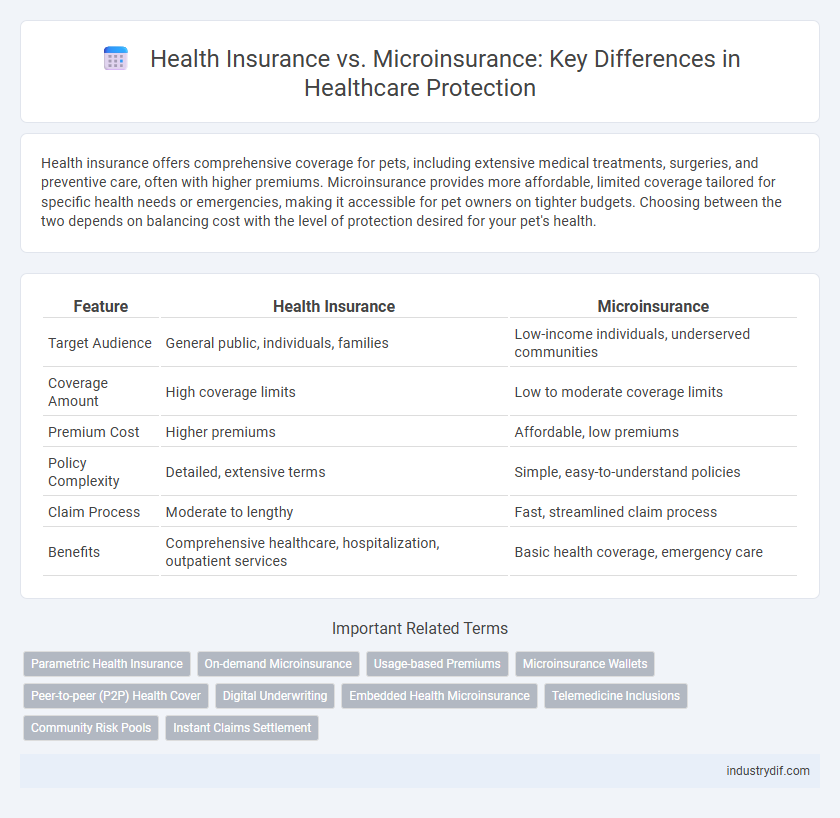
Health insurance offers comprehensive coverage for pets, including extensive medical treatments, surgeries, and preventive care, often with higher premiums. Microinsurance provides more affordable, limited coverage tailored for specific health needs or emergencies, making it accessible for pet owners on tighter budgets. Choosing between the two depends on balancing cost with the level of protection desired for your pet's health.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Health Insurance | Microinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | General public, individuals, families | Low-income individuals, underserved communities |
| Coverage Amount | High coverage limits | Low to moderate coverage limits |
| Premium Cost | Higher premiums | Affordable, low premiums |
| Policy Complexity | Detailed, extensive terms | Simple, easy-to-understand policies |
| Claim Process | Moderate to lengthy | Fast, streamlined claim process |
| Benefits | Comprehensive healthcare, hospitalization, outpatient services | Basic health coverage, emergency care |
Understanding Health Insurance: Key Features
Health insurance provides comprehensive coverage for a wide range of medical expenses including hospitalization, surgeries, and prescription drugs, typically involving higher premiums and deductibles. Microinsurance offers limited but affordable protection tailored for low-income individuals, covering specific health risks with simplified claim processes. Understanding these key features helps individuals select the appropriate health coverage based on their financial capacity and healthcare needs.
What is Microinsurance? An Overview
Microinsurance is a type of health insurance designed to provide affordable coverage to low-income individuals and families who typically lack access to traditional insurance markets. It offers basic health benefits with lower premiums and simplified claim processes, aiming to protect against health-related financial shocks. This insurance model supports vulnerable populations by improving access to essential healthcare services and promoting financial resilience.
Coverage Scope: Health Insurance vs Microinsurance
Health insurance offers comprehensive coverage including hospitalization, outpatient services, prescription drugs, and preventive care, typically designed for broader populations. Microinsurance provides limited, affordable health benefits targeted at low-income groups, often covering specific risks like minor illnesses, basic treatments, and emergency services. The scope of health insurance is extensive, while microinsurance focuses on accessible, essential coverage for underserved communities.
Premium Costs and Affordability Comparison
Health insurance premiums typically require higher monthly payments, making them less accessible to low-income individuals, while microinsurance offers significantly lower premium costs designed for affordability among vulnerable populations. Microinsurance schemes often distribute risk over smaller coverage amounts and shorter terms, resulting in cheaper options that maintain essential coverage for acute illnesses and emergencies. The affordability of microinsurance empowers broader health protection access in underserved areas, contrasting with the prohibitive costs of traditional health insurance plans.
Target Markets: Who Benefits Most?
Health insurance primarily targets middle- and high-income individuals who can afford comprehensive coverage, providing protection against significant medical expenses and access to a wide range of healthcare services. Microinsurance is designed for low-income populations in developing regions, offering affordable, basic health coverage that addresses immediate medical needs and reduces financial risk from illness. Both systems benefit distinct groups, with health insurance serving those seeking extensive protection and microinsurance supporting vulnerable communities with limited financial resources.
