Residential real estate offers private, long-term ownership or rental options suited for individuals or families seeking personal space and stability. Co-living emphasizes shared living environments with flexible lease terms, fostering community and affordability in urban areas. Choosing between these options depends on lifestyle preferences, budget constraints, and social interaction priorities.
Table of Comparison
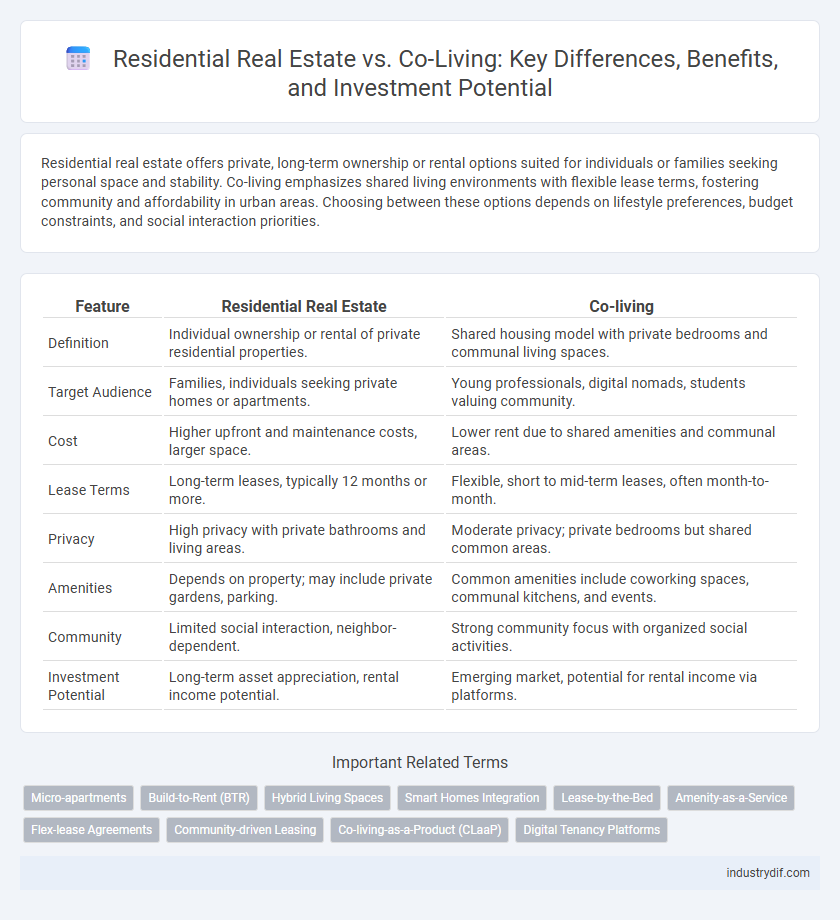
| Feature | Residential Real Estate | Co-living |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual ownership or rental of private residential properties. | Shared housing model with private bedrooms and communal living spaces. |
| Target Audience | Families, individuals seeking private homes or apartments. | Young professionals, digital nomads, students valuing community. |
| Cost | Higher upfront and maintenance costs, larger space. | Lower rent due to shared amenities and communal areas. |
| Lease Terms | Long-term leases, typically 12 months or more. | Flexible, short to mid-term leases, often month-to-month. |
| Privacy | High privacy with private bathrooms and living areas. | Moderate privacy; private bedrooms but shared common areas. |
| Amenities | Depends on property; may include private gardens, parking. | Common amenities include coworking spaces, communal kitchens, and events. |
| Community | Limited social interaction, neighbor-dependent. | Strong community focus with organized social activities. |
| Investment Potential | Long-term asset appreciation, rental income potential. | Emerging market, potential for rental income via platforms. |
Understanding Residential Real Estate: Key Features
Residential real estate typically involves properties designed for individual or family living, such as single-family homes, townhouses, and condominiums, emphasizing privacy and long-term ownership. Key features include personalized space, greater control over property modifications, and investment potential through appreciation. In contrast, co-living spaces prioritize shared amenities, flexible lease terms, and community-focused living, appealing to individuals seeking affordability and social interaction without the commitment of traditional homeownership.
What is Co-living? Definition and Core Concepts
Co-living is a modern residential real estate model where individuals rent private bedrooms within a shared living space, promoting community and affordability through shared amenities like kitchens, living areas, and coworking spaces. This concept emphasizes social interaction, flexibility in lease terms, and cost-efficiency, targeting urban professionals, students, and remote workers seeking convenience and connectivity. Unlike traditional residential real estate with standalone units, co-living combines private and communal lifestyles to meet evolving housing demands in high-density cities.
Differences in Living Arrangements
Residential real estate typically involves private ownership or long-term leasing of individual homes or apartments, offering residents full control over their living space and privacy. Co-living arrangements provide shared living environments with private bedrooms but communal kitchens and social areas, promoting community interaction and cost-sharing among occupants. This difference in living arrangements caters to distinct lifestyle preferences, with residential real estate appealing to those seeking independence and co-living attracting individuals prioritizing affordability and social connectivity.
Ownership vs. Renting Models
Residential real estate traditionally emphasizes ownership, granting homeowners equity, tax benefits, and long-term investment stability. Co-living models prioritize renting, offering flexible lease terms, shared amenities, and reduced upfront costs without property maintenance responsibilities. The distinction between ownership and renting influences financial commitment, property control, and lifestyle flexibility in housing choices.
Community and Social Aspects Compared
Residential real estate traditionally offers private living spaces prioritizing individual or family privacy, while co-living emphasizes shared amenities and communal areas designed to foster interaction and strong social bonds among residents. Co-living communities often feature organized events and collaborative spaces that enhance networking and collective activities, contrasting with the more isolated nature of conventional housing. This social architecture in co-living promotes a supportive environment beneficial for young professionals and those seeking active community engagement.
