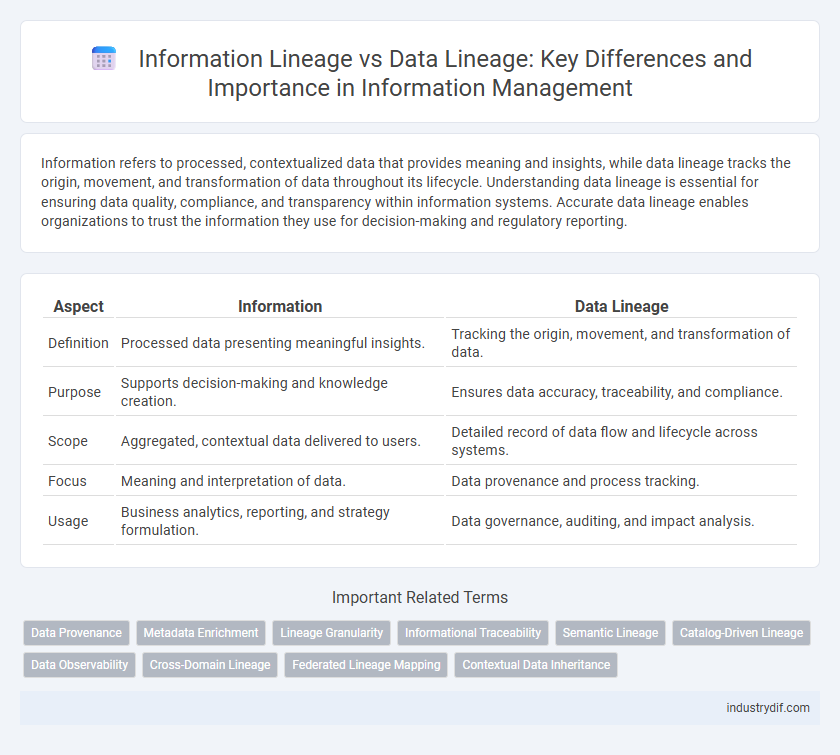
Information refers to processed, contextualized data that provides meaning and insights, while data lineage tracks the origin, movement, and transformation of data throughout its lifecycle. Understanding data lineage is essential for ensuring data quality, compliance, and transparency within information systems. Accurate data lineage enables organizations to trust the information they use for decision-making and regulatory reporting.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Information | Data Lineage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processed data presenting meaningful insights. | Tracking the origin, movement, and transformation of data. |
| Purpose | Supports decision-making and knowledge creation. | Ensures data accuracy, traceability, and compliance. |
| Scope | Aggregated, contextual data delivered to users. | Detailed record of data flow and lifecycle across systems. |
| Focus | Meaning and interpretation of data. | Data provenance and process tracking. |
| Usage | Business analytics, reporting, and strategy formulation. | Data governance, auditing, and impact analysis. |
Understanding Information and Data Lineage
Information lineage refers to the detailed tracking of information flow and transformations from origin to consumption, ensuring data accuracy and compliance. Data lineage focuses on the technical journey of data, capturing how raw data moves through systems, databases, and processes over time. Understanding both information and data lineage is crucial for organizations to enhance data governance, improve transparency, and support regulatory requirements.
Key Differences Between Information and Data Lineage
Information lineage tracks the flow and transformation of data as it evolves into meaningful information, emphasizing context, meaning, and usage. Data lineage strictly maps the origin, movement, and processing of raw data through systems and databases, focusing on data sources and technical processes. Key differences lie in their scope, with information lineage addressing semantic understanding, while data lineage centers on technical data tracking.
Importance of Data Lineage in Information Management
Data lineage is essential in information management as it provides a detailed map of data flow from its origin to its destination, ensuring transparency and traceability. Understanding data lineage improves data quality, enhances compliance with regulatory standards, and supports accurate decision-making by tracing data transformations and usage. Effective data lineage reduces risks related to data breaches and inconsistencies, promoting trust and accountability across information systems.
Role of Information in Data Governance
Information serves as the cornerstone of data governance by providing context, meaning, and relevance to raw data and lineage details. It enables organizations to trace the origin, transformation, and usage of data, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and accountability across all data processes. Effective information management enhances data lineage transparency, supports regulatory requirements, and drives strategic decision-making in data governance frameworks.
How Data Lineage Supports Regulatory Compliance
Data lineage provides a detailed map of data flow from origin to destination, enabling organizations to track and verify data transformations with precision. This transparency ensures adherence to regulatory requirements by facilitating accurate data auditing, impact analysis, and risk management. Maintaining comprehensive data lineage supports compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulations by proving data integrity and accountability.
