Impact Factor measures the average number of citations to articles published in a scientific journal, reflecting traditional academic influence. Altmetrics assess online attention and engagement, including social media mentions, news coverage, and downloads, providing a broader view of a publication's reach. Combining both metrics offers a comprehensive understanding of a scientific pet study's impact in academia and public discourse.
Table of Comparison
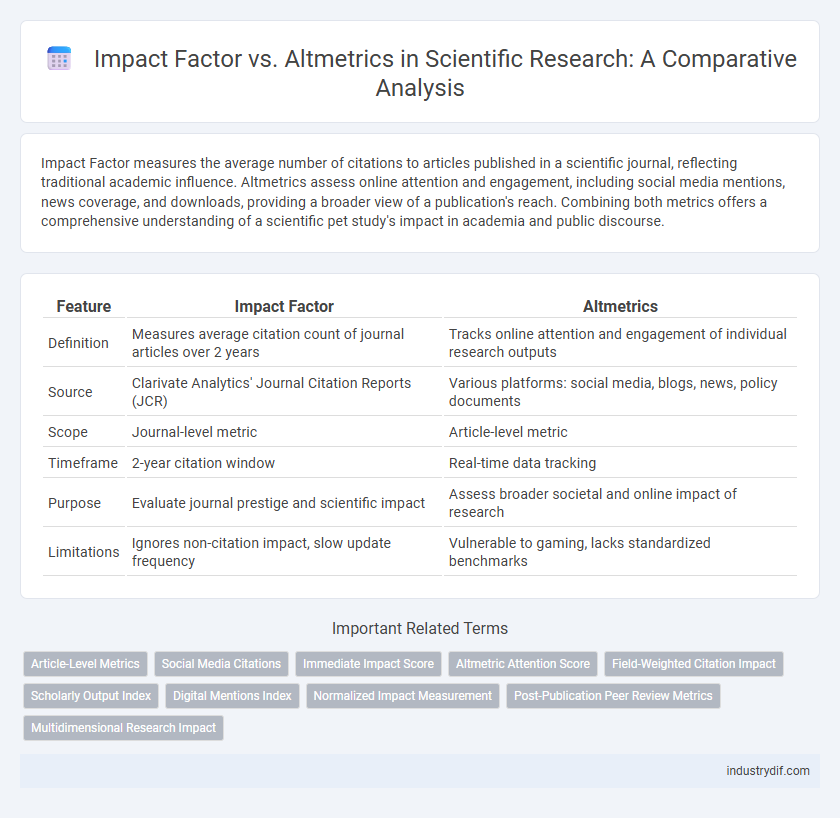
| Feature | Impact Factor | Altmetrics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures average citation count of journal articles over 2 years | Tracks online attention and engagement of individual research outputs |
| Source | Clarivate Analytics' Journal Citation Reports (JCR) | Various platforms: social media, blogs, news, policy documents |
| Scope | Journal-level metric | Article-level metric |
| Timeframe | 2-year citation window | Real-time data tracking |
| Purpose | Evaluate journal prestige and scientific impact | Assess broader societal and online impact of research |
| Limitations | Ignores non-citation impact, slow update frequency | Vulnerable to gaming, lacks standardized benchmarks |
Introduction to Impact Factor and Altmetrics
Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received by articles published in a journal, serving as a traditional metric for evaluating research influence. Altmetrics capture broader online engagement, including social media mentions, news coverage, and policy document citations, reflecting immediate and diverse impact. While Impact Factor emphasizes academic citation frequency, Altmetrics provide a comprehensive view of research visibility and societal reach.
Historical Evolution of Impact Factor
The Impact Factor, introduced by Eugene Garfield in the 1960s, originally provided a quantitative measure of journal citation frequency to assess research influence. Over decades, it became the dominant metric for academic evaluation, emphasizing citation-based impact within scholarly communication. The rise of altmetrics in the 2010s introduced alternative indicators capturing social media attention, online discussions, and broader engagement beyond traditional citations.
Emergence of Altmetrics in Scholarly Communication
Altmetrics have emerged as a complementary metric to traditional Impact Factor by capturing real-time engagement and broader societal impact of scholarly research through social media mentions, policy documents, and news coverage. Unlike Impact Factor, which relies on citation counts within academic journals, Altmetrics provide a multidimensional perspective on research influence, enhancing the evaluation of scholarly communication in a digital age. The integration of Altmetrics supports a more comprehensive understanding of research dissemination and public engagement beyond conventional citation-based metrics.
Core Differences: Impact Factor vs Altmetrics
Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received by articles published in a journal, reflecting traditional academic influence within scholarly communities. Altmetrics capture online engagement and attention from diverse sources such as social media, blogs, and news outlets, indicating broader public impact and real-time dissemination. Core differences lie in quantitative citation-based evaluation versus qualitative, multidimensional measures of social and digital interactions.
Measurement Metrics: Citation Count vs Online Engagement
Impact Factor primarily measures the average number of citations received by articles published in a journal, reflecting academic influence through citation count. Altmetrics capture online engagement by tracking social media mentions, downloads, and blog discussions, offering a broader view of an article's immediate reach and societal impact. Combining citation metrics with altmetrics provides a comprehensive assessment of scholarly impact by balancing traditional academic recognition with real-time digital interaction.
Advantages and Limitations of Impact Factor
Impact Factor remains a widely recognized metric for evaluating journal prestige based on citation frequency in scholarly articles, providing a standardized benchmark for academic impact. Its advantages include simplicity and historical data availability, enabling comparative assessments across disciplines. However, limitations involve susceptibility to citation manipulation, emphasis on quantity over research quality, and exclusion of broader societal or online engagement captured by alternative metrics.
