Safety culture represents the collective values and behaviors toward safety within an organization, while safety DNA refers to the ingrained, intrinsic mindset driving consistent safe practices at an individual level. Embedding safety DNA ensures that safety is not just a policy but a fundamental part of every pet owner's daily routine, reducing risks and promoting well-being. Cultivating both safety culture and safety DNA leads to a comprehensive approach that enhances protection for pets in diverse environments.
Table of Comparison
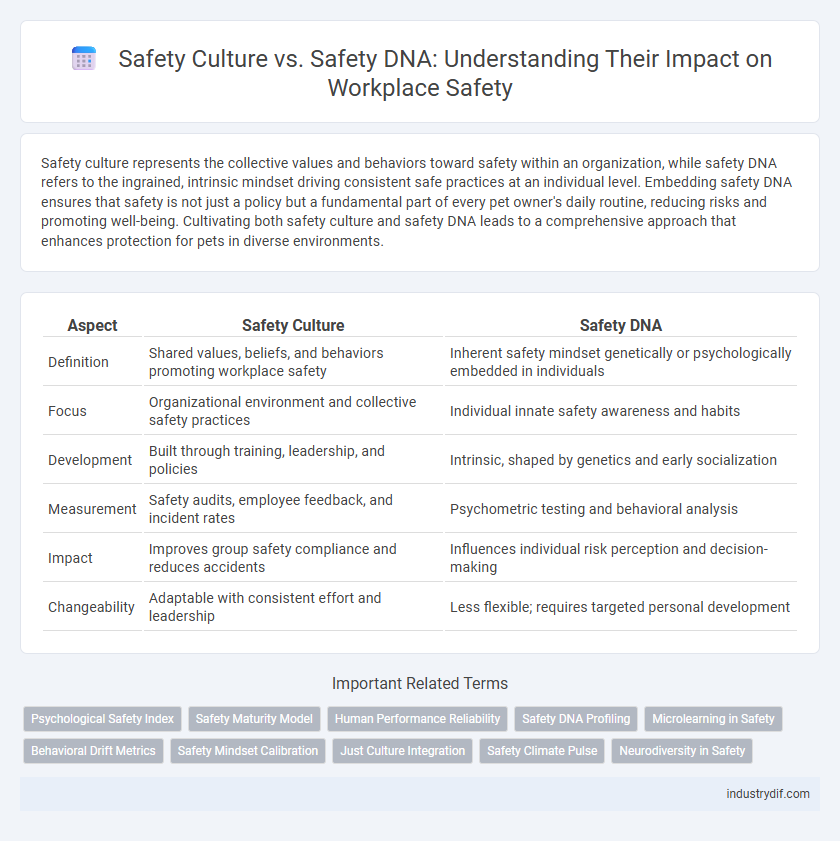
| Aspect | Safety Culture | Safety DNA |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared values, beliefs, and behaviors promoting workplace safety | Inherent safety mindset genetically or psychologically embedded in individuals |
| Focus | Organizational environment and collective safety practices | Individual innate safety awareness and habits |
| Development | Built through training, leadership, and policies | Intrinsic, shaped by genetics and early socialization |
| Measurement | Safety audits, employee feedback, and incident rates | Psychometric testing and behavioral analysis |
| Impact | Improves group safety compliance and reduces accidents | Influences individual risk perception and decision-making |
| Changeability | Adaptable with consistent effort and leadership | Less flexible; requires targeted personal development |
Understanding Safety Culture: Definition and Key Components
Safety culture encompasses the shared values, beliefs, and practices that prioritize safety within an organization, influencing employee behavior and decision-making. Key components include leadership commitment, effective communication, employee involvement, and continuous learning to proactively identify and mitigate risks. Understanding safety culture lays the foundation for fostering a work environment where safety is an integral part of every process and action.
