Late fees are commonly applied when renters fail to pay their rent by the due date, accumulating over time and adding a fixed or percentage-based cost to encourage timely payments. Instant payment penalties are immediate charges imposed the moment a payment is missed, designed to provide swift financial consequences and reduce payment delays. Understanding the differences between late fees and instant payment penalties helps landlords implement effective rent collection policies.
Table of Comparison
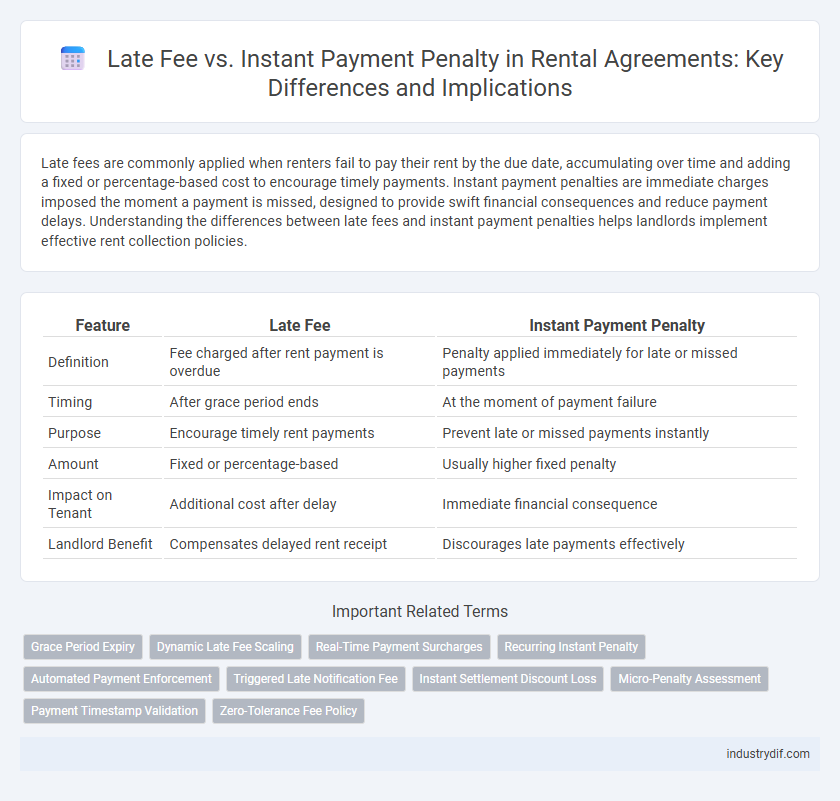
| Feature | Late Fee | Instant Payment Penalty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fee charged after rent payment is overdue | Penalty applied immediately for late or missed payments |
| Timing | After grace period ends | At the moment of payment failure |
| Purpose | Encourage timely rent payments | Prevent late or missed payments instantly |
| Amount | Fixed or percentage-based | Usually higher fixed penalty |
| Impact on Tenant | Additional cost after delay | Immediate financial consequence |
| Landlord Benefit | Compensates delayed rent receipt | Discourages late payments effectively |
Understanding Late Fees in the Rental Industry
Late fees in the rental industry are charged when tenants fail to pay rent by the due date, typically calculated as a percentage of the monthly rent or a fixed amount. Instant payment penalties, however, are immediate charges applied at the moment of late payment, designed to encourage prompt rent collection and reduce delinquencies. Understanding these distinctions helps landlords enforce contracts effectively while maintaining positive tenant relationships.
What Constitutes an Instant Payment Penalty?
An instant payment penalty is a charge imposed immediately when a tenant fails to pay rent by the due date, often calculated as a fixed percentage of the overdue amount or a flat fee. Unlike traditional late fees that may have a grace period, instant payment penalties activate the moment the payment deadline passes, incentivizing timely rent submission. Commonly outlined in lease agreements, these penalties serve to deter late payments and mitigate financial risks for landlords.
Key Differences Between Late Fees and Instant Payment Penalties
Late fees are charges applied after a specified grace period when rent is not paid on time, allowing tenants a brief window to avoid additional costs. Instant payment penalties are immediate charges imposed the moment a payment fails or is delayed, emphasizing prompt transaction completion. Key differences include timing of enforcement and tenant flexibility, with late fees offering a delay before penalties and instant payment penalties enforcing immediate financial consequences.
Legal Guidelines for Rental Late Fees
Legal guidelines for rental late fees vary by jurisdiction, often limiting the maximum amount landlords can charge and requiring clear disclosure in the lease agreement. Instant payment penalties may be subject to stricter regulations to prevent excessive or unfair charges, ensuring penalties are reasonable and proportionate to actual costs incurred. Compliance with these regulations protects landlords from legal disputes and safeguards tenants' rights against unjust financial burdens.
Instant Payment Penalty: Industry Practices
Instant Payment Penalties in rental agreements are increasingly adopted for enforcing timely rent collection, with many property management firms integrating automated payment systems that trigger immediate charges upon missed deadlines. Industry practices highlight that these penalties often exceed traditional late fees in urgency and financial impact, encouraging tenants to prioritize prompt payments. Data from real estate analytics show a rise of 20% in instant penalty enforcement among urban apartment complexes, reflecting a shift towards technology-driven compliance strategies.