Advantages and Limitations of Altmetrics
Altmetrics offer real-time insights into research impact by tracking online engagement such as social media mentions, news coverage, and policy document citations, providing a broader perspective beyond traditional citations measured by Impact Factor. These metrics capture diverse types of influence including public interest and interdisciplinary reach, which are often overlooked by Impact Factor's focus on journal citation frequency. However, Altmetrics can be susceptible to manipulation, varying platform algorithms, and may overemphasize popularity rather than scientific quality, limiting their ability to fully replace established bibliometric indicators.
Impact on Research Assessment and Funding
Impact Factor remains a dominant metric in research assessment and funding decisions due to its quantification of journal citation frequency, influencing academic reputation and grant allocations. Altmetrics capture a broader spectrum of research impact, including social media attention and policy document mentions, offering real-time insights beyond traditional citations. Combining Impact Factor with Altmetrics provides a more comprehensive evaluation of research influence, enhancing funding agencies' ability to identify high-impact studies and emerging scientific trends.
Role in Academic Reputation and Career Advancement
Impact Factor remains a key metric in assessing journal prestige and scholarly influence, directly impacting academic reputation and tenure evaluations. Altmetrics offers a broader spectrum by measuring digital engagement such as social media mentions, policy document citations, and online discussions, reflecting immediate societal impact and knowledge dissemination. Both indicators complement each other in career advancement, with Impact Factor emphasizing traditional citation-based recognition and Altmetrics capturing real-time visibility and public engagement.
Future Trends in Scholarly Impact Evaluation
Future trends in scholarly impact evaluation emphasize integrating traditional metrics like Impact Factor with Altmetrics to capture a comprehensive influence of research outputs. Altmetrics provide real-time, diverse data from social media, policy documents, and online platforms, reflecting broader societal engagement beyond citation counts. Advances in machine learning algorithms and data analytics will drive dynamic, multidimensional evaluation frameworks, enhancing the accuracy and relevance of research impact assessment.
Related Important Terms
Article-Level Metrics
Article-Level Metrics (ALMs) provide a nuanced evaluation of scientific impact by measuring diverse indicators such as citations, downloads, social media mentions, and media coverage, offering a real-time and article-specific assessment beyond the traditional Journal Impact Factor (JIF). Unlike the JIF, which averages citation impact at the journal level, ALMs capture the multifaceted reach and engagement of individual research articles, reflecting broader societal influence and immediate visibility.
Social Media Citations
Impact Factor remains a traditional metric measuring a journal's average citation rate, while Altmetrics capture the broader influence of research through social media citations, blog mentions, and online engagement. Social media citations, tracked by Altmetrics, reflect real-time dissemination and public interaction, often highlighting the immediate societal impact of scientific work beyond academic circles.
Immediate Impact Score
Immediate Impact Score offers a real-time quantification of an article's influence by tracking downloads, social media mentions, and citations shortly after publication, contrasting with the traditional Impact Factor's reliance on average citation counts over extended periods. This metric provides a more dynamic understanding of research visibility and engagement, especially useful for assessing the immediate dissemination and reception of scientific findings.
Altmetric Attention Score
The Altmetric Attention Score quantifies the online attention and engagement a scientific publication receives across social media, news outlets, and policy documents, offering a broader impact measurement than the traditional Impact Factor that primarily reflects citation frequency within academic journals. This metric captures real-time dissemination and public interest, providing valuable insights into the societal and interdisciplinary reach of research beyond citation-based metrics.
Field-Weighted Citation Impact
Field-Weighted Citation Impact (FWCI) provides a normalized measure of a publication's citation performance relative to the global average in its specific research field, offering a more precise understanding of its academic influence than raw Impact Factor metrics. Unlike traditional Impact Factor, which counts average citations per journal, FWCI accounts for disciplinary differences and citation context, while Altmetrics track broader, real-time engagement like social media mentions and policy document citations, reflecting diverse dimensions of research impact.
Scholarly Output Index
The Impact Factor quantifies journal citation frequency, emphasizing traditional scholarly output indexing through citation analysis, while Altmetrics measure broader digital engagement, capturing online attention and social media interactions related to research. Both metrics serve complementary roles in evaluating scholarly output, with Impact Factor reflecting academic influence and Altmetrics indicating public and interdisciplinary reach.
Digital Mentions Index
The Digital Mentions Index (DMI) offers a comprehensive alternative to traditional Impact Factor by quantifying the influence of scientific publications through social media, news outlets, and online platforms. Unlike Impact Factor, which measures citation frequency in academic journals, DMI captures real-time engagement and wider public discourse surrounding research outputs.
Normalized Impact Measurement
Normalized impact measurement integrates both Impact Factor and Altmetrics to provide a comprehensive evaluation of scientific influence by adjusting for disciplinary differences and publication age. This combined metric enhances accuracy in assessing research significance beyond traditional citation counts, incorporating real-time online attention and engagement data.
Post-Publication Peer Review Metrics
Post-publication peer review metrics, such as comments, shares, and expert evaluations, provide real-time assessment of scientific impact that complements traditional Impact Factor by capturing broader engagement and interdisciplinary influence. Unlike Impact Factor, which measures citation averages within journals, Altmetrics reflect immediate and diverse interactions across social media, policy documents, and public forums, highlighting dynamic scholarly discourse beyond formal citations.
Multidimensional Research Impact
Impact Factor primarily measures journal citation frequency, reflecting traditional academic influence, while Altmetrics capture diverse online engagement metrics such as social media mentions, downloads, and media coverage, offering a multidimensional perspective on research impact. Integrating both indicators provides a comprehensive assessment of scientific contributions across academic and public domains.
Impact Factor vs Altmetrics Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com