What is Safety DNA? Core Elements and Unique Traits
Safety DNA refers to the ingrained values, behaviors, and attitudes towards safety that define an organization's identity and guide employee actions consistently. Core elements include leadership commitment, employee engagement, transparent communication, and proactive risk management, forming a foundation that drives safety performance beyond formal policies. Unique traits of Safety DNA encompass an intuitive, shared sense of responsibility and continuous learning that fosters resilience and adaptability in dynamic work environments.
Historical Evolution: Safety Culture vs Safety DNA
The historical evolution of safety culture began in the 1980s, emphasizing organizational attitudes, values, and behaviors towards safety after major industrial accidents highlighted the need for systemic change. Safety DNA represents a more advanced concept, integrating intrinsic individual traits and psychological predispositions that influence safety behaviors, moving beyond cultural frameworks to embed safety at a genetic or deeply habitual level. This progression reflects a shift from external organizational influences to internalized, personal commitment to safety within both individuals and organizations.
Comparing Safety Culture and Safety DNA: Similarities and Differences
Safety Culture embodies the shared values, beliefs, and behaviors that prioritize safety within an organization, while Safety DNA represents the inherent safety mindset embedded in an individual's core traits and decision-making processes. Both emphasize the importance of proactive risk management and continuous improvement but differ in scope; Safety Culture is collective and shaped by organizational environment, whereas Safety DNA is intrinsic and influences personal accountability and vigilance. Understanding these distinctions enhances targeted strategies for fostering a resilient and effective safety framework across all organizational levels.
The Role of Leadership in Shaping Safety Culture and Safety DNA
Leadership plays a critical role in shaping both safety culture and safety DNA by setting clear safety expectations and modeling consistent safe behaviors. Effective leaders embed safety values into organizational processes and decision-making, influencing employee attitudes and actions toward safety at every level. This proactive leadership commitment drives a sustainable safety culture and transforms safety principles into an integral part of the organization's inherent identity, known as safety DNA.
Employee Behavior: Influence of Safety Culture vs Safety DNA
Employee behavior in safety-critical environments is profoundly shaped by the organizational safety culture, which encompasses shared values, norms, and practices promoting risk awareness and compliance. Safety DNA refers to inherent traits or predispositions influencing individual risk perception and decision-making, but its impact is often modulated by the prevailing safety culture. Research indicates that cultivating a robust safety culture effectively aligns diverse employee behaviors with safety objectives, mitigating risks where innate Safety DNA varies.
Measuring Safety Culture and Safety DNA in the Workplace
Measuring safety culture in the workplace involves evaluating employees' attitudes, behaviors, and perceptions related to safety protocols, often through surveys and observation of compliance metrics. Safety DNA measurement delves deeper into intrinsic safety values and decision-making patterns encoded within organizational practices and employee mindsets, which can be assessed using behavioral analytics and in-depth interviews. Combining both approaches provides a comprehensive view of how safety is embedded culturally and inherently within the workforce, enabling targeted interventions to enhance overall workplace safety performance.
Strategies for Enhancing Safety Culture and Safety DNA
Effective strategies for enhancing safety culture and safety DNA involve embedding safety values into everyday behaviors through continuous training and leadership commitment. Integrating safety performance metrics with employee accountability systems reinforces proactive risk management and hazard identification. Leveraging technology, such as real-time safety analytics and communication platforms, facilitates timely intervention and fosters a resilient safety mindset organization-wide.
Challenges in Integrating Safety Culture with Safety DNA
Integrating Safety Culture with Safety DNA faces challenges such as aligning behavioral norms with ingrained organizational values and overcoming resistance to change deeply embedded in workforce habits. Companies struggle to embed safety as a fundamental mindset rather than just a compliance requirement, which often leads to inconsistent safety practices. Effective integration requires continuous leadership commitment, transparent communication, and tailored training to bridge the gap between cultural aspirations and inherent safety behaviors.
Future Trends: The Integration of Safety Culture and Safety DNA
Future trends in workplace safety emphasize the integration of safety culture and safety DNA, creating a holistic approach where organizational values and individual behaviors align seamlessly. This fusion enhances predictive analytics and real-time monitoring, leveraging advanced technologies like AI and IoT to embed safety into every operational layer. Companies adopting this integrated model experience improved risk mitigation, employee engagement, and sustained safety performance over time.
