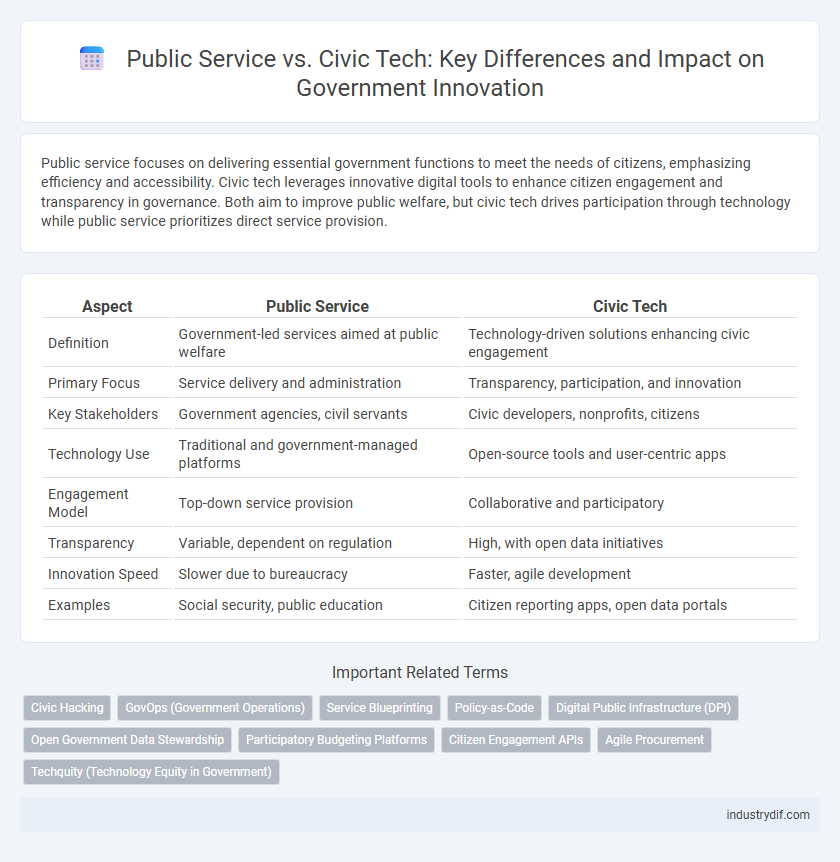
Public service focuses on delivering essential government functions to meet the needs of citizens, emphasizing efficiency and accessibility. Civic tech leverages innovative digital tools to enhance citizen engagement and transparency in governance. Both aim to improve public welfare, but civic tech drives participation through technology while public service prioritizes direct service provision.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Public Service | Civic Tech |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government-led services aimed at public welfare | Technology-driven solutions enhancing civic engagement |
| Primary Focus | Service delivery and administration | Transparency, participation, and innovation |
| Key Stakeholders | Government agencies, civil servants | Civic developers, nonprofits, citizens |
| Technology Use | Traditional and government-managed platforms | Open-source tools and user-centric apps |
| Engagement Model | Top-down service provision | Collaborative and participatory |
| Transparency | Variable, dependent on regulation | High, with open data initiatives |
| Innovation Speed | Slower due to bureaucracy | Faster, agile development |
| Examples | Social security, public education | Citizen reporting apps, open data portals |
Defining Public Service in the Modern Era
Public service in the modern era encompasses government and nonprofit initiatives focused on delivering essential services that improve societal well-being, such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. Civic tech leverages digital tools and platforms to enhance public service efficiency, transparency, and citizen engagement. Defining public service today involves integrating traditional governance with innovative technologies to create more responsive and inclusive communities.
What Is Civic Tech? An Industry Overview
Civic tech refers to technology designed to enhance public engagement, government transparency, and community participation by leveraging digital tools like open data platforms, mobile apps, and social media. Unlike traditional public service, which relies on bureaucratic systems and offline methods, civic tech fosters collaborative problem-solving and real-time communication between citizens and public institutions. Key players in the civic tech industry include non-profits, startups, and government agencies developing solutions to improve election monitoring, service delivery, and policy advocacy.
Key Differences Between Public Service and Civic Tech
Public service primarily involves government-run programs and agencies delivering essential services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure, governed by legal frameworks and bureaucratic processes. Civic tech leverages innovative digital tools and platforms to enhance citizen engagement, transparency, and participation in governance, often developed by nonprofits or private sectors. The key difference lies in public service's direct service provision role versus civic tech's focus on enabling public interaction and improving government accountability through technology.
Historical Evolution: Public Service and Civic Tech
Public service has evolved over centuries as government institutions expanded to meet societal needs, emphasizing bureaucratic efficiency and regulatory frameworks. Civic tech emerged more recently with digital innovations that empower citizens through transparency, participation, and data-driven decision-making tools. The historical shift reflects a transition from top-down public service delivery to interactive, technology-enabled civic engagement platforms.
