DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams to streamline software delivery through continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. GitOps builds on DevOps principles by using Git repositories as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application configurations, enabling automated, version-controlled deployments. This approach enhances observability, auditability, and rollback capabilities, making infrastructure changes more reliable and secure.
Table of Comparison
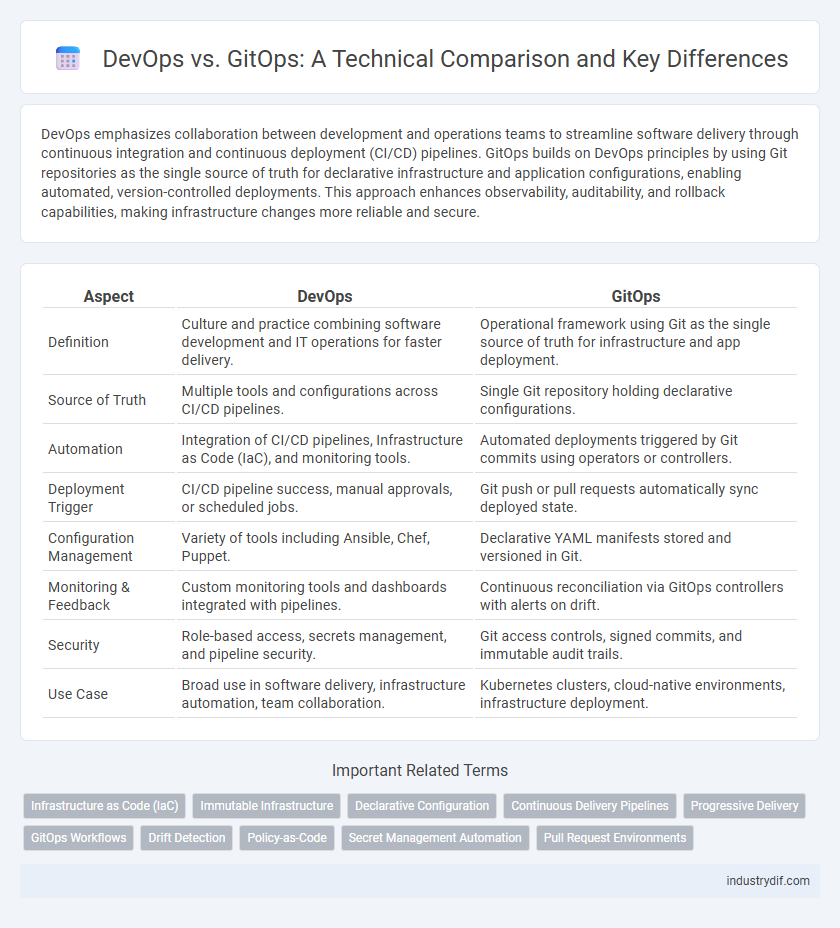
| Aspect | DevOps | GitOps |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Culture and practice combining software development and IT operations for faster delivery. | Operational framework using Git as the single source of truth for infrastructure and app deployment. |
| Source of Truth | Multiple tools and configurations across CI/CD pipelines. | Single Git repository holding declarative configurations. |
| Automation | Integration of CI/CD pipelines, Infrastructure as Code (IaC), and monitoring tools. | Automated deployments triggered by Git commits using operators or controllers. |
| Deployment Trigger | CI/CD pipeline success, manual approvals, or scheduled jobs. | Git push or pull requests automatically sync deployed state. |
| Configuration Management | Variety of tools including Ansible, Chef, Puppet. | Declarative YAML manifests stored and versioned in Git. |
| Monitoring & Feedback | Custom monitoring tools and dashboards integrated with pipelines. | Continuous reconciliation via GitOps controllers with alerts on drift. |
| Security | Role-based access, secrets management, and pipeline security. | Git access controls, signed commits, and immutable audit trails. |
| Use Case | Broad use in software delivery, infrastructure automation, team collaboration. | Kubernetes clusters, cloud-native environments, infrastructure deployment. |
Introduction to DevOps and GitOps
DevOps is a collaborative approach that integrates development and IT operations to accelerate software delivery through continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. GitOps leverages Git as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application deployment, enabling automated, version-controlled workflows in Kubernetes environments. Both methodologies aim to improve deployment speed, reliability, and scalability by emphasizing automation, collaboration, and infrastructure as code.