Related Important Terms
Psychological Safety Index
The Psychological Safety Index quantifies the extent to which employees feel secure to express ideas and concerns without fear of retribution, serving as a critical indicator for both Safety Culture and Safety DNA assessment. Organizations with a high Psychological Safety Index demonstrate ingrained Safety DNA, reflecting deep-rooted behaviors, whereas Safety Culture often represents more surface-level practices and policies.
Safety Maturity Model
Safety Culture represents the shared values, beliefs, and practices regarding safety within an organization, while Safety DNA refers to the ingrained behaviors and mindsets that drive consistent safety performance. The Safety Maturity Model assesses an organization's progression from reactive to proactive safety management by evaluating the development of both Safety Culture and Safety DNA, emphasizing continuous improvement and leadership commitment.
Human Performance Reliability
Safety culture emphasizes collective beliefs and behaviors that prioritize workplace safety, while Safety DNA integrates inherent human factors and cognitive patterns driving consistent safety performance. Human performance reliability is enhanced when organizations align safety culture initiatives with the intrinsic Safety DNA, minimizing errors and fostering proactive risk management.
Safety DNA Profiling
Safety DNA profiling provides a scientific approach to identifying inherent behavioral traits that influence safety performance, enabling organizations to predict and mitigate risks more effectively than traditional safety culture assessments. By analyzing individual and team safety DNA, companies can tailor training and interventions to foster proactive safety behaviors and enhance overall workplace safety resilience.
Microlearning in Safety
Safety culture emphasizes collective organizational behaviors and shared values that prioritize risk prevention, while Safety DNA refers to the ingrained personal attitudes and habits toward safety at an individual level. Microlearning in safety leverages short, focused training modules to reinforce Safety DNA by consistently embedding safe practices into daily routines, thereby strengthening overall safety culture within the workplace.
Behavioral Drift Metrics
Safety Culture measures collective attitudes and practices toward workplace safety, while Safety DNA reflects ingrained individual safety behaviors encoded in organizational routines. Behavioral Drift Metrics quantify deviations from established safety protocols, revealing gaps between Safety Culture ideals and actual Safety DNA execution.
Safety Mindset Calibration
Safety Culture reflects the collective behaviors and values emphasizing safety within an organization, whereas Safety DNA represents the ingrained mindset and inherent attitudes toward safety that drive individual actions. Calibrating the Safety Mindset aligns personal safety perceptions with organizational standards, fostering consistent risk awareness and proactive safety behaviors.
Just Culture Integration
Safety culture emphasizes shared values and behaviors promoting workplace safety, while Safety DNA integrates inherent individual traits influencing safety performance; Just Culture integration fosters accountability by balancing learning from mistakes with responsibility, enhancing both organizational trust and proactive risk management. Embedding Just Culture within Safety DNA and Safety Culture frameworks aligns employee mindset and systemic processes, driving continuous improvement in safety outcomes.
Safety Climate Pulse
Safety Culture reflects the shared values and behaviors shaping organizational safety outcomes, while Safety DNA represents the intrinsic attitudes and instincts toward risk management embedded in employees. Safety Climate Pulse surveys provide real-time insights into employees' perceptions and feelings about workplace safety, enabling targeted interventions to strengthen both Safety Culture and Safety DNA effectively.
Neurodiversity in Safety
Safety Culture integrates shared values, beliefs, and practices that prioritize workplace safety, while Safety DNA refers to the intrinsic, neurodiverse cognitive traits influencing individual risk perception and decision-making; recognizing neurodiversity enhances tailored safety strategies by leveraging diverse neurological strengths to improve hazard identification and response efficacy. Incorporating neurodiverse perspectives into Safety DNA fosters inclusive environments where unique sensory processing and cognitive approaches contribute to innovative safety solutions and reduce workplace incidents.
Safety Culture vs Safety DNA Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com