Shuttle services offer fixed routes and schedules ideal for predictable, high-demand corridors, while microtransit provides flexible, on-demand routing that adapts to real-time passenger requests. Microtransit leverages technology to optimize shared rides and reduce wait times, making it suitable for low-density areas or off-peak hours. Both solutions enhance urban mobility by reducing private vehicle use, but choosing between them depends on factors like route consistency, demand patterns, and operational costs.
Table of Comparison
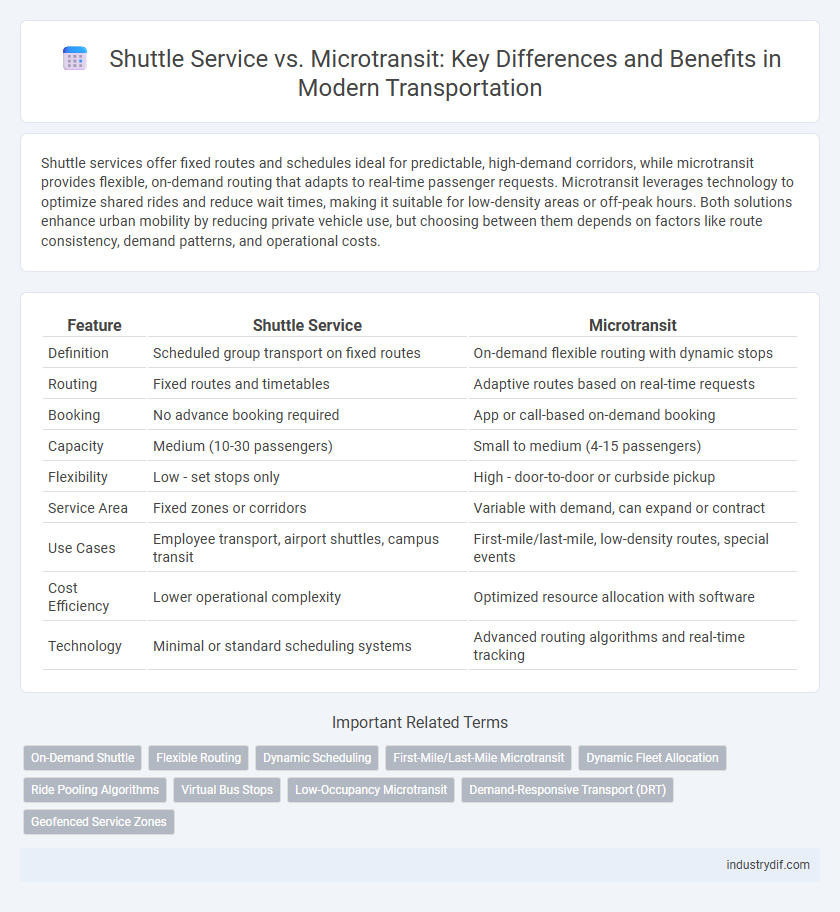
| Feature | Shuttle Service | Microtransit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scheduled group transport on fixed routes | On-demand flexible routing with dynamic stops |
| Routing | Fixed routes and timetables | Adaptive routes based on real-time requests |
| Booking | No advance booking required | App or call-based on-demand booking |
| Capacity | Medium (10-30 passengers) | Small to medium (4-15 passengers) |
| Flexibility | Low - set stops only | High - door-to-door or curbside pickup |
| Service Area | Fixed zones or corridors | Variable with demand, can expand or contract |
| Use Cases | Employee transport, airport shuttles, campus transit | First-mile/last-mile, low-density routes, special events |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational complexity | Optimized resource allocation with software |
| Technology | Minimal or standard scheduling systems | Advanced routing algorithms and real-time tracking |
Overview of Shuttle Service and Microtransit
Shuttle services operate on fixed routes and schedules, providing reliable, scheduled transportation primarily for short distances or specific communities such as corporate campuses or airports. Microtransit offers flexible, on-demand routing and scheduling using smaller vehicles, adapting dynamically to rider requests within defined service areas to enhance accessibility and efficiency. Both transportation modes aim to reduce congestion and complement public transit by filling first-mile/last-mile gaps.
Key Differences Between Shuttle Service and Microtransit
Shuttle service operates on fixed routes and schedules, providing consistent, predictable transportation primarily for specific groups or locations, such as airports or corporate campuses. Microtransit offers flexible routing and dynamic scheduling tailored to real-time demand, enhancing accessibility in urban and suburban areas often underserved by traditional public transit. Key differences include shuttle service's fixed operational framework versus microtransit's adaptive, technology-driven model designed for scalability and efficiency.
Operational Models: Fixed-Route vs On-Demand
Shuttle service operates on a fixed-route model, offering scheduled stops along predetermined paths ideal for consistent, high-demand corridors. Microtransit employs an on-demand operational model, utilizing dynamic routing and flexible scheduling to respond to real-time passenger requests in areas with variable demand. The choice between fixed-route shuttle services and on-demand microtransit affects fleet management, service efficiency, and passenger accessibility within urban transportation systems.
