Freight shipping relies on traditional methods like trucks, ships, and trains to move goods, offering established infrastructure and proven reliability. Hyperloop freight promises ultra-high-speed transport using pressurized tubes, significantly reducing delivery times and energy consumption. While freight shipping remains dominant for large-scale, long-distance cargo, hyperloop technology could revolutionize time-sensitive shipments with faster, more efficient logistics.
Table of Comparison
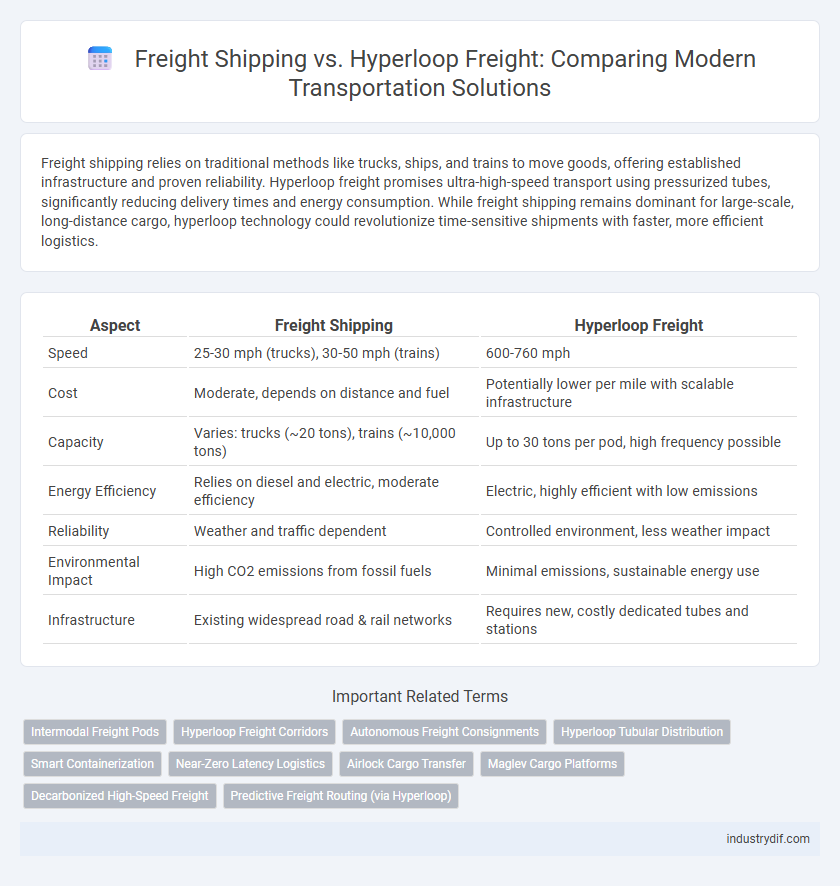
| Aspect | Freight Shipping | Hyperloop Freight |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | 25-30 mph (trucks), 30-50 mph (trains) | 600-760 mph |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on distance and fuel | Potentially lower per mile with scalable infrastructure |
| Capacity | Varies: trucks (~20 tons), trains (~10,000 tons) | Up to 30 tons per pod, high frequency possible |
| Energy Efficiency | Relies on diesel and electric, moderate efficiency | Electric, highly efficient with low emissions |
| Reliability | Weather and traffic dependent | Controlled environment, less weather impact |
| Environmental Impact | High CO2 emissions from fossil fuels | Minimal emissions, sustainable energy use |
| Infrastructure | Existing widespread road & rail networks | Requires new, costly dedicated tubes and stations |
Overview of Freight Shipping and Hyperloop Freight
Freight shipping traditionally involves the transportation of goods via trucks, ships, or airplanes, relying on established logistics networks to deliver cargo efficiently across regional and global markets. Hyperloop freight represents an emerging high-speed transport method using near-vacuum tubes to move pods carrying cargo at speeds exceeding 600 mph, promising significantly reduced transit times and lower emissions. While conventional freight shipping remains dominant due to infrastructure and capacity, hyperloop technology aims to revolutionize the supply chain by offering faster and more sustainable delivery options.