Impact of Payment Timing on Rental Agreements
Late fee policies in rental agreements typically impose a fixed or percentage-based charge after a grace period, directly affecting tenants who delay payment beyond the due date. Instant payment penalties apply immediately once the payment due date passes, creating a more stringent financial consequence that can strain tenant-landlord relations. The timing of these fees impacts rental income predictability and tenant compliance, making clear lease terms essential for managing cash flow and minimizing disputes.
How Late Fees Affect Tenants and Landlords
Late fees serve as a deterrent to ensure timely rent payments, helping landlords maintain consistent cash flow and reduce administrative costs associated with overdue rent. For tenants, accruing late fees can strain their finances, potentially leading to further payment delays and damage to rental history or credit scores. Instant payment penalties impose immediate financial consequences, increasing short-term burdens on tenants but incentivizing promptness that ultimately benefits landlords by minimizing payment delays.
Reducing Risks: Preventing Late Fees and Penalties
Implementing automated rent collection systems significantly reduces the risk of late payments and consequent late fees or instant payment penalties. Clear communication of payment deadlines and penalties in lease agreements encourages timely payments and helps prevent disputes. Utilizing reminders and grace periods effectively minimizes the financial impact on tenants while maintaining steady cash flow for landlords.
Negotiating Payment Terms in Rental Contracts
Negotiating payment terms in rental contracts requires a clear distinction between late fees and instant payment penalties to protect both landlords and tenants. Late fees typically accrue after a grace period for overdue rent, incentivizing timely payments without immediate penalty, while instant payment penalties charge tenants immediately upon missed payment. Defining these terms precisely in contracts reduces disputes and fosters transparent financial expectations.
Best Practices for Transparent Fee Structures in Rentals
Transparent fee structures in rental agreements enhance tenant trust and streamline payment processes by clearly distinguishing late fees from instant payment penalties. Best practices include explicitly defining the conditions triggering each fee, such as grace periods for late payments and immediate charges for missed auto-payments, to prevent disputes and confusion. Providing detailed fee schedules in rental contracts and maintaining open communication channels ensures tenants understand their financial obligations and fosters positive landlord-tenant relationships.
Related Important Terms
Grace Period Expiry
Late fees are typically assessed after the expiration of the grace period, usually ranging from 3 to 5 days post due date, ensuring tenants have a small window to pay without penalty. Instant payment penalties charge immediately once the rent due date passes, eliminating any grace period and incentivizing on-time payments through immediate financial consequences.
Dynamic Late Fee Scaling
Dynamic late fee scaling adjusts penalties based on the duration of the payment delay, allowing landlords to impose increasing charges that reflect the severity of late rent, unlike instant payment penalties which apply a fixed fee immediately after a missed due date. This scalable approach incentivizes tenants to pay promptly while providing landlords with a flexible, revenue-protecting mechanism responsive to extended payment lapses.
Real-Time Payment Surcharges
Real-time payment surcharges, often implemented as instant payment penalties, incentivize tenants to avoid late fees by encouraging immediate rent payments through automated systems. These surcharges differ from traditional late fees by being applied instantly upon payment delay, leveraging technology to enhance cash flow predictability for landlords in rental property management.
Recurring Instant Penalty
Recurring instant payment penalties impose immediate charges each time a late rent payment occurs, ensuring consistent enforcement and motivation for timely payments. Unlike traditional late fees applied once per billing cycle, recurring penalties can significantly increase the total cost for tenants who repeatedly miss deadlines.
Automated Payment Enforcement
Automated payment enforcement systems reduce late fees by instantly applying penalties when rent is not received by the due date, ensuring timely collections and minimizing manual intervention. This technology enhances cash flow consistency for landlords by triggering real-time instant payment penalties, which act as immediate deterrents against delayed payments.
Triggered Late Notification Fee
The triggered late notification fee applies when a rental payment surpasses the due date, serving as an immediate penalty distinct from ongoing late fees that accumulate daily. This fee incentivizes timely payments by alerting tenants promptly, reducing the likelihood of prolonged overdue balances and minimizing financial disruptions for landlords.
Instant Settlement Discount Loss
Late fees impose additional costs on tenants after delayed rent payments, while instant payment penalties reduce potential discounts by requiring immediate settlement, resulting in a loss of savings typically gained through early payment incentives. This shift discourages timely payments by removing benefits, ultimately affecting cash flow and tenant satisfaction.
Micro-Penalty Assessment
Micro-penalty assessment in rental agreements distinguishes between late fees, typically charged after a grace period for overdue rent, and instant payment penalties that apply immediately upon missed payments. This precise fee structure promotes timely rental payments while minimizing tenant financial strain through smaller, gradual charges instead of large lump-sum penalties.
Payment Timestamp Validation
Late fees are imposed based on the payment timestamp exceeding the agreed due date, whereas instant payment penalties apply immediately at the time of payment delay detection, emphasizing real-time timestamp validation to ensure accurate enforcement. Accurate Payment Timestamp Validation leverages automated systems to record precise payment times, minimizing disputes and ensuring compliance with rental agreements.
Zero-Tolerance Fee Policy
A Zero-Tolerance Fee Policy enforces strict penalties for late rental payments to encourage timely payment and minimize administrative delays. Unlike late fees applied after a grace period, instant payment penalties are charged immediately upon missed deadlines, reinforcing accountability and reducing arrears.
Late Fee vs Instant Payment Penalty Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com