Continuous Integration (CI) automates the process of merging code changes and running tests to detect issues early in the development cycle. Continuous Delivery (CD) extends CI by automating the deployment process, ensuring that code changes can be released to production reliably and at any time. Orchestration tools manage the workflow between CI and CD pipelines, coordinating tasks, dependencies, and environments to streamline software delivery.
Table of Comparison
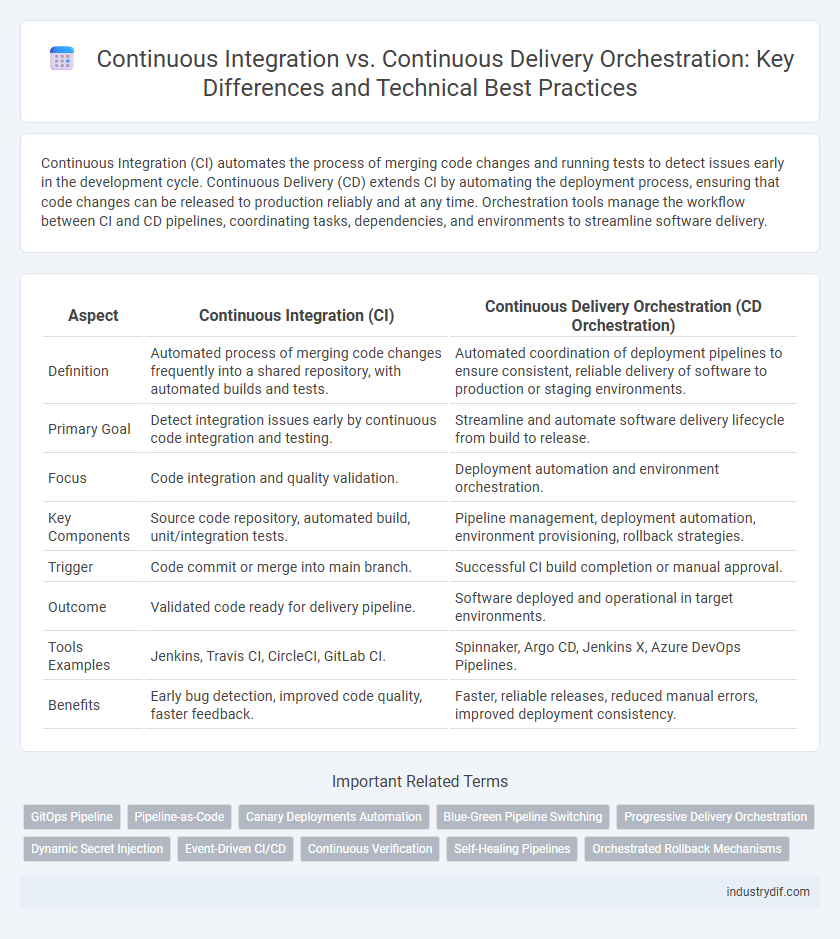
| Aspect | Continuous Integration (CI) | Continuous Delivery Orchestration (CD Orchestration) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated process of merging code changes frequently into a shared repository, with automated builds and tests. | Automated coordination of deployment pipelines to ensure consistent, reliable delivery of software to production or staging environments. |
| Primary Goal | Detect integration issues early by continuous code integration and testing. | Streamline and automate software delivery lifecycle from build to release. |
| Focus | Code integration and quality validation. | Deployment automation and environment orchestration. |
| Key Components | Source code repository, automated build, unit/integration tests. | Pipeline management, deployment automation, environment provisioning, rollback strategies. |
| Trigger | Code commit or merge into main branch. | Successful CI build completion or manual approval. |
| Outcome | Validated code ready for delivery pipeline. | Software deployed and operational in target environments. |
| Tools Examples | Jenkins, Travis CI, CircleCI, GitLab CI. | Spinnaker, Argo CD, Jenkins X, Azure DevOps Pipelines. |
| Benefits | Early bug detection, improved code quality, faster feedback. | Faster, reliable releases, reduced manual errors, improved deployment consistency. |
Defining Continuous Integration (CI) and Its Core Principles
Continuous Integration (CI) is a software development practice where developers frequently merge code changes into a shared repository, triggering automated builds and tests to detect integration errors early. Core principles of CI include maintaining a single source repository, automating the build and testing process, and ensuring that code changes are integrated continuously to reduce conflicts and improve software quality. By adhering to these principles, teams achieve faster feedback cycles and deliver more reliable software.
Introduction to Continuous Delivery (CD) in Modern Workflows
Continuous Delivery (CD) automates software deployment, ensuring rapid, reliable releases by integrating code changes into production-like environments frequently. It extends Continuous Integration (CI) by adding automated testing, staging, and release orchestration to maintain high software quality and reduce manual intervention. Modern workflows leverage CD pipelines to enhance deployment efficiency, improve collaboration between development and operations teams, and accelerate time-to-market.
Key Differences Between Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery
Continuous Integration (CI) emphasizes automated code merging and testing to identify defects early, ensuring code quality and reducing integration issues. Continuous Delivery (CD) builds upon CI by automating the release pipeline, enabling rapid and reliable deployment of software to production-like environments. The key difference lies in CI focusing on code integration and testing, whereas CD centers on automating delivery and deployment workflows for faster release cycles.
Understanding Orchestration in DevOps Pipelines
Orchestration in DevOps pipelines involves automating the coordination and management of continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) processes to ensure seamless code integration, testing, and deployment. Effective orchestration platforms integrate various tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, and Kubernetes to streamline workflows, reduce manual intervention, and enhance deployment frequency. Understanding orchestration enables DevOps teams to optimize pipeline efficiency, improve release velocity, and maintain high software quality through consistent and repeatable processes.
