Patient records provide a comprehensive history of a pet's medical background, including past treatments, vaccinations, and diagnoses, essential for accurate veterinary care. Smart health data uses real-time monitoring through wearable devices to track vital signs, activity levels, and behavioral changes, enabling proactive health management. Integrating patient records with smart health data enhances personalized treatment plans and early detection of potential health issues.
Table of Comparison
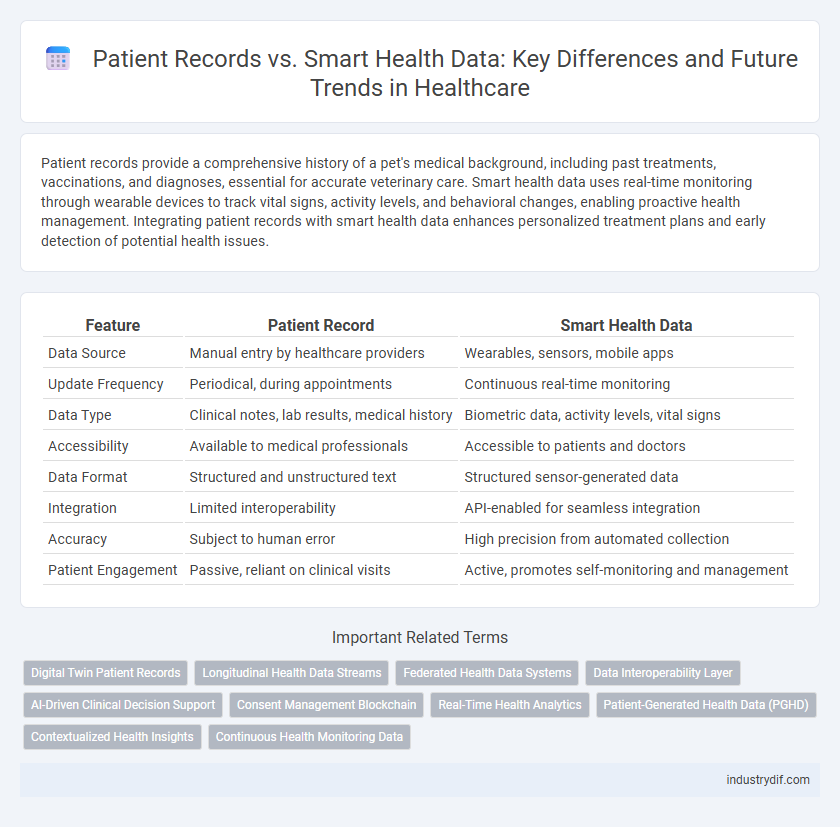
| Feature | Patient Record | Smart Health Data |
|---|---|---|
| Data Source | Manual entry by healthcare providers | Wearables, sensors, mobile apps |
| Update Frequency | Periodical, during appointments | Continuous real-time monitoring |
| Data Type | Clinical notes, lab results, medical history | Biometric data, activity levels, vital signs |
| Accessibility | Available to medical professionals | Accessible to patients and doctors |
| Data Format | Structured and unstructured text | Structured sensor-generated data |
| Integration | Limited interoperability | API-enabled for seamless integration |
| Accuracy | Subject to human error | High precision from automated collection |
| Patient Engagement | Passive, reliant on clinical visits | Active, promotes self-monitoring and management |
Understanding Patient Records: Traditional Approaches
Traditional patient records primarily consist of paper-based charts and static electronic health records (EHRs) that store clinician notes, diagnostic tests, and treatment histories. These formats often lack real-time data integration, limiting comprehensive patient insights and hindering proactive healthcare management. Understanding these conventional methods highlights the need for transitioning towards dynamic smart health data systems that enhance accuracy, accessibility, and personalized care.
What Sets Smart Health Data Apart?
Smart health data integrates real-time information from wearable devices, electronic health records, and genomic data to create a comprehensive and dynamic view of a patient's health. Unlike traditional patient records that store static historical data, smart health data uses advanced analytics and machine learning to provide predictive insights, personalized treatment plans, and continuous monitoring. This allows healthcare providers to make more informed decisions, improve patient outcomes, and enable proactive health management.
Key Components of Patient Records
Patient records primarily consist of structured data such as medical history, diagnoses, treatment plans, lab results, and medication lists, essential for accurate clinical decision-making. Key components include demographic information, allergy and immunization status, and clinician notes that provide context for ongoing care. Smart health data integrates these traditional elements with real-time monitoring, wearable device metrics, and predictive analytics to enhance personalized patient management.
Advanced Features of Smart Health Data
Smart health data integrates real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and AI-driven insights, enabling personalized treatment plans and proactive care management. Unlike traditional patient records, smart health data systems support seamless interoperability, continuous data updates from wearable devices, and advanced data visualization for improved clinical decision-making. This evolution enhances patient outcomes through precise diagnostics, early detection of health issues, and optimized healthcare resource allocation.
Data Interoperability: Bridging Patient Records and Smart Data
Data interoperability is crucial for integrating traditional patient records with smart health data, enabling seamless information exchange across diverse healthcare systems. Utilizing standardized protocols like HL7 FHIR enhances data sharing accuracy, promoting comprehensive patient insights and improved clinical decision-making. Bridging these data types fosters a unified health ecosystem that supports real-time monitoring, personalized treatments, and efficient care coordination.
