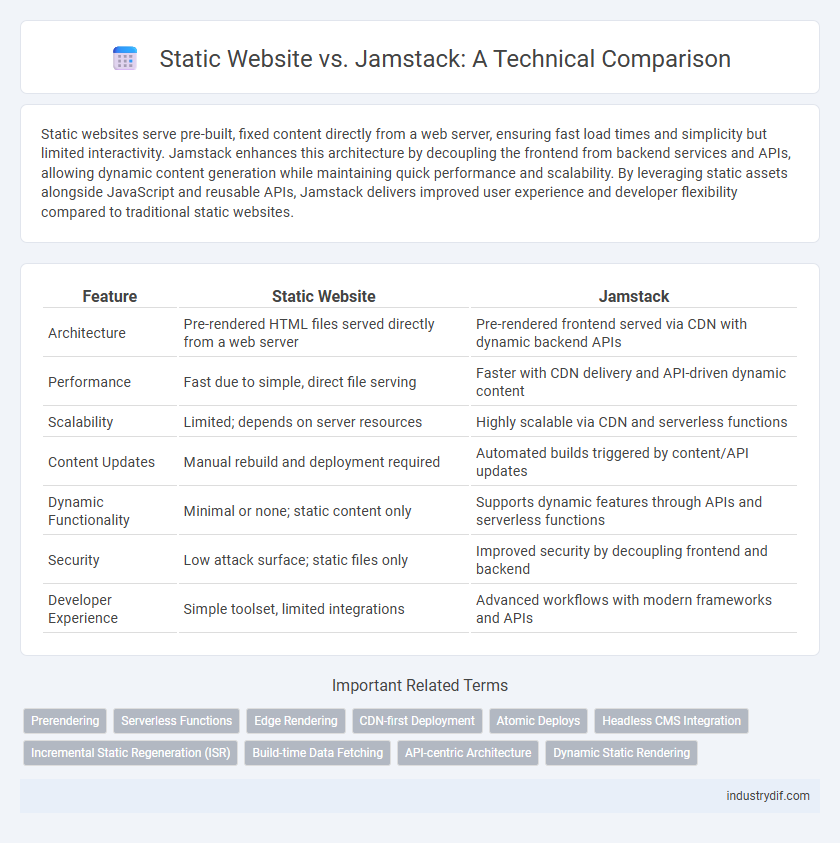
Static websites serve pre-built, fixed content directly from a web server, ensuring fast load times and simplicity but limited interactivity. Jamstack enhances this architecture by decoupling the frontend from backend services and APIs, allowing dynamic content generation while maintaining quick performance and scalability. By leveraging static assets alongside JavaScript and reusable APIs, Jamstack delivers improved user experience and developer flexibility compared to traditional static websites.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Static Website | Jamstack |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Pre-rendered HTML files served directly from a web server | Pre-rendered frontend served via CDN with dynamic backend APIs |
| Performance | Fast due to simple, direct file serving | Faster with CDN delivery and API-driven dynamic content |
| Scalability | Limited; depends on server resources | Highly scalable via CDN and serverless functions |
| Content Updates | Manual rebuild and deployment required | Automated builds triggered by content/API updates |
| Dynamic Functionality | Minimal or none; static content only | Supports dynamic features through APIs and serverless functions |
| Security | Low attack surface; static files only | Improved security by decoupling frontend and backend |
| Developer Experience | Simple toolset, limited integrations | Advanced workflows with modern frameworks and APIs |
Understanding Static Websites: Key Concepts
Static websites consist of fixed HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files delivered directly to the browser without server-side processing, resulting in faster load times and enhanced security. Jamstack extends static websites by decoupling the frontend from backend services, leveraging APIs and prebuilt markup for dynamic functionality. Understanding these fundamental concepts clarifies how Jamstack optimizes performance and scalability compared to traditional static sites.
What is Jamstack? An Overview
Jamstack is a modern web development architecture designed to improve performance, security, and scalability by decoupling the frontend from backend services and leveraging static site generators, APIs, and CDN delivery. Unlike traditional static websites, Jamstack sites enhance user experience through dynamic functionalities powered by JavaScript and reusable APIs. This approach optimizes load speed, reduces server dependency, and facilitates seamless integration with third-party services, making it ideal for high-performance web applications.
Core Technologies Behind Static Websites
Static websites rely primarily on HTML, CSS, and JavaScript served directly from a web server or Content Delivery Network (CDN), ensuring fast load times and low server overhead. Jamstack builds on static site foundations by integrating APIs and prebuilt Markup generated during a build process, leveraging static site generators like Gatsby or Next.js to enhance scalability and dynamic functionality. The core technologies behind Jamstack enable decoupling of the frontend and backend, improving security and developer experience compared to traditional static websites.
Jamstack Architecture: Components and Workflow
Jamstack architecture enhances web performance by pre-rendering static pages and decoupling the frontend from backend services, utilizing APIs for dynamic content delivery. Core components include static site generators, reusable APIs, and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) that collectively optimize scalability and security. The workflow involves building static assets during deployment, serving them rapidly via CDNs, and fetching dynamic data asynchronously through JavaScript-driven API calls.
Performance Comparison: Static Sites vs Jamstack
Static websites deliver fast load times by serving pre-rendered HTML files directly from a CDN, minimizing server processing and reducing latency. Jamstack enhances performance by combining static site generation with client-side JavaScript and APIs, enabling dynamic functionality while maintaining quick page loads. The Jamstack architecture often outperforms traditional static sites in scalability and responsiveness, particularly for content-rich, interactive applications.
