A Bill of Lading (BOL) serves as a physical document representing the ownership and receipt of goods during transportation, whereas an Electronic Bill of Lading (eBOL) digitizes this process for faster, more secure handling. Electronic Bills of Lading enhance efficiency by reducing paper use, minimizing errors, and enabling real-time tracking and transfer of cargo ownership. The adoption of eBOL streamlines logistics operations and fosters global trade by simplifying documentation and improving transparency.
Table of Comparison
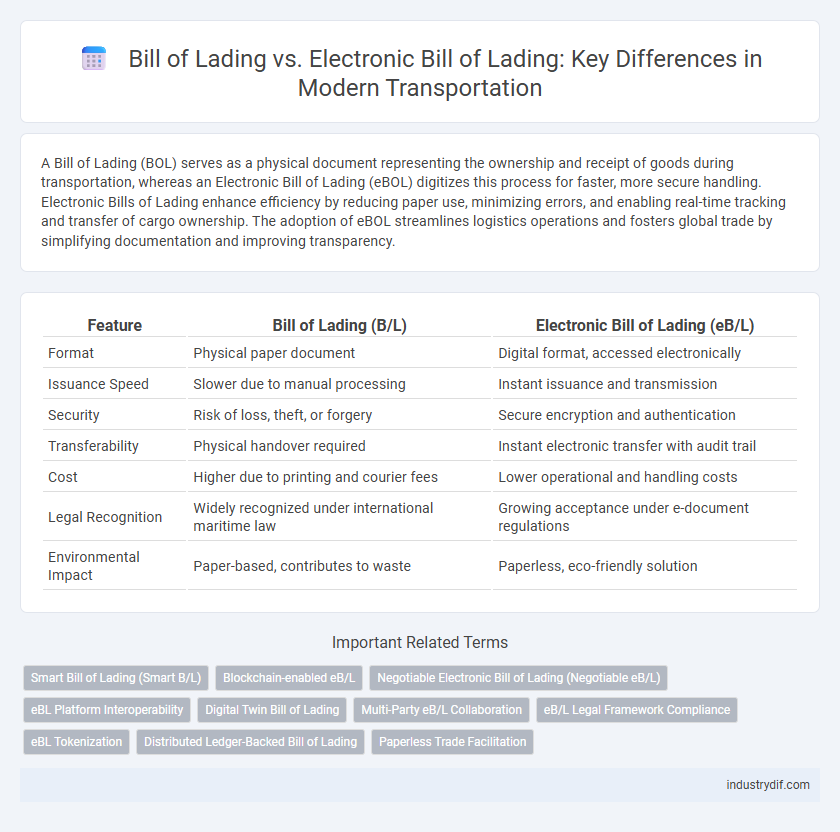
| Feature | Bill of Lading (B/L) | Electronic Bill of Lading (eB/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Format | Physical paper document | Digital format, accessed electronically |
| Issuance Speed | Slower due to manual processing | Instant issuance and transmission |
| Security | Risk of loss, theft, or forgery | Secure encryption and authentication |
| Transferability | Physical handover required | Instant electronic transfer with audit trail |
| Cost | Higher due to printing and courier fees | Lower operational and handling costs |
| Legal Recognition | Widely recognized under international maritime law | Growing acceptance under e-document regulations |
| Environmental Impact | Paper-based, contributes to waste | Paperless, eco-friendly solution |
Introduction to Bill of Lading and Electronic Bill of Lading
A Bill of Lading (BOL) serves as a legal document issued by a carrier to acknowledge receipt of cargo for shipment and outlines the terms of transport between the shipper and carrier. An Electronic Bill of Lading (eBOL) functions as the digital counterpart, utilizing secure technology to streamline documentation, enhance traceability, and reduce paperwork processing time. Both documents are critical in facilitating smooth transactions in international and domestic transportation logistics.
Definition and Purpose of Bill of Lading
The Bill of Lading is a legal document issued by a carrier to acknowledge receipt of cargo for shipment, serving as a contract of carriage and proof of ownership. The Electronic Bill of Lading (eBOL) digitizes this process, facilitating faster, more secure, and efficient documentation transfer in global transportation. Both forms ensure cargo accountability and streamline trade compliance, but eBOL enhances tracking and reduces administrative delays.
