Waterfall is a linear and sequential project management methodology commonly used in traditional software development, where each phase must be completed before moving to the next, often leading to slower delivery and less flexibility. DevOps integrates development and operations teams to enable continuous integration, continuous delivery, and faster feedback loops, promoting collaboration and iterative releases. Choosing between Waterfall and DevOps depends on project complexity, urgency, and the need for adaptability in software development processes.
Table of Comparison
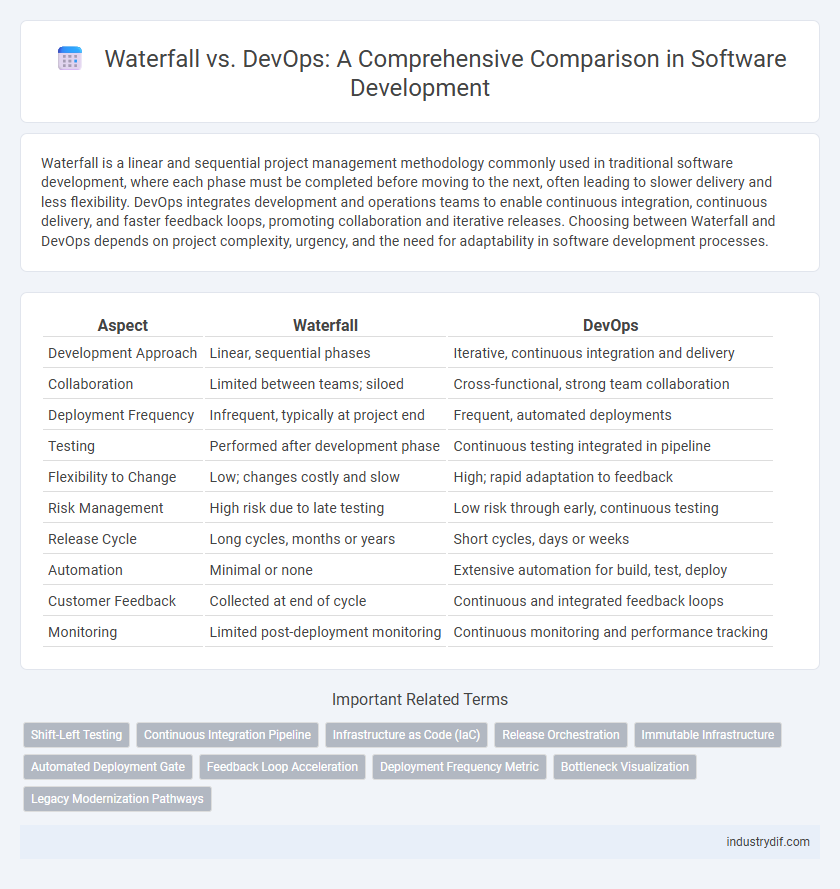
| Aspect | Waterfall | DevOps |
|---|---|---|
| Development Approach | Linear, sequential phases | Iterative, continuous integration and delivery |
| Collaboration | Limited between teams; siloed | Cross-functional, strong team collaboration |
| Deployment Frequency | Infrequent, typically at project end | Frequent, automated deployments |
| Testing | Performed after development phase | Continuous testing integrated in pipeline |
| Flexibility to Change | Low; changes costly and slow | High; rapid adaptation to feedback |
| Risk Management | High risk due to late testing | Low risk through early, continuous testing |
| Release Cycle | Long cycles, months or years | Short cycles, days or weeks |
| Automation | Minimal or none | Extensive automation for build, test, deploy |
| Customer Feedback | Collected at end of cycle | Continuous and integrated feedback loops |
| Monitoring | Limited post-deployment monitoring | Continuous monitoring and performance tracking |
Understanding Waterfall and DevOps Methodologies
Waterfall methodology follows a linear, sequential approach where each phase--requirements, design, implementation, verification, and maintenance--must be completed before the next begins, making it suitable for projects with fixed scopes and clear objectives. DevOps integrates development and operations teams to enable continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), and automated testing, promoting rapid, iterative releases and enhanced collaboration. Understanding these methodologies helps organizations choose between structured, plan-driven processes and flexible, feedback-oriented practices for software development.
Key Principles of Waterfall Development
Waterfall development follows a linear and sequential approach where each phase, such as requirements gathering, design, implementation, testing, and deployment, must be completed before the next begins. This model emphasizes detailed documentation, strict project timelines, and a clear scope definition to minimize changes during development. Key principles involve comprehensive upfront planning, phase gate reviews, and fixed deliverables to ensure predictability and control over the project lifecycle.
Core Concepts of DevOps Practices
DevOps practices emphasize continuous integration, continuous delivery, and automation to enhance collaboration between development and operations teams, contrasting with the linear and sequential Waterfall model. Key DevOps concepts include infrastructure as code, automated testing, and real-time monitoring, which accelerate software deployment and improve reliability. This approach fosters a culture of shared responsibility and rapid feedback, enabling faster iteration and innovation.
Workflow Comparison: Sequential vs. Iterative Processes
Waterfall methodology follows a sequential workflow where each phase, from requirements gathering to deployment, is completed before moving to the next, ensuring structured progress but limited flexibility. DevOps employs an iterative workflow that integrates continuous development, testing, and deployment, facilitating rapid feedback and frequent releases. This iterative process enhances collaboration between development and operations teams, accelerating delivery and improving adaptability to change.