Key Differences Between Traditional Freight and Hyperloop
Traditional freight shipping relies primarily on trucks, ships, and trains, operating on established road, rail, and sea networks with average speeds ranging from 30 to 60 mph. Hyperloop freight utilizes magnetically levitated pods traveling through low-pressure tubes, achieving speeds exceeding 600 mph, drastically reducing transit times and energy consumption. The hyperloop system offers enhanced efficiency, lower carbon emissions, and minimized logistical delays compared to conventional freight transportation methods.
Speed and Efficiency: Freight Shipping vs Hyperloop
Hyperloop freight offers unprecedented speed, capable of transporting goods at speeds up to 700 mph, significantly outperforming traditional freight shipping methods that typically average 25-30 mph for land transport. This rapid transit reduces delivery times from days to mere hours, enhancing supply chain efficiency and responsiveness. The energy-efficient, automated system of hyperloop freight also minimizes operational delays, making it a more reliable and time-effective solution compared to conventional trucking and rail shipping.
Cost Comparison: Freight Shipping vs Hyperloop Freight
Freight shipping costs vary widely depending on distance, weight, and mode, with traditional truck or rail freight averaging $1.50 to $5.00 per mile. Hyperloop freight aims to reduce costs significantly by leveraging high-speed, low-energy transportation, potentially lowering costs to $0.50 to $1.50 per mile due to automation and reduced labor expenses. Initial infrastructure investments for hyperloop are substantial, but long-term operational expenses could provide a competitive advantage over conventional freight shipping.
Environmental Impact of Both Transport Methods
Freight shipping primarily relies on diesel-powered trucks and cargo ships, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, while hyperloop freight utilizes magnetic levitation and electric propulsion, resulting in near-zero carbon emissions during transit. The reduced energy consumption and minimal land use of hyperloop systems lower the environmental footprint compared to traditional freight shipping, which often involves extensive fuel consumption and habitat disruption. Transitioning to hyperloop freight can drastically decrease transportation-related carbon emissions, supporting global sustainability and climate goals.
Infrastructure and Technology Requirements
Freight shipping relies on extensive infrastructure including ports, railroads, and highways designed to handle diverse cargo volumes and types, with mature technology like containerization and GPS tracking enhancing efficiency. Hyperloop freight demands futuristic infrastructure featuring vacuum-sealed tubes, magnetic levitation tracks, and advanced propulsion systems, requiring significant innovation in materials science and energy management. While traditional freight benefits from established technology and widespread networks, hyperloop freight aims to revolutionize speed and sustainability but faces substantial engineering and regulatory challenges before widespread deployment.
Safety and Security in Freight Shipping and Hyperloop
Freight shipping utilizes established safety protocols including GPS tracking, tamper-evident seals, and comprehensive insurance, ensuring secure handling of goods over long distances. Hyperloop freight systems promise enhanced safety through enclosed, automated transport pods operating in vacuum tubes, significantly reducing risks from weather and accidents. Both methods prioritize security, but hyperloop technology offers futuristic advantages in minimizing cargo theft and damage via advanced monitoring and controlled environments.
Scalability and Capacity Considerations
Freight shipping currently relies on extensive infrastructure and established logistics networks that offer high capacity for bulk transport but face scalability limits due to congestion and environmental constraints. Hyperloop freight proposes a revolutionary scalable system utilizing low-pressure tubes to transport cargo at speeds exceeding 700 mph, significantly increasing throughput and reducing transit times. The modular design of hyperloop capsules allows flexible scaling of capacity while minimizing land use and energy consumption compared to traditional freight methods.
Global Adoption and Case Studies
Global adoption of freight shipping remains dominant due to extensive infrastructure, with maritime and rail networks facilitating over 80% of international cargo transport. Hyperloop freight, while in pilot stages, attracts investment for its potential to reduce transit times by up to 90% and lower carbon emissions significantly. Case studies from regions like the United States and Europe highlight experimental corridors demonstrating hyperloop's feasibility for short-haul, high-value goods, positioning it as a transformative complement rather than replacement to traditional freight shipping.
