Information systems process, store, and manage data through hardware and software, enabling organizations to make informed decisions. Cognitive systems simulate human thought processes by using artificial intelligence and machine learning to interpret data, learn from experiences, and adapt to new information. These systems enhance decision-making by understanding context and providing insights beyond traditional data analysis.
Table of Comparison
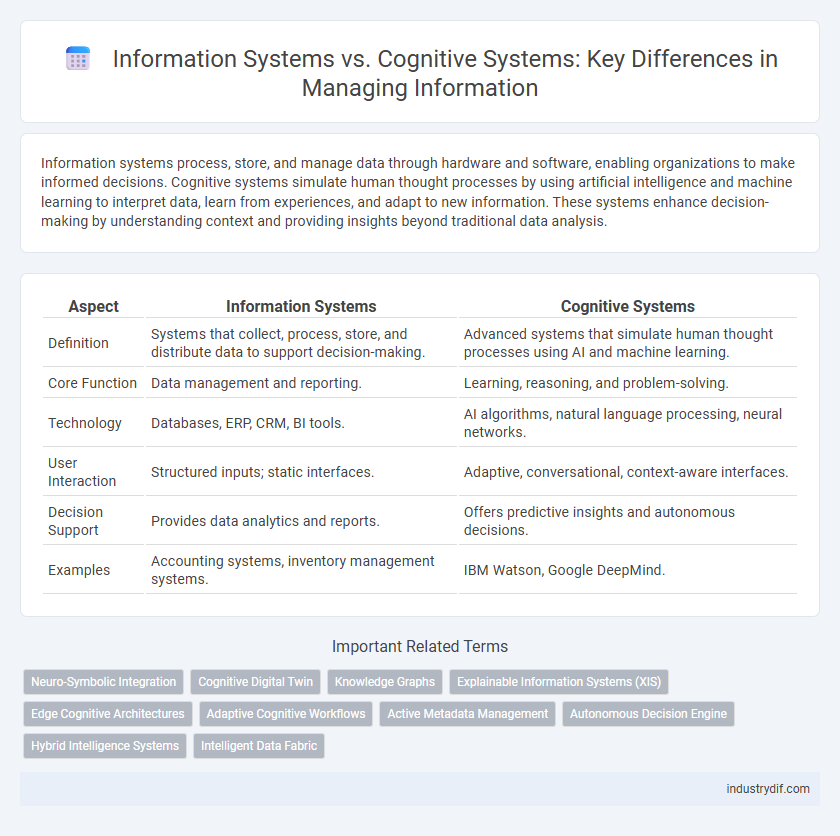
| Aspect | Information Systems | Cognitive Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systems that collect, process, store, and distribute data to support decision-making. | Advanced systems that simulate human thought processes using AI and machine learning. |
| Core Function | Data management and reporting. | Learning, reasoning, and problem-solving. |
| Technology | Databases, ERP, CRM, BI tools. | AI algorithms, natural language processing, neural networks. |
| User Interaction | Structured inputs; static interfaces. | Adaptive, conversational, context-aware interfaces. |
| Decision Support | Provides data analytics and reports. | Offers predictive insights and autonomous decisions. |
| Examples | Accounting systems, inventory management systems. | IBM Watson, Google DeepMind. |
Definition of Information Systems
Information Systems refer to structured frameworks that collect, process, store, and distribute data to support decision-making and organizational operations. These systems integrate hardware, software, data, people, and procedures to manage information effectively within a business environment. By automating workflows and enabling data-driven insights, Information Systems play a critical role in enhancing operational efficiency and strategic planning.
Definition of Cognitive Systems
Cognitive systems refer to advanced computing frameworks designed to simulate human thought processes by integrating artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. Unlike traditional information systems that primarily store and manage data, cognitive systems interpret, analyze, and learn from complex, unstructured data to support decision-making and problem-solving. These systems adapt over time, enhancing their performance through continuous interaction with evolving datasets and user inputs.
Core Components of Information Systems
Information systems consist of core components such as hardware, software, data, people, and processes that interact to collect, process, store, and disseminate information efficiently. Hardware provides the physical infrastructure, while software includes applications and operating systems that manage data and user interactions. Data serves as the foundation for decision-making, supported by skilled personnel and well-defined processes that ensure accurate and timely information flow.
Core Components of Cognitive Systems
Cognitive systems integrate core components such as natural language processing, machine learning, and sensory data interpretation to mimic human thought processes, unlike traditional information systems that primarily focus on data storage, retrieval, and processing. These components enable cognitive systems to understand context, learn from interactions, and adapt over time, driving advancements in artificial intelligence and decision-making. Incorporating knowledge representation and reasoning further distinguishes cognitive systems by allowing them to generate insights and offer nuanced responses.
Key Differences Between Information and Cognitive Systems
Information systems primarily handle the collection, storage, and processing of data using structured hardware and software components to support decision-making and operations. Cognitive systems integrate advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to simulate human thought processes, enabling adaptive learning and problem-solving capabilities. While information systems focus on data management and retrieval, cognitive systems emphasize understanding, reasoning, and autonomous decision-making.
Use Cases in Modern Industries
Information systems streamline data management and operational processes in industries such as finance, healthcare, and retail, enhancing decision-making through structured data analysis. Cognitive systems utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning to interpret unstructured data, enabling advanced applications like predictive maintenance in manufacturing and personalized customer experiences in e-commerce. Both systems integrate to optimize efficiency, improve accuracy, and foster innovation in modern business environments.