Deployment Frequency: Waterfall vs. DevOps
Deployment frequency in Waterfall methodology is typically low, often occurring only at the end of the project lifecycle due to its sequential phases and rigid structure. DevOps emphasizes continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD), enabling multiple deployments daily by automating testing, integration, and release processes. Organizations adopting DevOps experience faster feedback loops, reduced downtime, and accelerated delivery of new features compared to the infrequent releases commonly seen in Waterfall projects.
Change Management in Waterfall and DevOps
Change management in Waterfall follows a linear, rigid process with predefined stages and formal approval gates, emphasizing thorough documentation and minimal scope changes. In contrast, DevOps integrates change management into continuous integration and continuous delivery pipelines, enabling faster, automated, and iterative deployments that enhance collaboration between development and operations teams. The shift from Waterfall to DevOps significantly reduces lead time for changes, improves feedback cycles, and increases overall system reliability through automated testing and monitoring.
Collaboration and Communication Differences
Waterfall methodology follows a linear, sequential approach with limited collaboration between distinct project phases, often causing communication silos. DevOps emphasizes continuous collaboration between development and operations teams through integrated workflows, real-time communication, and shared responsibilities. This fosters faster feedback loops, transparent information exchange, and improved alignment with business objectives.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Waterfall methodology emphasizes risk mitigation through detailed upfront planning, rigid phase transitions, and comprehensive documentation, ensuring risks are identified early and controlled before progressing. DevOps integrates continuous monitoring, automated testing, and frequent releases to detect and address risks in real-time, minimizing the impact on production environments. These contrasting strategies highlight Waterfall's proactive risk containment versus DevOps' dynamic risk management approach.
Quality Assurance Approaches
Waterfall quality assurance involves sequential testing phases occurring after development completion, with a strong emphasis on documentation and defect tracking, ensuring thorough validation at each stage. DevOps QA integrates continuous testing within automated pipelines, promoting rapid feedback and early defect detection through collaboration between development and operations teams. This results in enhanced release frequency and improved software reliability by leveraging automated tools and real-time monitoring throughout the software lifecycle.
Choosing Between Waterfall and DevOps for Your Project
Choosing between Waterfall and DevOps depends on project complexity, flexibility needs, and delivery timelines. Waterfall suits projects with clearly defined requirements and linear phases, ensuring structured progress and documentation. DevOps accelerates development and deployment cycles by promoting collaboration, continuous integration, and iterative testing, ideal for dynamic environments requiring rapid adaptation.
Related Important Terms
Shift-Left Testing
Shift-Left Testing in DevOps enables early defect detection by integrating automated testing at the initial stages of development, reducing costly late-stage fixes compared to the traditional Waterfall model where testing occurs after the build phase. This proactive approach accelerates delivery cycles and improves software quality through continuous feedback and collaboration among cross-functional teams.
Continuous Integration Pipeline
Waterfall methodology follows a linear, sequential approach, resulting in delayed feedback and integration phases, whereas DevOps leverages a continuous integration pipeline to automate code integration, testing, and deployment, enabling rapid identification of defects and faster delivery cycles. Continuous integration pipelines in DevOps utilize tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, or Bamboo, streamlining version control, automated build processes, and unit testing to maintain code quality throughout the development lifecycle.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Waterfall's rigid, sequential phases limit Infrastructure as Code (IaC) integration, resulting in slower infrastructure provisioning and manual configuration drift risks. DevOps leverages IaC for automated, consistent environment deployment, accelerating continuous integration and delivery pipelines while enhancing infrastructure scalability and reliability.
Release Orchestration
Waterfall release orchestration follows a rigid, sequential process that often leads to bottlenecks and delayed delivery, limiting flexibility in managing complex software releases. DevOps emphasizes automated, continuous release orchestration, enabling faster feedback loops, seamless integration, and rapid deployment to optimize software delivery pipelines.
Immutable Infrastructure
Immutable infrastructure in DevOps ensures consistent environments by replacing servers rather than modifying them, reducing configuration drift and deployment errors, whereas Waterfall relies on static, manually updated servers that increase risk during sequential phases. This paradigm shift enhances automation, scalability, and rapid rollback capabilities, contrasting the rigidity and slower feedback loops inherent in Waterfall methodologies.
Automated Deployment Gate
Automated Deployment Gate in DevOps enables continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) by enforcing automated quality checks and approvals before code progresses to production, significantly reducing human errors compared to the manual approval steps typical in Waterfall methodologies. This automation accelerates release cycles, ensures consistent compliance with security and performance standards, and enhances deployment reliability in complex software environments.
Feedback Loop Acceleration
Waterfall development features a linear feedback loop where testing and review occur late, often delaying problem detection and resolution. DevOps accelerates feedback loops through continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, enabling real-time collaboration, rapid iteration, and immediate issue identification across development and operations teams.
Deployment Frequency Metric
Deployment frequency measures how often new code reaches production, with DevOps enabling multiple deployments per day through automation and continuous integration. In contrast, Waterfall models typically have infrequent, large releases, resulting in lower deployment frequency and slower feedback cycles.
Bottleneck Visualization
Waterfall methodology often suffers from limited bottleneck visualization due to its linear and sequential phases, causing delayed identification of project impediments. DevOps enhances bottleneck detection by integrating continuous monitoring tools and real-time feedback loops, enabling faster resolution and improved workflow efficiency.
Legacy Modernization Pathways
Waterfall methodology follows a linear, sequential approach often hindering legacy modernization due to inflexible stages and delayed testing, while DevOps integrates continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, accelerating testing and deployment cycles essential for modernizing legacy systems. Organizations leveraging DevOps achieve faster feedback loops, automated workflows, and improved collaboration, enabling more adaptive and scalable legacy modernization pathways compared to the rigid Waterfall process.
Waterfall vs DevOps Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com