Stakeholders in Public Service vs. Civic Tech
Public service stakeholders primarily include government agencies, elected officials, and citizens who rely on traditional bureaucratic systems for service delivery. Civic tech stakeholders encompass technology developers, nonprofit organizations, community activists, and users who collaborate to create digital tools that enhance transparency, participation, and accountability. Both sectors share a focus on improving public outcomes but differ in their engagement models and technological integration.
Impact on Communities: Comparing Outcomes
Public service traditionally delivers essential support and infrastructure directly, ensuring reliable access to health, education, and safety for communities. Civic tech leverages digital tools and platforms to enhance citizen engagement, transparency, and real-time problem-solving, fostering more participatory governance. Combined, these approaches improve community outcomes by integrating efficient service delivery with innovative public involvement.
Technology Adoption in Public Service and Civic Tech
Technology adoption in public service emphasizes integrating legacy systems with modern solutions to enhance efficiency and transparency in government operations. Civic tech focuses on user-centric applications that empower citizens through open data platforms, real-time feedback tools, and participatory decision-making processes. Both sectors prioritize scalable technology frameworks, but public service often deals with regulatory compliance while civic tech drives innovation through community engagement.
Collaboration Models: Government, Nonprofits, and Civic Tech
Collaboration models between government, nonprofits, and civic tech organizations enhance public service delivery by integrating technological innovation with community-driven approaches. Governments provide regulatory frameworks and resources, nonprofits contribute grassroots expertise and social capital, while civic tech leverages digital tools for transparency and citizen engagement. This tripartite partnership fosters efficient problem-solving, data-driven decision-making, and inclusive participation in public sector initiatives.
Challenges and Opportunities Facing Both Sectors
Public service faces challenges such as bureaucratic inertia, limited funding, and difficulties in adopting digital innovations, while civic tech struggles with data privacy concerns, user engagement, and scalability issues. Both sectors have opportunities to enhance transparency, improve citizen participation, and leverage emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and blockchain for better service delivery. Collaboration between public institutions and civic tech developers can drive more inclusive, efficient, and responsive governance models.
Future Trends: The Intersection of Public Service and Civic Tech
The future of public service is increasingly shaped by the integration of civic technology, leveraging AI-driven platforms, blockchain, and IoT to enhance transparency, citizen engagement, and service delivery. Emerging trends emphasize personalized digital interfaces and real-time data analytics to optimize resource allocation and policy implementation. This convergence fosters collaborative governance models that empower communities through accessible, data-informed decision-making tools.
Related Important Terms
Civic Hacking
Civic hacking leverages open data and technology to improve government transparency, accountability, and citizen engagement, contrasting traditional public service that often relies on bureaucratic processes. By fostering collaborative problem-solving and innovation, civic hacking enhances public services through community-driven digital tools and platforms.
GovOps (Government Operations)
GovOps enhances public service efficiency by integrating civic tech solutions that streamline government operations, improve data transparency, and facilitate citizen engagement. These digital tools enable real-time process automation and cross-agency collaboration, transforming traditional bureaucratic workflows into agile, user-centered services.
Service Blueprinting
Service blueprinting in public service maps customer interactions and internal processes to enhance service delivery efficiency, transparency, and user satisfaction. In civic tech, service blueprinting integrates digital tools to co-create solutions with citizens, fostering innovation and real-time feedback mechanisms.
Policy-as-Code
Policy-as-Code transforms public service by embedding legal and regulatory frameworks directly into software, enabling automated compliance and real-time policy updates. Civic tech leverages this approach to enhance transparency, streamline government operations, and empower citizen participation through programmable, enforceable policy rules.
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) serves as the foundational technology framework enabling efficient public services and empowering civic tech innovations to enhance citizen engagement. By integrating secure, interoperable digital platforms, DPI bridges government resources with community-driven solutions, optimizing service delivery and promoting transparent governance.
Open Government Data Stewardship
Open Government Data Stewardship enhances transparency and accountability by systematically managing and publishing public service datasets, enabling civic tech applications to innovate user-centric solutions that address community needs effectively. Public service institutions ensure data quality and accessibility while civic tech leverages this open data to foster citizen engagement, streamline services, and promote participatory governance.
Participatory Budgeting Platforms
Participatory budgeting platforms enable citizens to directly influence government spending, enhancing transparency and accountability in public service delivery. These digital tools leverage civic technology to facilitate collaborative decision-making, promoting active community engagement and more equitable allocation of public resources.
Citizen Engagement APIs
Citizen Engagement APIs enable seamless interaction between governments and residents by providing real-time access to public services, enhancing transparency and responsiveness. These APIs facilitate data exchange, streamline feedback mechanisms, and empower citizens to actively participate in policy-making and community development.
Agile Procurement
Agile procurement in public service enables faster, more flexible acquisition processes that better align with rapidly evolving civic tech solutions, enhancing transparency and citizen engagement. This approach prioritizes iterative development and stakeholder collaboration, driving efficient delivery of innovative technologies tailored to public needs.
Techquity (Technology Equity in Government)
Techquity in government bridges public service and civic tech by ensuring equitable access to digital tools and platforms, enhancing inclusivity and transparency. Prioritizing technology equity addresses digital divides, empowering underserved communities to participate fully in civic processes and benefit from government services.
public service vs civic tech Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com