Information Quality vs. Data Lineage Accuracy
Information quality focuses on the reliability, relevance, and timeliness of data to ensure meaningful insights, whereas data lineage accuracy tracks the precise origin and transformation path of data across systems. High information quality depends on accurate data lineage to validate data provenance and maintain trustworthiness in decision-making processes. Enhancing data lineage accuracy supports improved information quality by enabling effective data governance, auditability, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Impact of Data Lineage on Business Intelligence
Data lineage enhances business intelligence by providing a clear map of data origin, movement, and transformation across systems, enabling more accurate and trustworthy analytics. Businesses leveraging detailed data lineage experience improved decision-making due to increased transparency and data governance, reducing errors and compliance risks. This traceability supports faster issue resolution and optimizes data integration processes, directly impacting operational efficiency and strategic insights.
Best Practices for Managing Information and Data Lineage
Effective management of information and data lineage requires implementing robust metadata management systems that track data origins, transformations, and usage across platforms. Establishing clear governance policies ensures data integrity, compliance, and accountability, while leveraging automation tools enhances lineage accuracy and reduces manual errors. Prioritizing continuous monitoring and validation of lineage maps supports proactive issue detection and fosters trusted data environments.
Challenges in Distinguishing Information from Data Lineage
Distinguishing information from data lineage presents significant challenges due to their overlapping attributes in data governance frameworks. Information refers to processed, meaningful content, whereas data lineage tracks the origin, movement, and transformation of raw data through systems, complicating clear separation. The complexity of modern data ecosystems, involving multiple sources and transformations, exacerbates difficulties in accurately categorizing lineage metadata versus actionable information insights.
Future Trends in Information and Data Lineage Management
Future trends in information and data lineage management emphasize the integration of AI and machine learning to enhance automated tracking and accuracy. Emerging technologies like blockchain offer immutable records for improved data traceability and compliance. Increasing adoption of real-time data lineage solutions supports dynamic analysis and faster decision-making in complex data ecosystems.
Related Important Terms
Data Provenance
Data provenance captures the origin and history of data by tracing its lineage through various transformations, ensuring accuracy, trustworthiness, and compliance in data management. Unlike basic data lineage, which maps data flow, data provenance provides detailed metadata about the creation, modification, and usage of data across systems.
Metadata Enrichment
Metadata enrichment enhances data lineage by embedding detailed context such as data source, transformation processes, and usage history, which improves traceability and impact analysis. Differentiating information from data lineage hinges on metadata's role in enriching raw data with meaning, enabling better governance and analytics.
Lineage Granularity
Lineage granularity in data lineage refers to the level of detail at which the movement and transformation of data are tracked, ranging from coarse-grained sources like entire databases to fine-grained elements such as individual columns or records. Information lineage requires finer granularity to ensure precise traceability and impact analysis, enabling accurate tracking of data origin, processing steps, and usage across complex systems.
Informational Traceability
Informational traceability ensures comprehensive tracking of information flow across systems, highlighting the transformation from raw data to actionable insights. Unlike data lineage, which maps the origin and movement of data, informational traceability emphasizes the contextual understanding and semantic integrity throughout the information lifecycle.
Semantic Lineage
Semantic lineage tracks the evolution and transformation of data by capturing the meaning and context changes throughout its lifecycle, enabling better data governance and trust. Unlike traditional data lineage that focuses on the technical flow of data, semantic lineage emphasizes understanding data definitions, relationships, and business logic for enhanced analytics and decision-making.
Catalog-Driven Lineage
Catalog-driven lineage leverages metadata catalogs to automatically track the origin, movement, and transformation of data within an organization, enhancing data governance and compliance. This approach contrasts with traditional data lineage by providing a unified, semantic-rich view that integrates both information and data flow details for more accurate impact analysis and auditing.
Data Observability
Data lineage tracks the origin and movement of data, enabling transparency and compliance, while data observability provides real-time insights into the health and quality of data pipelines for proactive issue detection. Integrating data observability with lineage enhances the ability to monitor data integrity, detect anomalies, and maintain reliable information flow across complex systems.
Cross-Domain Lineage
Cross-domain lineage enables comprehensive tracking of data flow and transformations across diverse systems and organizational boundaries, ensuring accurate impact analysis and regulatory compliance. This integrated approach enhances data governance by uncovering relationships between disparate data sources, improving transparency and decision-making in complex information ecosystems.
Federated Lineage Mapping
Federated Lineage Mapping integrates diverse data sources across multiple systems to create a unified view of information flow and transformation, enhancing traceability and governance beyond traditional data lineage. This approach enables organizations to track data provenance and impact at an enterprise scale, supporting compliance, auditability, and decision-making processes with comprehensive semantic context.
Contextual Data Inheritance
Information lineage emphasizes the transformation and context of data as it flows through systems, highlighting contextual data inheritance where attributes and meaning evolve based on usage and environment. Data lineage focuses primarily on tracking the origin and movement of raw data elements without inherently capturing the dynamic context shaping the information's interpretation.
Information vs Data Lineage Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com