Core Principles of DevOps
DevOps centers on core principles such as continuous integration, continuous delivery, and collaboration between development and operations teams to streamline software deployment. It emphasizes automation, infrastructure as code, and monitoring to ensure faster, reliable, and scalable application delivery. These foundational practices foster a culture of shared responsibility and rapid feedback loops in the software development lifecycle.
Core Principles of GitOps
GitOps centers on declarative infrastructure, using version-controlled repositories as the single source of truth to manage deployments and operational procedures. Automation is fundamental, leveraging Kubernetes operators and continuous reconciliation loops to ensure system state consistency with the desired configuration. Emphasizing observability, GitOps delivers auditability and rollback capabilities by tracking every change through Git commits, enhancing security and operational reliability.
Key Differences Between DevOps and GitOps
DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams to automate and streamline software delivery pipelines, utilizing a broad range of tools and practices across the software lifecycle. GitOps centers on using Git repositories as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application configurations, automating deployment and operational tasks through Git-based workflows. Key differences include DevOps' focus on culture and process integration versus GitOps' strict reliance on Git for version control and automated infrastructure management.
Workflow Comparison: DevOps vs GitOps
DevOps workflows emphasize continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) through automated pipelines, focusing on collaboration between development and operations teams. GitOps streamlines these processes by using Git repositories as the single source of truth, enabling declarative infrastructure and automated reconciliation via Kubernetes controllers. This approach improves version control, auditability, and rollback capabilities compared to traditional DevOps methodologies.
Infrastructure as Code in DevOps vs GitOps
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) in DevOps emphasizes provisioning and managing infrastructure through code and automation tools like Ansible, Terraform, and Chef, enabling consistent environment setups and rapid scaling. GitOps extends IaC by using Git repositories as the single source of truth, where infrastructure and application configurations are declaratively defined, versioned, and automatically deployed through continuous reconciliation loops with tools like Flux or Argo CD. This declarative approach in GitOps enhances security, auditability, and rollback capabilities, reinforcing infrastructure stability and compliance in cloud-native environments.
Toolchain Overview: DevOps and GitOps
DevOps toolchains integrate continuous integration, continuous delivery, automated testing, and infrastructure provisioning using platforms like Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, and Ansible, enabling collaborative development and operations workflows. GitOps toolchains leverage Git repositories as the single source of truth, utilizing tools such as Flux, Argo CD, and Terraform to automate deployment, configuration management, and observability through declarative infrastructure as code. Both approaches emphasize automation and version control, but GitOps centralizes state management in Git, streamlining rollback processes and enhancing security through immutable change histories.
Benefits and Challenges of DevOps and GitOps
DevOps enhances collaboration between development and operations teams, accelerating software delivery and improving system reliability through continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) practices. GitOps leverages Git as a single source of truth for infrastructure and application configurations, enabling automated, version-controlled deployments that improve auditability and reduce human error. Challenges of DevOps include cultural resistance and tool integration complexities, while GitOps faces limitations with managing non-cloud-native environments and requires expertise in Kubernetes and Git workflows.
Adoption Strategies for DevOps and GitOps
Adoption strategies for DevOps emphasize continuous integration, automated testing, and collaboration between development and operations teams to accelerate software delivery. GitOps adoption focuses on managing infrastructure and application deployments declaratively through Git repositories, ensuring version-controlled, auditable, and reliable operations. Both methodologies require organizational culture shifts, tooling investments, and incremental rollout plans to achieve successful integration and operational efficiency.