Claims Process Differences Explained
Health insurance typically involves a more complex claims process requiring detailed documentation, longer approval times, and higher premiums. Microinsurance, designed for low-income populations, offers a simplified claims procedure with minimal paperwork and faster payouts to improve accessibility and affordability. Insurers implement digital tools and mobile platforms in microinsurance to expedite claims, contrasting with traditional health insurance's extensive verification steps.
Accessibility and Distribution Channels
Health insurance generally offers broader coverage but often requires formal enrollment processes and higher premiums, limiting accessibility for low-income populations. Microinsurance targets underserved communities by providing affordable, simplified policies accessible through local agents, mobile platforms, and community networks. Distribution channels for microinsurance leverage technology and grassroots partnerships, enhancing reach in remote or informal markets where traditional health insurance penetration is low.
Policy Limitations and Exclusions
Health insurance policies often have higher coverage limits and broader protection but include extensive exclusions such as pre-existing conditions and specific treatments. Microinsurance offers lower policy limits designed for low-income populations, with simplified terms and fewer exclusions to enhance accessibility. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting appropriate coverage based on individual health risks and financial capacity.
Impact on Healthcare Access
Health insurance generally offers broader coverage and higher financial protection, significantly improving access to comprehensive healthcare services. Microinsurance targets low-income populations with affordable, limited coverage, enhancing access to basic healthcare but often excluding specialized or costly treatments. Studies indicate microinsurance increases healthcare utilization among underserved communities while traditional health insurance reduces out-of-pocket expenses across diverse demographics.
Choosing the Right Option: Factors to Consider
When choosing between health insurance and microinsurance, consider factors such as coverage scope, premium affordability, and claim processing time. Health insurance typically offers comprehensive benefits suitable for long-term healthcare needs, while microinsurance provides targeted, low-cost protection for specific risks or short-term medical expenses. Assess personal health requirements, budget constraints, and risk tolerance to select the most effective financial protection.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Health Insurance
Parametric health insurance offers predefined payouts based on specific health-related triggers, reducing claim processing time and enhancing transparency compared to traditional health and microinsurance schemes. Unlike conventional indemnity-based health insurance, parametric models mitigate administrative costs and provide rapid financial support during pandemics or widespread health emergencies.
On-demand Microinsurance
On-demand microinsurance offers flexible, affordable health coverage tailored for low-income individuals or those with irregular incomes, providing essential benefits without the high premiums of traditional health insurance. This innovative model leverages digital platforms to enable users to activate and pay for coverage only when needed, increasing accessibility and financial protection in underserved communities.
Usage-based Premiums
Usage-based premiums in health insurance adjust costs according to individual health behaviors and risk profiles, promoting personalized coverage and potentially lowering expenses for healthier individuals. Microinsurance leverages usage-based models to offer affordable, targeted protection for low-income populations by aligning premiums with actual healthcare utilization and risks.
Microinsurance Wallets
Microinsurance wallets offer an affordable and accessible solution for low-income populations to manage health expenses, providing tailored coverage and seamless digital payment options that enhance financial inclusion. These wallets integrate health insurance with mobile technology, enabling users to store, pay premiums, and claim benefits securely, driving greater adoption and improved health outcomes in underserved communities.
Peer-to-peer (P2P) Health Cover
Peer-to-peer (P2P) health cover leverages microinsurance models to provide affordable, community-based health protection that contrasts traditional health insurance's institutional approach. By pooling resources directly among members, P2P health cover reduces administrative costs and enhances transparency, making it especially effective for underserved populations.
Digital Underwriting
Digital underwriting in health insurance leverages advanced data analytics and AI algorithms to streamline risk assessment, enabling personalized policy pricing and faster approval processes. Microinsurance employs simplified digital underwriting models to enhance accessibility for low-income populations by minimizing paperwork and using alternative data sources for swift underwriting decisions.
Embedded Health Microinsurance
Embedded health microinsurance integrates affordable, low-cost coverage directly into everyday financial products like mobile wallets and savings accounts, enhancing access for low-income populations and reducing gaps in traditional health insurance markets. This model leverages digital platforms and local networks to provide streamlined claims processing and increased financial protection against medical expenses for underserved communities.
Telemedicine Inclusions
Health insurance plans generally offer comprehensive telemedicine inclusions, providing policyholders with virtual consultations, remote diagnostics, and digital prescription services. Microinsurance, while more affordable and targeted towards low-income groups, typically features limited telemedicine coverage, often restricted to basic virtual health services and essential remote care options.
Community Risk Pools
Health insurance typically operates through large-scale risk pools that spread costs across a broad population, while microinsurance leverages smaller, community-based risk pools designed to provide affordable coverage for low-income or underserved groups. Community risk pools in microinsurance enhance localized risk-sharing and improve access to essential health services by minimizing administrative expenses and tailoring benefits to specific community needs.
Instant Claims Settlement
Health insurance typically offers comprehensive coverage with longer claim processing times, while microinsurance emphasizes affordability and accessibility, enabling instant claims settlement tailored for low-income populations. Instant claims settlement in microinsurance reduces financial stress by providing rapid payouts, enhancing timely access to healthcare services.
Health Insurance vs Microinsurance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com