Delivery vans offer reliable, high-capacity transportation for urban and suburban logistics, efficiently handling bulky goods and large shipments. Cargo drones provide rapid, flexible delivery solutions, especially useful for last-mile transport and hard-to-reach areas, reducing traffic congestion and carbon emissions. Choosing between delivery vans and cargo drones depends on factors like delivery volume, distance, speed requirements, and environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
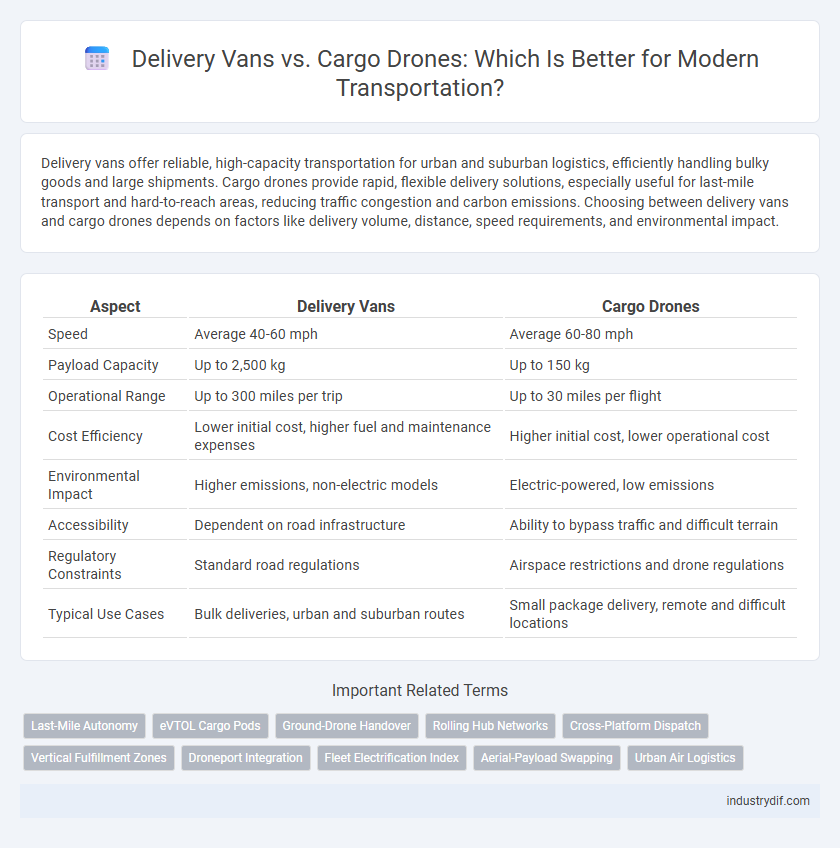
| Aspect | Delivery Vans | Cargo Drones |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Average 40-60 mph | Average 60-80 mph |
| Payload Capacity | Up to 2,500 kg | Up to 150 kg |
| Operational Range | Up to 300 miles per trip | Up to 30 miles per flight |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower initial cost, higher fuel and maintenance expenses | Higher initial cost, lower operational cost |
| Environmental Impact | Higher emissions, non-electric models | Electric-powered, low emissions |
| Accessibility | Dependent on road infrastructure | Ability to bypass traffic and difficult terrain |
| Regulatory Constraints | Standard road regulations | Airspace restrictions and drone regulations |
| Typical Use Cases | Bulk deliveries, urban and suburban routes | Small package delivery, remote and difficult locations |
Overview of Delivery Vans and Cargo Drones
Delivery vans remain the backbone of urban and suburban logistics, offering high payload capacity and established route flexibility for transporting goods over medium to long distances. Cargo drones provide innovative solutions for fast, last-mile delivery with the ability to bypass traffic congestion and access hard-to-reach areas, though they are limited by payload size and flight range. Both delivery vans and cargo drones contribute to modern transportation networks by optimizing efficiency and expanding delivery options based on package weight and delivery urgency.
Key Differences Between Vans and Drones
Delivery vans offer higher payload capacity and extended range suitable for bulk shipments across urban and rural areas, whereas cargo drones excel in speed and maneuverability for lightweight, urgent deliveries within congested or hard-to-reach locations. Vans operate primarily on established road networks, incurring fuel or maintenance costs, while drones leverage aerial routes reducing transit time but face limitations in battery life and regulatory restrictions. The choice between vans and drones depends on factors such as delivery volume, geographic constraints, and urgency of shipment.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Delivery vans typically offer consistent speed and high payload capacity, making them ideal for bulk shipments over urban and suburban routes, while cargo drones excel in rapid delivery for lightweight parcels across congested or hard-to-reach areas. Cargo drones reduce delivery time through direct aerial routes, bypassing ground traffic delays, thereby enhancing efficiency in time-sensitive deliveries. However, their limited battery life and payload restrict widespread use compared to the versatile range and load capabilities of delivery vans.
Cost Analysis: Vans vs Drones
Delivery vans typically involve higher operational costs due to fuel consumption, maintenance, and driver wages, averaging around $0.60 to $1.00 per mile. Cargo drones offer lower per-delivery expenses by reducing labor costs and fuel use, with estimates ranging from $0.10 to $0.30 per mile, though initial technology investments remain high. Evaluating total cost of ownership and scalability is crucial when comparing these transportation modes for urban and last-mile delivery services.
Payload Capacity and Size Limits
Delivery vans typically offer payload capacities ranging from 1,000 to 3,000 kilograms, accommodating larger and bulkier shipments with flexible size limits. Cargo drones, however, usually have payload capacities under 50 kilograms, restricting them to smaller packages but providing enhanced speed and access to hard-to-reach locations. Size limitations of cargo drones are influenced by aviation regulations and battery technology, whereas vans face fewer volumetric constraints but are limited by road infrastructure and traffic conditions.
