Suburban living offers spacious homes and serene environments, ideal for families seeking privacy and larger properties. In contrast, the 15-minute city concept prioritizes walkability and proximity to amenities, promoting sustainable urban lifestyles with reduced reliance on cars. Choosing between these options depends on preferences for space versus convenience and community connectivity.
Table of Comparison
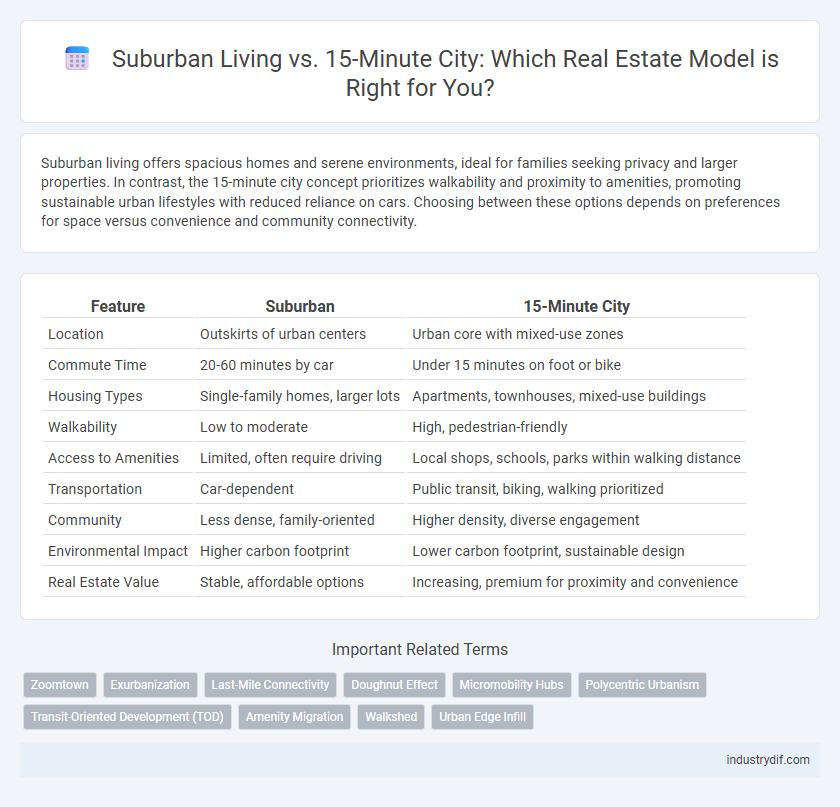
| Feature | Suburban | 15-Minute City |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Outskirts of urban centers | Urban core with mixed-use zones |
| Commute Time | 20-60 minutes by car | Under 15 minutes on foot or bike |
| Housing Types | Single-family homes, larger lots | Apartments, townhouses, mixed-use buildings |
| Walkability | Low to moderate | High, pedestrian-friendly |
| Access to Amenities | Limited, often require driving | Local shops, schools, parks within walking distance |
| Transportation | Car-dependent | Public transit, biking, walking prioritized |
| Community | Less dense, family-oriented | Higher density, diverse engagement |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint | Lower carbon footprint, sustainable design |
| Real Estate Value | Stable, affordable options | Increasing, premium for proximity and convenience |
Urban Planning Paradigms: Suburban vs 15-Minute City
Urban planning paradigms contrast sharply between suburban sprawl and the 15-minute city concept, with suburbs emphasizing low-density, car-dependent living and single-use zoning. The 15-minute city promotes mixed-use development, walkability, and proximity to essential services within a 15-minute radius, reducing reliance on automobiles. This shift aims to enhance sustainability, improve quality of life, and support local economies in real estate development.
Housing Density and Land Use Efficiency
Housing density in suburban areas typically features lower-density, single-family homes with larger lots, resulting in less efficient land use compared to 15-minute cities. The 15-minute city model emphasizes mixed-use developments and higher-density housing to maximize land use efficiency while supporting walkability and access to amenities within a short distance. This approach reduces urban sprawl and promotes sustainable living by integrating residential, commercial, and recreational spaces in compact neighborhoods.
Mobility and Transportation Networks
Suburban areas typically rely on personal vehicles due to limited public transit options, resulting in longer commute times and increased traffic congestion. In contrast, 15-minute cities prioritize dense, mixed-use developments with extensive public transportation networks, enabling residents to access work, shopping, and recreation within a short walk or bike ride. Efficient mobility in 15-minute cities reduces carbon emissions and enhances urban livability by minimizing dependence on cars.
Mixed-Use Development Comparisons
Mixed-use developments in suburban areas typically feature larger plots with separated residential, commercial, and recreational zones, promoting car dependency and lower walkability. In contrast, 15-minute cities integrate diverse amenities within close proximity, combining residential, retail, offices, and green spaces to enhance accessibility and reduce the need for vehicular travel. This compact urban planning model fosters vibrant, walkable neighborhoods that support local economies and sustainable living.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Suburban developments typically involve higher car dependency and urban sprawl, leading to increased carbon emissions and reduced green spaces. In contrast, 15-minute cities emphasize walkability, mixed-use areas, and accessible public transit, significantly lowering energy consumption and promoting local biodiversity. Sustainable real estate strategies prioritize compact, efficient land use and renewable energy integration to minimize environmental footprints.
Lifestyle and Community Engagement
Suburban living offers spacious homes and tranquil neighborhoods, favoring family-oriented lifestyles with access to schools and parks, while often requiring car travel for work and errands. The 15-minute city concept emphasizes walkability, mixed-use development, and local amenities within a short distance, fostering stronger community engagement and reducing reliance on vehicles. Residents in 15-minute cities experience enhanced social interaction and convenience, promoting sustainable urban living and active participation in local events.