Popular Tools for CI and CD Orchestration
Jenkins remains a dominant tool for continuous integration, offering extensive plugin support and scalability for CI orchestration. For continuous delivery orchestration, Spinnaker and Argo CD are popular choices, providing robust deployment automation and multi-cloud support. GitLab CI/CD integrates both CI and CD orchestration capabilities, streamlining the entire DevOps pipeline within a single platform.
Enhancing Deployment Efficiency with Orchestration Platforms
Continuous Integration (CI) automates code integration and testing, while Continuous Delivery (CD) ensures rapid, reliable deployment readiness. Orchestration platforms enhance deployment efficiency by automating complex workflows, coordinating multiple tools, and enabling real-time monitoring and rollback capabilities. This integration reduces deployment errors, accelerates release cycles, and optimizes resource allocation across development pipelines.
Best Practices in CI/CD Orchestration for Scalable Systems
Implementing best practices in CI/CD orchestration for scalable systems involves automating build, test, and deployment pipelines to ensure rapid and reliable software delivery. Leveraging containerization and infrastructure as code (IaC) enables consistent environments and easy scaling across multiple stages. Monitoring pipeline performance and integrating feedback loops allow proactive issue resolution and continuous improvement in the deployment process.
Common Challenges in CI/CD Orchestration and How to Solve Them
Common challenges in CI/CD orchestration include pipeline complexity, integration issues across diverse tools, and inconsistent environment configurations, which can lead to deployment failures and increased downtime. Resolving these issues requires implementing standardized workflows, leveraging containerization for environment consistency, and adopting automated testing to ensure reliable integration. Effective monitoring and real-time feedback mechanisms also enhance pipeline visibility, enabling quick identification and remediation of failures.
Impact of Automated Testing on CI/CD Pipelines
Automated testing significantly enhances Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) pipelines by ensuring rapid feedback and early bug detection, which reduces integration risks and accelerates release cycles. High test coverage combined with parallel execution in CI environments increases pipeline efficiency, minimizes manual intervention, and maintains software quality. Integrating automated testing frameworks like Selenium, JUnit, or Cypress into CD orchestration optimizes deployments by validating code changes continuously and enabling reliable delivery to production environments.
Future Trends in CI vs. CD Orchestration Technologies
Future trends in Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) orchestration emphasize AI-driven automation to enhance pipeline efficiency and predictive analytics for proactive error detection. Integration of cloud-native technologies and serverless architectures is advancing scalability and resource optimization in CI/CD workflows. Enhanced security protocols and compliance automation are becoming critical features to address growing cybersecurity challenges in software delivery.
Related Important Terms
GitOps Pipeline
GitOps pipelines streamline Continuous Integration (CI) by automating code integration and testing within Kubernetes environments, leveraging declarative configurations stored in Git repositories. Continuous Delivery (CD) orchestration extends this by automating deployment and environment synchronization, ensuring consistent and reliable software releases through infrastructure-as-code practices.
Pipeline-as-Code
Pipeline-as-Code enables seamless automation by embedding Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery orchestration within version-controlled scripts, ensuring consistent, repeatable, and auditable deployment processes. This approach leverages declarative pipeline definitions to integrate build, test, and release stages, enhancing collaboration and accelerating software delivery cycles.
Canary Deployments Automation
Canary deployment automation enhances continuous integration and continuous delivery orchestration by enabling incremental software release cycles that minimize risk through automated traffic routing to a subset of users. This process leverages automated monitoring and rollback mechanisms to ensure stable, reliable rollout of new features while maintaining system integrity.
Blue-Green Pipeline Switching
Blue-Green pipeline switching in Continuous Integration versus Continuous Delivery orchestration minimizes downtime by maintaining two identical production environments, allowing seamless traffic redirection between blue (current) and green (new) deployments. This approach ensures rapid rollback capabilities and enhances deployment reliability by isolating changes until validation in the green environment is complete, crucial for minimizing risks in automated delivery workflows.
Progressive Delivery Orchestration
Progressive Delivery Orchestration enhances Continuous Integration by automating phased deployments to targeted user segments, enabling controlled rollouts and rapid rollback capabilities. This approach optimizes Continuous Delivery pipelines by reducing deployment risks and improving feature validation through incremental exposure and real-time monitoring.
Dynamic Secret Injection
Dynamic secret injection enhances Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery orchestration by automatically providing ephemeral credentials during build and deployment processes, reducing the risk of secret exposure. This method integrates with secret management tools like HashiCorp Vault or AWS Secrets Manager to improve security posture and streamline automated pipeline operations.
Event-Driven CI/CD
Event-driven CI/CD leverages real-time triggers to automate both Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery orchestration, enhancing deployment speed and reducing manual interventions. By integrating event-driven architectures with CI/CD pipelines, development teams achieve faster feedback loops and more reliable software releases through automated event processing and dynamic workflow management.
Continuous Verification
Continuous Verification enhances Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery orchestration by automating real-time quality checks and validation of code changes, reducing deployment risks. This process integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines, ensuring consistent application performance and compliance through automated testing, monitoring, and feedback loops.
Self-Healing Pipelines
Self-healing pipelines in Continuous Integration enhance development velocity by automatically detecting and resolving build failures, minimizing downtime through automated rollback and retry mechanisms. Continuous Delivery orchestration integrates these adaptive pipelines to ensure consistent, reliable deployments by dynamically adjusting workflows based on real-time system feedback and error correction protocols.
Orchestrated Rollback Mechanisms
Orchestrated rollback mechanisms in continuous delivery orchestration automate the process of reverting deployments upon failure detection, minimizing downtime and ensuring system stability. By integrating with CI pipelines, these mechanisms enable faster recovery through automated version control, health checks, and coordinated service restarts.
Continuous Integration vs Continuous Delivery Orchestration Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com