Choosing Between DevOps and GitOps for Your Organization
Choosing between DevOps and GitOps depends on your organization's need for automation and code-driven infrastructure management; DevOps emphasizes collaboration and continuous integration across development and operations teams, while GitOps leverages Git repositories as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application deployment. Organizations prioritizing version-controlled, automated infrastructure with rollback capabilities benefit from GitOps, whereas those seeking broader cultural and procedural integration may prefer DevOps. Understanding team expertise and existing toolchains is critical for selecting the approach that maximizes efficiency and reliability in software delivery.
Related Important Terms
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
DevOps leverages Infrastructure as Code (IaC) to automate and streamline infrastructure management through scripts and configurations integrated into CI/CD pipelines. GitOps extends this by using Git repositories as the single source of truth, enabling declarative IaC and continuous reconciliation of infrastructure state for enhanced version control and auditability.
Immutable Infrastructure
DevOps emphasizes automation and collaboration to streamline software delivery, while GitOps extends these principles by using Git repositories as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure management. Immutable infrastructure in GitOps ensures that every change is version-controlled and reproducible, reducing configuration drift and enabling consistent environment provisioning.
Declarative Configuration
Declarative configuration in GitOps enables the entire system state to be defined as code stored in version control, ensuring consistent and automated deployments through pull requests and continuous reconciliation. DevOps often incorporates declarative practices but may rely more on imperative scripting and manual processes, making GitOps a more robust approach for maintaining infrastructure as code and streamlining continuous delivery.
Continuous Delivery Pipelines
DevOps integrates continuous delivery pipelines by combining development and operations to automate software release processes, enhancing collaboration and reducing deployment frequency. GitOps extends this paradigm by using Git repositories as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application configurations, enabling automated, version-controlled continuous delivery pipelines with improved auditability and rollback capabilities.
Progressive Delivery
DevOps emphasizes continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines to automate software delivery, while GitOps leverages Git repositories as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application management. Progressive Delivery benefits from GitOps by enabling controlled, automated rollouts and rollbacks through versioned Git commits, enhancing deployment safety and reliability.
GitOps Workflows
GitOps workflows automate deployment processes by using Git repositories as the single source of truth for infrastructure and application configurations, enabling continuous delivery through pull requests and automated reconciliation loops. This approach enhances auditability, rollback capabilities, and consistency by leveraging Kubernetes controllers to continuously ensure system state aligns with the desired configuration defined in Git.
Drift Detection
Drift detection in DevOps relies on manual scripting and monitoring tools to identify configuration inconsistencies, whereas GitOps automates this process by continuously reconciling the desired state defined in Git repositories with the actual cluster state. GitOps enhances security and reliability by providing an immutable audit trail and immediate alerts when drift occurs, reducing configuration drift and operational overhead compared to traditional DevOps practices.
Policy-as-Code
Policy-as-Code in DevOps integrates security and compliance policies directly into CI/CD pipelines, enabling automated enforcement and continuous validation of infrastructure configurations. GitOps extends this by managing policy definitions as declarative code within Git repositories, ensuring versioned, auditable, and reproducible policy enforcement aligned with infrastructure state.
Secret Management Automation
GitOps automates secret management by integrating Kubernetes-native tools like Sealed Secrets and External Secrets, ensuring continuous synchronization and secure handling of sensitive data. DevOps relies on traditional secret management solutions such as HashiCorp Vault or Azure Key Vault, which require manual intervention or scripting to maintain secret lifecycle and access controls.
Pull Request Environments
Pull Request Environments in GitOps automate the deployment pipeline by using declarative configurations stored in Git repositories, ensuring version-controlled and auditable infrastructure changes. In contrast, traditional DevOps Pull Request Environments often rely on imperative scripts and manual deployments, which can increase the risk of drift between environments and reduce repeatability.
DevOps vs GitOps Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com