Environmental Impact & Sustainability
Delivery vans contribute significantly to carbon emissions, consuming large amounts of fossil fuels and increasing urban air pollution. Cargo drones, powered by electricity, offer a sustainable alternative with zero direct emissions and reduced noise pollution, making them ideal for eco-friendly last-mile delivery. Transitioning to cargo drones can substantially lower the carbon footprint of logistics operations while promoting greener urban environments.
Urban vs Rural Delivery Suitability
Delivery vans excel in rural areas due to their larger payload capacity and ability to navigate longer distances on established road networks. Cargo drones provide faster, more efficient delivery in urban environments, where dense populations and traffic congestion hinder ground vehicle movement. The scalability of drone technology supports frequent, last-mile deliveries in cities, whereas delivery vans remain the preferred solution for bulk shipments in rural regions.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Delivery vans must comply with established road safety regulations, including driver licensing, vehicle inspections, and traffic laws, ensuring reliable and accountable operation within urban and suburban areas. Cargo drones face evolving regulatory frameworks emphasizing airspace management, flight permissions, and stringent safety protocols to prevent collisions and protect public safety, with agencies like the FAA leading these efforts. Both delivery methods require ongoing coordination with regulators to address privacy concerns, noise pollution, and emergency response measures essential for safe and lawful operation.
Technology Integration and Automation
Delivery vans increasingly incorporate advanced telematics, GPS tracking, and automated routing systems to enhance efficiency and reduce delivery times. Cargo drones leverage cutting-edge autonomous flight technology, AI-powered navigation, and real-time sensor data to enable precise, contactless deliveries in urban and remote areas. Both vehicles utilize Internet of Things (IoT) integration for fleet management, though drones emphasize automation to minimize human intervention and optimize last-mile logistics.
Future Trends in Last-Mile Delivery
Delivery vans remain dominant in last-mile delivery due to their capacity and established infrastructure, but cargo drones are rapidly gaining traction for their speed and accessibility in urban and remote areas. Advancements in autonomous technology, battery efficiency, and air traffic management systems are expected to enhance drone deployment, reducing delivery times and operational costs. Integration of hybrid models combining vans and drones will optimize route efficiency and address increasing consumer demand for faster, eco-friendly deliveries.
Related Important Terms
Last-Mile Autonomy
Delivery vans offer robust payload capacity and established infrastructure integration for last-mile autonomy, ensuring reliable transport of diverse goods in urban and suburban areas. Cargo drones enhance efficiency by bypassing traffic congestion and reducing delivery times through aerial routes, providing agile solutions for lightweight, time-sensitive parcels.
eVTOL Cargo Pods
eVTOL cargo pods integrated into delivery vans enhance urban logistics by providing versatile, efficient last-mile delivery, reducing traffic congestion and carbon emissions. Cargo drones with eVTOL technology offer rapid deployment for lightweight parcels, complementing delivery vans by covering hard-to-reach areas and optimizing supply chain resilience.
Ground-Drone Handover
Delivery vans provide reliable bulk transport capacity while cargo drones enable rapid aerial delivery, and efficient ground-drone handover systems integrate these strengths by transferring packages from vans to drones at designated hubs, optimizing last-mile logistics. This hybrid approach reduces delivery times, lowers carbon emissions, and expands reach in urban and suburban areas where drone autonomy is limited.
Rolling Hub Networks
Rolling hub networks optimize delivery efficiency by enabling delivery vans to serve as mobile distribution centers, reducing last-mile transit times and increasing route flexibility. Cargo drones complement these networks by rapidly transporting parcels between hubs, bypassing ground traffic congestion and expanding the reach of urban logistics systems.
Cross-Platform Dispatch
Cross-platform dispatch integrates delivery vans and cargo drones, optimizing route efficiency and enabling real-time load balancing between ground and aerial transport. Leveraging GPS tracking and AI-driven logistics platforms, this synergy reduces delivery times and enhances fleet utilization in urban and rural environments.
Vertical Fulfillment Zones
Delivery vans dominate traditional urban logistics with high payload capacity and established infrastructure, yet face challenges navigating congested streets and limited access to vertical fulfillment zones in dense cityscapes. Cargo drones excel in vertical fulfillment zones by bypassing ground traffic, enabling rapid aerial delivery directly to elevated pickup points or rooftop warehouses, optimizing last-mile efficiency in multi-level urban environments.
Droneport Integration
Integrating droneports within urban logistics networks enhances the efficiency of cargo drone deliveries by enabling rapid loading, unloading, and battery swaps, significantly reducing turnaround times compared to traditional delivery vans. This infrastructure supports scalable drone operations, optimizing last-mile delivery routes while minimizing traffic congestion and carbon emissions in densely populated areas.
Fleet Electrification Index
The Fleet Electrification Index highlights a growing shift toward electric delivery vans, which currently lead with higher adoption rates due to established infrastructure and payload capacity. Cargo drones, while promising faster last-mile delivery, face challenges in electrification scalability and regulatory approvals that impact their fleet integration.
Aerial-Payload Swapping
Cargo drones enhance delivery efficiency by utilizing aerial-payload swapping, enabling quick exchanges of packages mid-flight to cover longer distances without returning to base. Delivery vans offer larger payload capacities but lack the agility and speed of cargo drones, making them less effective for urgent or remote deliveries in congested urban areas.
Urban Air Logistics
Cargo drones offer faster urban air logistics with reduced traffic congestion and lower emissions compared to traditional delivery vans, which face road delays and limited maneuverability in dense city environments. Leveraging advanced drone technology enhances delivery efficiency for last-mile solutions by overcoming ground traffic challenges and enabling access to hard-to-reach urban areas.
Delivery Vans vs Cargo Drones Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com