What is an Electronic Bill of Lading?
An Electronic Bill of Lading (eB/L) is a digital version of the traditional Bill of Lading used in the transportation industry to document the shipment of goods. It serves as a legally binding receipt and contract of carriage between the shipper and carrier, facilitating faster and more secure transfer of title and cargo information. By leveraging blockchain or secure digital platforms, eB/Ls reduce paperwork, minimize fraud risk, and enhance efficiency in international trade logistics.
Key Differences: Paper vs. Electronic Bill of Lading
A Bill of Lading (B/L) is a traditional paper document serving as a contract and receipt for shipped goods, while an Electronic Bill of Lading (eB/L) is a digital version that facilitates faster processing and real-time tracking. Key differences include the physical nature of the paper B/L, which requires manual handling and is susceptible to loss or forgery, compared to the eB/L's secure, encrypted electronic format that enhances transparency and reduces administrative costs. Electronic Bills of Lading streamline international shipping by enabling instantaneous transfer of ownership and improved compliance with regulatory standards.
Legal Framework Governing Both Formats
The legal framework governing the Bill of Lading (B/L) is well-established under international conventions such as the Hague-Visby Rules and the Maritime Labour Convention, mandating its role as a document of title, receipt, and contract of carriage. Electronic Bill of Lading (eB/L) operates within evolving legal standards, with frameworks like the United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) Model Law on Electronic Transferable Records providing legal recognition and enforceability. Both formats require strict compliance with jurisdiction-specific regulations to ensure validity, secure transfer of ownership, and protection of carrier and consignee rights in global transport transactions.
Advantages of Electronic Bill of Lading
Electronic Bill of Lading offers significant advantages over traditional paper versions, including faster processing times and enhanced security through blockchain technology. It reduces risks of document loss or fraud by providing tamper-proof digital records accessible in real-time. The digital format also facilitates seamless international trade by enabling easier document transfer and verification across global supply chains.
Challenges and Limitations of E-Bill of Lading
Electronic Bill of Lading (e-BL) faces challenges including legal recognition discrepancies across jurisdictions, limited interoperability among diverse maritime platforms, and concerns over cybersecurity vulnerabilities that may compromise document integrity. Unlike traditional paper Bills of Lading, e-BLs require robust digital infrastructure and standardized protocols to ensure secure issuance, transfer, and acceptance by stakeholders such as carriers, shippers, and banks. The transition to e-BL is also hindered by resistance within the shipping industry due to regulatory uncertainties and the need for widespread adoption of electronic signature and verification technologies.
Security and Authentication in Electronic Bills of Lading
Electronic Bills of Lading utilize advanced encryption and blockchain technology to enhance security and prevent tampering, ensuring the authenticity of shipment data. Digital signatures and secure access protocols authenticate parties involved, reducing the risk of fraud compared to traditional paper-based Bills of Lading. These features facilitate seamless verification, traceability, and a reliable audit trail in global transportation logistics.
Adoption Trends in Global Shipping
The adoption of Electronic Bill of Lading (eBL) in global shipping is accelerating due to increased demand for digital transformation and efficiency in supply chain management. Unlike traditional paper-based Bills of Lading, eBLs enable faster transaction processing, enhanced security through blockchain technology, and reduced risk of document loss. Major shipping lines and trade centers are progressively integrating eBL systems to comply with environmental regulations and meet the growing need for real-time cargo tracking and automation.
Future Outlook: Digital Transformation in Transport Documentation
The future of transport documentation is rapidly shifting toward digital transformation, with Electronic Bills of Lading (eBOL) poised to replace traditional paper-based Bills of Lading due to enhanced efficiency and security. Blockchain technology and smart contracts are driving increased adoption of eBOL, enabling real-time tracking, reduced fraud, and streamlined customs processing. Shipping companies and logistics providers investing in interoperable digital platforms are expected to accelerate global trade by minimizing delays associated with manual documentation.
