Deposit renting requires tenants to pay a security amount upfront, often equivalent to one or two months' rent, which can be refundable at the end of the lease if no damages occur. Deposit-free renting eliminates this initial financial barrier by offering alternative protections like insurance or third-party guarantees, making it easier for tenants to move in without a large sum of money. Choosing between deposit and deposit-free options depends on balancing upfront costs with long-term security and convenience.
Table of Comparison
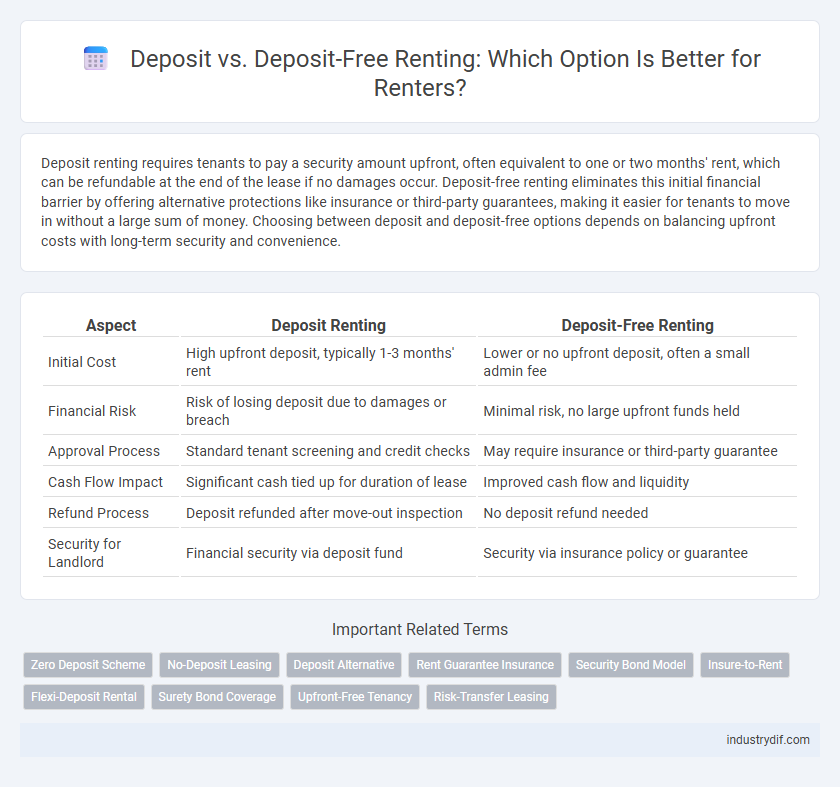
| Aspect | Deposit Renting | Deposit-Free Renting |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | High upfront deposit, typically 1-3 months' rent | Lower or no upfront deposit, often a small admin fee |
| Financial Risk | Risk of losing deposit due to damages or breach | Minimal risk, no large upfront funds held |
| Approval Process | Standard tenant screening and credit checks | May require insurance or third-party guarantee |
| Cash Flow Impact | Significant cash tied up for duration of lease | Improved cash flow and liquidity |
| Refund Process | Deposit refunded after move-out inspection | No deposit refund needed |
| Security for Landlord | Financial security via deposit fund | Security via insurance policy or guarantee |
Introduction to Deposit and Deposit-Free Renting
Deposit renting requires tenants to pay a security deposit upfront, typically equivalent to one or two months' rent, which protects landlords against damages or unpaid rent. Deposit-free renting offers an alternative by allowing renters to move in without a large upfront payment, often using insurance or guarantor services to secure the agreement. This option increases affordability and accessibility for renters while ensuring landlords have financial protection.
Traditional Rental Deposits: How They Work
Traditional rental deposits typically require tenants to pay a security amount upfront, often equivalent to one or two months' rent, held by the landlord to cover potential damages or unpaid rent. This deposit is refundable at the end of the lease term, provided the property is returned in good condition. Landlords use this financial safeguard to mitigate risks associated with tenant defaults and property damage.
What Is Deposit-Free Renting?
Deposit-free renting allows tenants to move in without paying a traditional security deposit, typically by purchasing a low-cost insurance policy or bond that protects landlords against potential damages or unpaid rent. This method reduces upfront costs for renters while providing landlords with financial security similar to that of a standard deposit. By eliminating the need to freeze large sums of money, deposit-free renting increases affordability and accessibility for tenants.
Key Differences Between Deposit and Deposit-Free Models
Deposit renting requires tenants to pay a security deposit upfront, typically equivalent to one or two months' rent, which is refundable upon lease termination if no damages occur. Deposit-free renting replaces this upfront cost with alternative protections, such as insurance or a guarantee fee, reducing initial financial burden for tenants. The key difference lies in financial risk allocation: traditional deposits hold tenant funds, while deposit-free models shift risk management to third-party providers or landlords.
Benefits of Deposit-Free Renting for Tenants
Deposit-free renting offers tenants increased financial flexibility by eliminating large upfront security deposits, allowing for easier budget management and quicker move-ins. Tenants benefit from reduced financial risk since they do not lose a deposit to potential damages or disputes at the end of the tenancy. This option also streamlines the rental process, enhancing accessibility for tenants with limited savings or those seeking more affordable housing solutions.