Security Implications of Static and Jamstack Approaches
Static websites offer robust security advantages by serving pre-rendered HTML files, minimizing server-side vulnerabilities and eliminating dependencies on databases or server-side scripts that are common attack targets. Jamstack enhances security further by decoupling the frontend from backend services, utilizing APIs and serverless functions that reduce the attack surface and enable granular access controls. Both approaches mitigate risks such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting, but Jamstack's modular architecture provides superior flexibility in implementing advanced security measures and rapid updates.
Scalability Analysis: Which Solution Fits?
Static websites offer straightforward scalability by serving pre-rendered HTML files directly from a Content Delivery Network (CDN), minimizing server load and ensuring fast load times during high traffic spikes. Jamstack architecture enhances scalability further by decoupling the frontend from backend services, utilizing APIs and microservices, which allows for dynamic content updates without compromising performance. Choosing between static websites and Jamstack depends on project complexity and scalability needs, with Jamstack providing superior flexibility for rapidly growing applications requiring dynamic capabilities.
Content Management: Static Generators vs Headless CMS
Static website generators build content at compile time, producing pre-rendered HTML files for fast loading and simple hosting. Jamstack leverages headless CMSs to decouple content management from the frontend, enabling dynamic content updates via APIs without full site rebuilds. This separation improves scalability, enhances developer experience, and allows seamless integration with modern workflows and services.
Deployment and Hosting Differences
Static websites are traditionally hosted on basic web servers with simple FTP deployment, requiring manual updates for every content change. Jamstack architecture leverages modern deployment platforms like Netlify and Vercel, enabling continuous integration with Git repositories and automated builds that improve scalability and performance. Hosting Jamstack sites often includes edge CDN distribution, which reduces latency and enhances global content delivery compared to conventional static hosting methods.
Use Cases: When to Choose Static or Jamstack
Static websites excel for simple portfolios, landing pages, or brochure sites where content changes infrequently and fast load times are critical. Jamstack architecture suits dynamic applications requiring API integrations, serverless functions, or real-time data updates, such as e-commerce platforms and interactive dashboards. Choosing between Static and Jamstack depends on project complexity, scalability needs, and the necessity for backend interactions.
Related Important Terms
Prerendering
Static websites rely on prerendering all content at build time, delivering fast load speeds by serving prebuilt HTML files directly from a CDN. Jamstack enhances this approach by combining prerendered static assets with dynamic JavaScript and APIs, enabling scalable, interactive user experiences without sacrificing performance.
Serverless Functions
Static websites deliver pre-rendered HTML files directly from a CDN, optimizing load times but lacking dynamic capabilities without client-side scripting. Jamstack architecture leverages serverless functions to execute backend logic on-demand, enabling scalable, event-driven interactions while maintaining the performance benefits of static content.
Edge Rendering
Static websites deliver pre-built HTML files directly from a CDN, minimizing server load and reducing latency, while Jamstack leverages edge rendering to dynamically generate content closer to users by executing serverless functions on the edge. This approach enhances performance and scalability by combining static assets with real-time data fetching and personalization at the network edge.
CDN-first Deployment
Jamstack architecture leverages CDN-first deployment by pre-rendering static assets and serving them directly from globally distributed Content Delivery Networks, resulting in faster load times and improved scalability compared to traditional static websites that may rely more heavily on origin servers for content delivery. This approach reduces latency, enhances security through decentralized hosting, and streamlines the developer workflow by separating frontend and backend concerns.
Atomic Deploys
Atomic deploys in Jamstack enable precise, incremental updates to specific site components without redeploying the entire static website, significantly reducing downtime and deployment risks. Unlike traditional static websites that require full rebuilds, Jamstack's atomic deploys leverage decoupled architecture and CDN caching for faster, more efficient content delivery and instant rollbacks.
Headless CMS Integration
Static websites deliver pre-rendered HTML files for fast loading but lack dynamic content flexibility, whereas Jamstack architecture leverages headless CMS integration through APIs, enabling real-time content updates, enhanced scalability, and improved developer experience. Headless CMS decouples the content management from the frontend, allowing Jamstack sites to fetch structured content dynamically while maintaining static site performance benefits.
Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR)
Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR) enables Jamstack sites to update static content on-demand without rebuilding the entire site, offering improved scalability and fresh content delivery compared to traditional static website generation. This approach leverages serverless functions and CDN caching, optimizing performance and reducing latency for large-scale web applications.
Build-time Data Fetching
Static websites generate all content at build time, ensuring fast load speeds but limiting dynamic data updates without rebuilding. Jamstack leverages build-time data fetching combined with client-side APIs, enabling scalable, performant sites with dynamic content delivered through pre-rendered static pages.
API-centric Architecture
Static websites serve pre-built HTML without dynamic content, limiting interactivity and scalability, whereas Jamstack employs an API-centric architecture that decouples frontend delivery from backend services, enabling faster load times and seamless integration with third-party APIs. This approach enhances performance, security, and developer experience by leveraging serverless functions, headless CMSs, and microservices to deliver dynamic content without traditional server-side processes.
Dynamic Static Rendering
Dynamic static rendering in Jamstack combines pre-rendered static pages with on-demand serverless functions, enabling real-time content updates without sacrificing performance. Unlike traditional static websites, Jamstack architectures leverage APIs and JavaScript to deliver dynamic user experiences while maintaining fast load times and scalability.
Static Website vs Jamstack Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com