Future Trends in Freight Transportation
Freight shipping continues to rely heavily on trucks, ships, and planes, while Hyperloop freight promises ultra-fast, energy-efficient transport through vacuum-sealed tunnels, revolutionizing delivery speeds and reducing carbon emissions. The integration of Hyperloop systems into existing logistics networks could drastically cut transit times for bulk and high-value goods, positioning it as a flagship future technology in smart freight solutions. Industry projections indicate that Hyperloop freight could capture significant market share within the next decade, driven by rising demand for sustainable and rapid freight transport options.
Related Important Terms
Intermodal Freight Pods
Intermodal freight pods streamline cargo transfer between trucks, ships, and trains by providing standardized, secure containers that minimize handling damage and accelerate logistics. Hyperloop freight systems enhance these pods' efficiency with ultra-high-speed transit in low-pressure tubes, reducing delivery times from days to hours and lowering carbon emissions compared to traditional freight shipping methods.
Hyperloop Freight Corridors
Hyperloop freight corridors offer significantly faster transit times compared to traditional freight shipping methods by utilizing near-vacuum tubes to reduce air resistance and friction. This innovative transportation technology enhances cargo efficiency, reduces carbon emissions, and promises disruptive improvements in supply chain logistics across urban and intercity routes.
Autonomous Freight Consignments
Autonomous freight consignments in traditional freight shipping rely on driverless trucks equipped with AI and GPS for route optimization and real-time tracking, enhancing delivery efficiency and safety. Hyperloop freight systems leverage autonomous pods traveling at high speeds within vacuum tubes, significantly reducing transit times and minimizing human intervention in supply chain logistics.
Hyperloop Tubular Distribution
Hyperloop tubular distribution leverages vacuum-sealed tubes to transport freight at speeds exceeding 600 mph, significantly reducing transit times compared to traditional freight shipping methods. This cutting-edge system offers enhanced energy efficiency, reduced carbon emissions, and improved cargo security by isolating shipments from external environmental factors.
Smart Containerization
Smart containerization in freight shipping enhances logistics efficiency through real-time tracking, automated loading, and optimized space utilization, reducing costs and delivery times. Hyperloop freight integrates advanced smart containers designed for high-speed transit, maintaining cargo integrity and enabling seamless intermodal transfers, revolutionizing supply chain dynamics.
Near-Zero Latency Logistics
Freight shipping relies on traditional transportation methods that often encounter delays due to traffic congestion, customs processing, and handling times, resulting in higher latency in supply chain operations. Hyperloop freight offers near-zero latency logistics by utilizing vacuum-sealed tubes for ultra-fast, uninterrupted transit, drastically reducing delivery times and enabling real-time inventory management.
Airlock Cargo Transfer
Airlock cargo transfer in hyperloop freight ensures airtight, rapid loading and unloading of goods, minimizing contamination and pressure variation during transit compared to traditional freight shipping methods. This technology significantly enhances cargo safety and speed by maintaining controlled atmospheric conditions throughout the transport process.
Maglev Cargo Platforms
Maglev cargo platforms offer a revolutionary advancement in freight shipping by enabling ultra-high-speed, frictionless transport for hyperloop freight systems, significantly reducing transit times compared to traditional trucking and rail. The integration of maglev technology in hyperloop freight enhances efficiency through magnetic levitation, decreasing mechanical wear and energy consumption while supporting higher payload capacities and geospatial connectivity.
Decarbonized High-Speed Freight
Freight shipping traditionally relies on diesel-powered trucks and cargo ships, contributing significantly to carbon emissions, whereas hyperloop freight leverages magnetic levitation and electrification to enable decarbonized high-speed freight transport with near-zero emissions. The hyperloop system promises faster delivery times and reduced environmental impact, making it a revolutionary solution for sustainable logistics and supply chain optimization.
Predictive Freight Routing (via Hyperloop)
Predictive freight routing in Hyperloop systems leverages real-time data analytics and high-speed sensor networks to optimize shipment paths, reducing transit times and improving reliability compared to traditional freight shipping. Advanced algorithms forecast traffic patterns, system capacity, and maintenance schedules, enabling more precise scheduling and dynamic rerouting that enhances supply chain efficiency and lowers operational costs.
Freight Shipping vs Hyperloop Freight Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com