Accuracy and Real-Time Updates in Health Information
Patient records traditionally offer structured health information but often lack real-time updates, which can result in delayed clinical decisions. Smart health data integrates continuous monitoring devices and AI algorithms to provide accurate, real-time updates, enhancing diagnostic precision and personalized treatment plans. This shift towards dynamic data captures patient health status instantaneously, reducing errors and improving overall care outcomes.
Security and Privacy: Protecting Sensitive Health Data
Patient records typically consist of static, manually updated data stored in electronic health record (EHR) systems, making them vulnerable to unauthorized access and data breaches without stringent security protocols. Smart health data, generated from wearable devices and IoT sensors, requires advanced encryption and real-time monitoring to safeguard continuous streams of sensitive information against cyber threats. Implementing robust access controls, data anonymization, and blockchain technology enhances the protection of sensitive health data, ensuring patient privacy and compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
Enhanced Patient Care with Smart Health Data
Smart health data integrates real-time analytics and comprehensive patient information to deliver personalized treatment plans, surpassing the static nature of traditional patient records. This dynamic approach enables healthcare providers to detect early warning signs, optimize medication dosages, and improve chronic disease management. The use of wearable devices and IoT sensors enhances continuous health monitoring, resulting in more accurate diagnoses and better patient outcomes.
Challenges in Transitioning from Patient Records to Smart Data
Transitioning from traditional patient records to smart health data systems presents challenges such as data interoperability, where diverse formats and standards hinder seamless information exchange. Ensuring data privacy and security becomes more complex with the integration of IoT devices and real-time health monitoring technologies. Additionally, healthcare providers must address the difficulties in managing vast volumes of unstructured data while maintaining accuracy and clinical relevance.
Future Trends: The Evolution from Patient Records to Smart Health Data
Future trends in healthcare emphasize the transition from traditional patient records to smart health data systems powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning. Smart health data integrates real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and personalized care plans, enhancing diagnosis accuracy and patient outcomes. This evolution supports interoperability across healthcare platforms, enabling seamless data exchange and accelerating medical research advancements.
Related Important Terms
Digital Twin Patient Records
Digital Twin Patient Records integrate real-time health data from wearable devices and electronic health records, creating dynamic, individualized simulations that improve diagnosis accuracy and personalized treatment plans. This advanced approach surpasses traditional patient records by enabling continuous monitoring and predictive analytics for proactive health management.
Longitudinal Health Data Streams
Longitudinal health data streams provide a continuous, real-time flow of patient health metrics, enabling a more dynamic and comprehensive understanding of individual health trends compared to traditional patient records that capture static, episodic information. Integrating smart health data enhances predictive analytics and personalized treatment plans by leveraging wearable sensors, mobile health apps, and electronic health records for seamless data aggregation.
Federated Health Data Systems
Patient records store individual medical histories in centralized databases, while smart health data leverages Federated Health Data Systems to enable secure, decentralized access and analysis across multiple institutions. This approach enhances data privacy, interoperability, and real-time insights by allowing healthcare providers to collaborate without sharing sensitive information directly.
Data Interoperability Layer
Patient records traditionally store static health information within isolated systems, limiting data exchange and integration. The data interoperability layer in smart health data enables seamless communication across diverse healthcare platforms, enhancing real-time access and comprehensive patient insights.
AI-Driven Clinical Decision Support
AI-driven clinical decision support leverages smart health data to analyze extensive patient records, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and personalized treatment plans. Integrating real-time sensor data, genetic information, and historical medical records enables AI algorithms to provide proactive, evidence-based recommendations that improve patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Consent Management Blockchain
Patient record systems store and manage individual health information, while smart health data integrates real-time biometric and behavioral data for enhanced personalized care. Consent management blockchain technology ensures secure, transparent, and immutable control over patient permissions, enabling trustworthy data sharing and compliance with healthcare regulations.
Real-Time Health Analytics
Real-time health analytics leverage smart health data to continuously monitor patient conditions, enabling proactive interventions and personalized treatment plans. In contrast, traditional patient records offer static historical information that lacks the immediacy and dynamic insights critical for urgent clinical decision-making.
Patient-Generated Health Data (PGHD)
Patient-Generated Health Data (PGHD) offers real-time, personalized insights directly from patients, enhancing traditional patient records that rely primarily on clinical encounters. Integrating PGHD with electronic health records enables more comprehensive health monitoring, improved patient engagement, and tailored treatment plans.
Contextualized Health Insights
Patient records provide static, historical data limited to individual visits, whereas smart health data integrates real-time monitoring and contextualized health insights to enable proactive and personalized care. Leveraging AI algorithms on smart health data enhances early detection of health trends and supports dynamic treatment adjustments based on a comprehensive view of patient health behavior and environmental factors.
Continuous Health Monitoring Data
Continuous health monitoring data offers real-time insights into patients' physiological status, enhancing the static nature of traditional patient records by providing dynamic, longitudinal datasets. This shift enables proactive health management and personalized interventions, leveraging wearable devices and remote sensors to track vital signs, activity levels, and biometric trends continuously.
Patient record vs Smart health data Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com