Data Processing: Structured vs Unstructured Approaches
Information systems excel at processing structured data by organizing it into predefined schemas, enabling efficient querying and analysis using relational databases and data warehouses. Cognitive systems handle unstructured data such as natural language, images, and videos by leveraging machine learning algorithms and neural networks to interpret context and generate insights. This distinction highlights the complementary roles of structured data management in information systems and adaptive learning in cognitive systems for comprehensive data processing.
Integration of Cognitive Technologies in Information Systems
Information systems increasingly incorporate cognitive technologies such as natural language processing, machine learning, and advanced analytics to enhance decision-making and automate complex tasks. The integration of these cognitive capabilities allows information systems to process unstructured data, recognize patterns, and adapt through learning, improving operational efficiency and user experience. This convergence drives the evolution of intelligent information systems capable of supporting dynamic business environments and real-time insights.
Impact on Business Intelligence and Decision-Making
Information Systems enable structured data collection, storage, and analysis, significantly improving business intelligence by providing accurate, real-time reports and dashboards. Cognitive Systems leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to interpret unstructured data, uncover patterns, and generate predictive insights, driving more proactive and nuanced decision-making. Integrating Cognitive Systems with traditional Information Systems enhances operational efficiency, supports complex problem-solving, and fosters adaptive strategies in dynamic business environments.
Future Trends: Merging Information and Cognitive Systems
Future trends in technology reveal a convergence between Information Systems and Cognitive Systems, driven by advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics. This integration enables enhanced decision-making capabilities, real-time data processing, and adaptive learning mechanisms within enterprise environments. Organizations adopting merged systems experience improved operational efficiency, smarter automation, and predictive insights that transform digital transformation strategies.
Related Important Terms
Neuro-Symbolic Integration
Neuro-symbolic integration combines the strengths of information systems, which excel in data storage and retrieval, with cognitive systems that mimic human reasoning and learning through neural networks; this fusion enhances semantic understanding and decision-making accuracy. By bridging symbolic logic with deep learning models, neuro-symbolic systems improve interpretability and adaptability in complex information processing tasks.
Cognitive Digital Twin
Cognitive Digital Twins leverage advanced AI algorithms and real-time data integration to simulate human cognitive processes, enabling dynamic decision-making and predictive analytics beyond traditional Information Systems. Unlike conventional Information Systems that primarily handle data storage and processing, Cognitive Systems focus on understanding, reasoning, and learning, enhancing digital twin models with adaptive intelligence for complex problem-solving and operational optimization.
Knowledge Graphs
Knowledge Graphs serve as a critical bridge in Information Systems by structuring and linking vast datasets into meaningful relationships, enabling efficient data retrieval and integration. Cognitive Systems leverage Knowledge Graphs to enhance machine understanding and reasoning, transforming raw information into actionable knowledge through semantic context and inferencing capabilities.
Explainable Information Systems (XIS)
Explainable Information Systems (XIS) enhance traditional Information Systems by integrating transparency and interpretability features that enable users to understand and trust the decision-making processes of complex algorithms. Unlike Cognitive Systems, which mimic human cognition for adaptive learning and reasoning, XIS prioritize clarity in data processing and model outcomes to ensure accountability and facilitate informed decision support.
Edge Cognitive Architectures
Edge cognitive architectures integrate advanced machine learning and artificial intelligence capabilities directly within distributed information systems, enabling real-time data processing and decision-making at the network edge. This fusion enhances system autonomy, reduces latency, and improves adaptive responses compared to traditional information systems that primarily rely on centralized processing centers.
Adaptive Cognitive Workflows
Adaptive cognitive workflows enhance information systems by integrating machine learning and artificial intelligence to dynamically adjust processes based on real-time data and user behavior. These systems improve decision-making accuracy and operational efficiency by mimicking human cognitive functions such as learning, reasoning, and problem-solving within automated workflows.
Active Metadata Management
Active Metadata Management in Information Systems enables automated data cataloging, lineage tracking, and real-time governance, enhancing data quality and decision-making efficiency. Cognitive Systems leverage AI-driven active metadata to understand context, infer relationships, and proactively recommend insights, significantly advancing knowledge management and operational intelligence.
Autonomous Decision Engine
Information systems process and manage data through predefined algorithms and structured inputs to support human decision-making, while cognitive systems leverage machine learning and natural language processing to emulate human thought and adapt over time. Autonomous Decision Engines within cognitive systems enable real-time, self-governing decisions by integrating contextual data, predictive analytics, and continuous learning models.
Hybrid Intelligence Systems
Hybrid intelligence systems integrate information systems' data processing capabilities with cognitive systems' adaptive learning and reasoning functions to enhance decision-making efficiency. These systems combine structured data management with human-like cognitive processes, enabling advanced problem-solving and contextual understanding in complex environments.
Intelligent Data Fabric
Intelligent Data Fabric integrates advanced AI algorithms within Information Systems to enhance data management, enabling seamless, real-time data accessibility and analytics across distributed environments. Cognitive Systems harness machine learning and natural language processing to interpret, learn, and make decisions from complex data, complementing Intelligent Data Fabric by providing adaptive insights and automated problem-solving capabilities.
Information Systems vs Cognitive Systems Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com