Cost Analysis: Residential vs. Co-living
Residential real estate typically involves higher upfront costs, including down payments, property taxes, and maintenance expenses, while co-living offers a cost-effective alternative with shared utilities and amenities lowering monthly payments. Renters in co-living spaces benefit from flexible lease terms and reduced individual financial burdens, making it ideal for urban professionals and students. Evaluating long-term investment potential, traditional homeownership builds equity over time, whereas co-living prioritizes affordability and community without property ownership benefits.
Target Demographics and Market Trends
Residential real estate primarily targets families, long-term renters, and homeowners seeking stability and privacy, while co-living spaces appeal to young professionals, digital nomads, and millennials prioritizing affordability and community. Market trends show increasing demand for flexible, short-term leases in co-living due to urbanization and remote work growth, contrasting with the more traditional, investment-driven residential market. Developers are adapting by incorporating shared amenities and modular designs in co-living to attract tech-savvy, socially connected demographics.
Amenities and Lifestyle Offerings
Residential real estate typically offers private amenities such as spacious kitchens, personal gardens, and dedicated parking, catering to homeowners seeking autonomy and long-term investment. Co-living spaces emphasize shared amenities like communal lounges, coworking areas, and organized social events, fostering community engagement and flexibility. The lifestyle in residential properties favors privacy and permanence, whereas co-living promotes social interaction and convenience for transient or urban professionals.
Investment Potential and ROI
Residential real estate offers stable long-term appreciation and predictable rental income, appealing to investors seeking traditional asset growth and lower management complexity. Co-living spaces generate higher rental yields due to shared amenities and flexible leasing, attracting younger demographics and maximizing space efficiency in urban markets. Enhanced cash flow potential and faster occupancy rates make co-living an innovative alternative with strong ROI prospects, especially in high-demand metropolitan areas.
Future Outlook: Residential Real Estate vs. Co-living
Residential real estate remains a cornerstone of long-term wealth building with steady appreciation driven by demographic trends and urban expansion. Co-living models are rapidly gaining traction, particularly among millennials and Gen Z, due to affordability, flexibility, and community-oriented lifestyles in high-demand urban centers. Technology integration and changing social dynamics suggest co-living will increasingly complement traditional residential real estate, reshaping urban living solutions over the next decade.
Related Important Terms
Micro-apartments
Micro-apartments in residential real estate offer compact, affordable living spaces tailored for individual urban dwellers, emphasizing privacy and personal ownership. Co-living spaces, however, prioritize shared amenities and social interaction, appealing to residents seeking community-oriented living within micro-apartment layouts that optimize space efficiency.
Build-to-Rent (BTR)
Build-to-Rent (BTR) developments in residential real estate focus on purpose-built properties designed specifically for long-term rental, contrasting traditional co-living spaces that emphasize shared amenities and communal living. BTR offers private, self-contained units with professional management, catering to renters seeking stability and individual space, while co-living targets affordability and social interaction through shared environments.
Hybrid Living Spaces
Hybrid living spaces blend traditional residential real estate with co-living concepts to maximize flexibility, community engagement, and cost-efficiency for urban dwellers. These innovative environments incorporate private living areas alongside shared amenities, fostering social interaction while providing personal privacy.
Smart Homes Integration
Residential real estate increasingly incorporates smart home technologies such as automated lighting, security systems, and energy management, enhancing convenience and efficiency for individual homeowners. Co-living spaces leverage smart home integration to optimize shared utilities, improve community safety, and enable seamless access controls, promoting a tech-enabled communal lifestyle.
Lease-by-the-Bed
Lease-by-the-bed in co-living spaces offers flexibility and affordability compared to traditional residential real estate leases, which typically require committing to an entire unit. This model appeals to urban professionals and students seeking individual leases within shared housing, optimizing cost-efficiency and community living.
Amenity-as-a-Service
Residential real estate traditionally offers fixed amenities included in purchase or rent, whereas co-living spaces leverage Amenity-as-a-Service models to provide flexible, on-demand access to premium services such as housekeeping, wellness programs, and community events. This shift enhances resident experience by adapting amenities to individual needs, driving higher satisfaction and fostering a sense of community within shared living environments.
Flex-lease Agreements
Flex-lease agreements in residential real estate offer traditional long-term rental stability, whereas co-living spaces provide flexible, short-term leases designed for communal living and adaptability to changing tenant needs. This flexibility in co-living attracts young professionals and remote workers seeking affordability and convenience without the commitment of standard lease terms.
Community-driven Leasing
Community-driven leasing in co-living spaces fosters stronger social connections and shared amenities, enhancing resident engagement beyond traditional residential real estate models where individual leasing dominates. This approach optimizes occupancy rates and tenant satisfaction by promoting collaborative living environments that appeal to millennials and urban professionals seeking flexible, community-oriented housing solutions.
Co-living-as-a-Product (CLaaP)
Co-living-as-a-Product (CLaaP) redefines residential real estate by offering modular, fully furnished shared living spaces with integrated community amenities and flexible lease terms, targeting urban professionals and millennials seeking affordability and social connectivity. This innovative housing model leverages technology-driven management and scalable design to optimize occupancy rates and enhance tenant experience compared to traditional single-family or apartment living.
Digital Tenancy Platforms
Digital tenancy platforms streamline property management in both residential real estate and co-living spaces by enabling seamless online lease agreements, rent payments, and maintenance requests. These platforms enhance tenant engagement and operational efficiency, addressing the distinct demands of traditional residential tenants and the more dynamic, community-focused co-living residents.
Residential real estate vs Co-living Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com