Real Estate Values and Investment Trends
Real estate values in suburban areas often reflect larger property sizes and proximity to natural spaces, appealing to families seeking spacious homes and long-term growth potential. In contrast, 15-minute city developments prioritize walkability and mixed-use amenities, driving higher demand and elevated prices in compact urban neighborhoods. Investment trends show a growing preference for 15-minute city projects due to their sustainable design and strong rental yield prospects, though suburban markets remain attractive for affordable housing and future expansion opportunities.
Infrastructure and Public Services Accessibility
Suburban areas often feature larger homes and more green spaces but typically require reliance on personal vehicles due to limited public transit options. In contrast, 15-minute cities prioritize dense infrastructure with essential services, shops, and public transit all accessible within a short walk or bike ride. This urban design enhances accessibility to healthcare, education, and recreational facilities while reducing commute times and promoting sustainable living.
Zoning Regulations and Policy Implications
Zoning regulations significantly shape the development of suburban areas and 15-minute cities, with suburban zones typically emphasizing single-family residential lots and separated land uses, while 15-minute cities promote mixed-use zoning to enhance walkability and reduce commute times. Policy implications for suburbs often include challenges like urban sprawl and increased car dependency, whereas 15-minute city policies focus on sustainability, local economic growth, and improved public transit infrastructure. Effective urban planning must balance these zoning regulations to foster equitable, accessible, and environmentally friendly communities.
Future Trends in Residential Demand
Future trends in residential demand highlight a shift towards 15-minute cities, where residents prioritize walkability, mixed-use developments, and easy access to amenities within a short distance. Suburban areas will continue to attract families seeking larger homes and more green space but must adapt by integrating transit options and local services to remain competitive. Urban planners increasingly emphasize sustainable development and smart infrastructure to meet evolving preferences for convenience and quality of life in both environments.
Related Important Terms
Zoomtown
Zoomtowns have gained popularity as suburban communities that offer a blend of affordable housing, green spaces, and proximity to urban job centers, bridging the gap between traditional suburbs and 15-minute cities. Unlike the compact 15-minute city model designed for walkability and immediate access to amenities, Zoomtowns prioritize car-friendly infrastructure while gradually incorporating mixed-use developments to enhance local accessibility and community engagement.
Exurbanization
Exurbanization drives the expansion of residential developments beyond suburban boundaries, offering larger properties and natural surroundings contrasted with the compact, walkable design of 15-minute cities that prioritize proximity to amenities and reduce car dependency. Real estate market trends reveal rising demand for exurban homes as remote work enables residents to seek affordable, spacious living outside traditional suburban areas while 15-minute cities attract urban buyers focused on convenience and sustainable lifestyles.
Last-Mile Connectivity
Last-mile connectivity in suburban areas often relies heavily on personal vehicles or limited public transit options, resulting in longer commute times and higher transportation costs. In contrast, 15-minute cities prioritize walkability, cycling infrastructure, and efficient public transit, enabling residents to access daily amenities quickly and reducing reliance on cars.
Doughnut Effect
The Doughnut Effect describes the urban trend where populations and amenities concentrate in suburban rings while city centers decline, challenging the compact design of 15-minute cities that promote walkability and mixed-use developments. Suburban areas often prioritize longer commutes and car dependency, whereas 15-minute cities aim to reduce carbon footprints by integrating residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within a short distance.
Micromobility Hubs
Micromobility hubs in suburban areas tend to prioritize car parking and limited bike-sharing stations, whereas 15-minute cities integrate dense networks of e-scooters, bike shares, and pedestrian pathways to facilitate seamless last-mile connectivity. These hubs in 15-minute cities enhance accessibility to essential services within a short radius, reducing reliance on private vehicles and promoting sustainable urban mobility.
Polycentric Urbanism
Polycentric urbanism enhances suburban living by creating multiple, well-connected hubs within a 15-minute city framework, promoting accessibility to amenities and reducing dependence on central urban cores. This approach balances real estate development by integrating residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, fostering sustainable growth and improving quality of life.
Transit-Oriented Development (TOD)
Transit-Oriented Development (TOD) in suburban areas emphasizes creating walkable, mixed-use neighborhoods centered around public transit hubs, reducing car dependency and promoting sustainable growth. In contrast, 15-Minute City models integrate diverse amenities within a short walk or bike ride, prioritizing accessibility and community cohesion while leveraging efficient transit links to connect broader urban regions.
Amenity Migration
Amenity migration drives homebuyers to prioritize access to essential services and recreational facilities, making 15-minute cities with walkable neighborhoods and dense local amenities more attractive compared to sprawling suburban areas. Suburban developments often lack this concentration of amenities, prompting residents to rely heavily on cars, whereas 15-minute cities reduce commute times and enhance quality of life by integrating housing, work, and leisure spaces within close proximity.
Walkshed
The walkshed in suburban areas typically spans larger distances due to lower population density and car-dependent infrastructure, limiting access to amenities within a 15-minute walk. In contrast, 15-minute cities prioritize dense, mixed-use development where essential services and recreational spaces are accessible within a compact walkshed, enhancing walkability and reducing reliance on automobiles.
Urban Edge Infill
Urban edge infill developments maximize land use efficiency by revitalizing underutilized suburban spaces near city borders, promoting walkability and mixed-use environments typical of 15-minute cities. This approach reduces urban sprawl while enhancing access to amenities, public transit, and green spaces within a short distance, aligning with sustainable real estate trends.
Suburban vs 15-Minute City Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com