Related Important Terms
Smart Bill of Lading (Smart B/L)
Smart Bill of Lading (Smart B/L) integrates blockchain technology to enhance transparency, security, and efficiency compared to traditional Bill of Lading and Electronic Bill of Lading, enabling real-time tracking and immutable record-keeping throughout the transportation process. This innovation reduces fraud risks, accelerates documentation workflows, and supports seamless digital trade finance and dispute resolution.
Blockchain-enabled eB/L
Blockchain-enabled electronic Bill of Lading (eB/L) enhances traditional Bill of Lading by providing immutable, secure, and traceable shipping documents that streamline cargo transfer and reduce fraud. This decentralized technology ensures real-time verification and seamless integration across stakeholders, significantly improving transparency and efficiency in global transportation logistics.
Negotiable Electronic Bill of Lading (Negotiable eB/L)
The Negotiable Electronic Bill of Lading (Negotiable eB/L) serves as a digital alternative to the traditional Bill of Lading, streamlining the transfer of ownership and facilitating faster, more secure transactions in global shipping. Leveraging blockchain technology and cryptographic signatures, the Negotiable eB/L ensures authenticity, reduces fraud risks, and enables seamless document exchange across multiple parties without the need for physical paper handling.
eBL Platform Interoperability
The Electronic Bill of Lading (eBL) enhances supply chain efficiency by enabling seamless data exchange across different eBL platforms through standardized protocols and APIs, reducing delays and error risks inherent in traditional paper-based Bills of Lading. Interoperability among eBL systems promotes global trade digitization by allowing carriers, freight forwarders, and banks to securely share transactional and ownership data in real-time, accelerating cargo release and payment processes.
Digital Twin Bill of Lading
The Digital Twin Bill of Lading represents an advanced evolution of traditional and electronic bills of lading by creating a real-time, digital replica of the physical shipment document, enhancing tracking accuracy and security throughout the supply chain. This technology integrates IoT data and blockchain to provide immutable, up-to-date information on cargo status, streamlining customs clearance and reducing fraud risk in international transportation.
Multi-Party eB/L Collaboration
Multi-Party eB/L collaboration enables real-time updates and secure document transfer among shippers, carriers, and consignees, enhancing transparency and reducing risks in global supply chains. Unlike traditional paper Bill of Lading, electronic Bills of Lading streamline endorsements and approvals through blockchain technology, ensuring tamper-proof records and faster cargo release.
eB/L Legal Framework Compliance
Electronic Bill of Lading (eB/L) complies with international legal frameworks such as the United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CISG) and the Rotterdam Rules, facilitating secure and efficient digital transfer of ownership while ensuring legal validity equivalent to traditional paper Bills of Lading. The eB/L's adherence to protocols like the UNCITRAL Model Law on Electronic Transferable Records (MLETR) enhances contractual certainty and reduces risks associated with document handling in global shipping logistics.
eBL Tokenization
Electronic Bill of Lading (eBL) tokenization leverages blockchain technology to enhance security, transparency, and efficiency in cargo transactions by transforming traditional paper-based B/Ls into immutable, digital tokens. This process reduces fraud risk, streamlines transfer of ownership, and enables real-time tracking, providing significant advantages over conventional Bills of Lading in global transportation logistics.
Distributed Ledger-Backed Bill of Lading
A Distributed Ledger-Backed Bill of Lading leverages blockchain technology to enhance security, transparency, and immutability compared to traditional paper Bills of Lading, streamlining cargo documentation in global transportation. This electronic solution reduces fraud risk, enables real-time tracking, and facilitates faster settlements by providing a decentralized and tamper-proof record for all stakeholders in the supply chain.
Paperless Trade Facilitation
The Bill of Lading (B/L) is a traditional, paper-based document that serves as a contract and receipt for shipped goods, while the Electronic Bill of Lading (e-B/L) enables seamless, digital transfer of ownership and shipment information, significantly enhancing paperless trade facilitation. E-B/L reduces processing time, minimizes errors, and supports real-time tracking, driving efficiency and cost savings in global supply chain management.
Bill of Lading vs Electronic Bill of Lading Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com