Advantages of Traditional Deposits for Landlords
Traditional deposits offer landlords financial security by covering potential damages and unpaid rent, reducing the risk of financial loss. They provide a tangible assurance that tenants are committed to maintaining the property, facilitating smoother dispute resolution. This upfront security enhances landlords' confidence in tenant reliability and property preservation.
Risks and Considerations: Deposit vs Deposit-Free
Deposit renting requires tenants to provide a security deposit, typically equivalent to one to two months' rent, which protects landlords against damages and unpaid rent but can pose a financial burden for tenants upfront. Deposit-free renting often involves third-party insurance or guarantees that shift the risk from tenants to specialized companies, reducing the initial payment barrier but potentially leading to higher overall costs or limited coverage in case of disputes. Tenants must carefully evaluate financial flexibility, the extent of coverage offered, and possible long-term expenses when choosing between traditional deposit and deposit-free rental agreements.
Cost Implications: Financial Impact on Renters
Deposit renting often requires upfront cash equivalent to several weeks' rent, creating a significant financial burden for tenants. Deposit-free renting typically involves a smaller fee or insurance premium, reducing immediate costs but potentially increasing overall expense if claims arise. Renters must weigh the upfront affordability against long-term financial risk when choosing between these options.
Legal Protections and Compliance Issues
Deposit renting requires landlords to comply with strict legal protections such as tenancy deposit schemes that safeguard tenant funds and facilitate dispute resolution. Deposit-free renting often uses insurance guarantees, which may lack equivalent regulatory oversight, potentially exposing tenants to less legal protection in case of disagreements. Understanding the compliance frameworks and tenant rights in both options is essential to ensure security and fairness in rental agreements.
Choosing the Right Option: Deposit or Deposit-Free Renting
Choosing between a traditional rental deposit and deposit-free renting depends on your financial flexibility and rental history. A standard deposit typically requires upfront payment equal to one or two months' rent, providing landlords security against damages or unpaid rent. Deposit-free renting offers upfront insurance alternatives that reduce initial costs but may involve ongoing fees or eligibility criteria, making it essential to evaluate your budget and risk tolerance before deciding.
Related Important Terms
Zero Deposit Scheme
The Zero Deposit Scheme offers renters a cost-effective alternative by replacing traditional cash deposits with a secure, non-refundable fee, allowing immediate move-in without upfront large sums. This scheme reduces the financial barrier for tenants while providing landlords with comparable protection against damages and unpaid rent through insurance-backed guarantees.
No-Deposit Leasing
No-deposit leasing offers tenants the advantage of moving in without upfront security payments, making rental properties more accessible and reducing initial financial barriers. This approach often includes alternative risk management strategies such as insurance policies or higher monthly fees, providing landlords with protection while enhancing tenant flexibility.
Deposit Alternative
Deposit alternatives offer tenants flexible options by replacing traditional security deposits with upfront fees or insurance policies, easing initial financial burdens during rental agreements. These solutions protect landlords against damages or missed payments while enabling renters to secure properties without large cash deposits.
Rent Guarantee Insurance
Rent Guarantee Insurance offers tenants an alternative to traditional cash deposits by protecting landlords against unpaid rent without requiring upfront deposit payments, enhancing rental affordability and cash flow flexibility. This insurance model reduces financial barriers for renters while ensuring landlords receive coverage equivalent to conventional deposits.
Security Bond Model
Security bond models in rental agreements require tenants to provide a refundable deposit, typically equivalent to 4-6 weeks' rent, which protects landlords against damages and unpaid rent. Deposit-free renting alternatives replace upfront cash deposits with insurance-based solutions, reducing financial barriers for tenants while maintaining landlord security through third-party guarantees.
Insure-to-Rent
Insure-to-Rent offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional rental deposits by allowing tenants to pay a non-refundable insurance premium instead of a lump-sum security deposit, enhancing affordability and cash flow management. This innovative approach reduces upfront rental costs for tenants while providing landlords with financial protection against potential property damages or missed payments.
Flexi-Deposit Rental
Flexi-deposit rental offers tenants a flexible alternative to traditional fixed deposits by allowing smaller, manageable payments instead of a lump sum upfront, enhancing affordability and budgeting ease. This model reduces the financial barrier to entry while still providing landlords security through incremental deposit accumulation or insurance-backed guarantees.
Surety Bond Coverage
Surety bond coverage in deposit-free renting offers tenants an alternative financial guarantee to traditional security deposits, reducing upfront costs while ensuring landlords are protected against potential damages or unpaid rent. This method streamlines rental agreements by converting large cash deposits into an insured bond, improving cash flow for tenants and minimizing risks for property owners.
Upfront-Free Tenancy
Upfront-free tenancy eliminates the need for a traditional security deposit, allowing tenants to move in without paying large sums upfront, which improves cash flow and accessibility. This model often involves insurance or guarantees that protect landlords against damages or unpaid rent, making it a secure and flexible alternative to conventional deposit-based rentals.
Risk-Transfer Leasing
Deposit-free renting transfers the financial risk from tenants to landlords or third-party guarantors, eliminating upfront security deposits and reducing initial move-in costs for tenants. This risk-transfer leasing model enhances cash flow flexibility for renters while providing landlords with alternative risk mitigation through insurance or guarantee services.
Deposit vs Deposit-Free Renting Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com