Fleet Types and Vehicle Capacities
Shuttle services typically utilize larger vehicles such as minibuses or vans with capacities ranging from 10 to 30 passengers, designed for fixed routes or scheduled stops. Microtransit employs smaller, flexible vehicles like vans or small buses that accommodate approximately 6 to 15 passengers, operating on-demand or with dynamic routing to serve dispersed areas. Fleet composition in shuttle services emphasizes higher capacity and consistent schedules, whereas microtransit fleets prioritize adaptability and efficiency for variable passenger demand.
Technology Integration in Shuttle Service and Microtransit
Shuttle services leverage GPS tracking and real-time scheduling software to optimize fixed routes, ensuring timely pickups and drop-offs for commuters. Microtransit integrates advanced algorithms with dynamic routing and mobile app platforms to provide flexible, demand-responsive transportation tailored to individual passenger needs. Both systems utilize IoT sensors and data analytics to enhance efficiency, reduce wait times, and improve overall user experience in urban transit ecosystems.
Cost Efficiency and Funding Models
Shuttle service typically operates on fixed routes and schedules, leading to predictable operating costs and easier budgeting for municipalities or private operators. Microtransit offers flexible, demand-responsive routing, which can optimize vehicle utilization and reduce per-trip expenses but often requires dynamic pricing or subsidies to remain cost-efficient. Funding models for shuttle services commonly rely on steady farebox revenue and public grants, while microtransit may depend more on variable subsidies, partnerships, and advanced technology investments to manage operational costs.
Convenience and User Experience Comparison
Shuttle services provide fixed routes and schedules, offering predictable and reliable transportation ideal for commuters and event attendees. Microtransit uses on-demand routing with flexible stops, enhancing convenience by adapting to passenger requests and reducing wait times. User experience in microtransit often scores higher due to personalized service and real-time booking, while shuttle services excel in simplicity and consistency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Shuttle service typically operates on fixed routes and schedules, which can lead to underutilized vehicles and higher emissions per passenger compared to microtransit. Microtransit offers flexible routing and on-demand pickups, optimizing vehicle capacity and reducing overall emissions by minimizing empty miles. By integrating electric or hybrid vehicles, microtransit significantly enhances sustainability efforts over traditional shuttle services.
Application Scenarios: When to Use Shuttle vs Microtransit
Shuttle services excel in fixed-route, high-demand corridors such as corporate campuses, airports, and universities where predictability and scheduled stops are critical. Microtransit provides flexible, on-demand transit solutions ideal for low-density suburban areas, first-mile/last-mile connections, and off-peak times when traditional fixed routes are inefficient. Choosing shuttle or microtransit depends on factors like passenger volume, route flexibility requirements, and service area density.
Future Trends in Urban Mobility Solutions
Shuttle services and microtransit both represent evolving urban mobility solutions designed to optimize last-mile connectivity and reduce congestion in growing cities. Emerging trends point to microtransit integrating advanced AI routing algorithms and on-demand scheduling, increasing efficiency over fixed-route shuttle services by adapting dynamically to real-time passenger demand. Future urban transportation frameworks will likely blend shuttle reliability with microtransit flexibility, incorporating electric and autonomous vehicle technologies to enhance sustainability and accessibility.
Related Important Terms
On-Demand Shuttle
On-demand shuttle service offers flexible, real-time route adjustments powered by dynamic dispatch systems, enhancing accessibility compared to fixed-route microtransit models. This approach optimizes vehicle utilization and reduces wait times, making it a cost-effective solution for urban and suburban transportation networks.
Flexible Routing
Shuttle services typically follow fixed routes and schedules, limiting flexibility in pick-up and drop-off locations, whereas microtransit offers dynamic, on-demand routing that adapts to real-time passenger requests and traffic conditions for optimized travel efficiency. Integrating advanced algorithms and GPS technology, microtransit provides a scalable solution that enhances last-mile connectivity and reduces wait times compared to conventional shuttle systems.
Dynamic Scheduling
Dynamic scheduling in shuttle services typically follows fixed routes with flexible timing to accommodate peak demand, optimizing rider convenience while maintaining operational efficiency. Microtransit enhances dynamic scheduling by utilizing real-time data and algorithm-driven routing that adapts continuously to user requests, offering a more responsive and scalable urban transportation solution.
First-Mile/Last-Mile Microtransit
First-mile/last-mile microtransit provides flexible, on-demand transportation solutions connecting riders from transit hubs to final destinations, enhancing accessibility beyond fixed-route shuttle services. Unlike traditional shuttle service with fixed schedules and routes, microtransit optimizes route efficiency through dynamic scheduling and real-time data, improving rider convenience and reducing wait times.
Dynamic Fleet Allocation
Dynamic fleet allocation in shuttle service utilizes fixed routes with scheduled pickups, optimizing vehicle use for predictable demand patterns. Microtransit employs real-time data to dynamically route and assign vehicles, enhancing flexibility and efficiency in responding to variable passenger requests across diverse urban areas.
Ride Pooling Algorithms
Ride pooling algorithms in shuttle service optimize fixed routes by efficiently grouping passengers with similar origins and destinations to minimize detours and wait times. In contrast, microtransit leverages dynamic, real-time routing algorithms that adapt to passenger demand and traffic conditions, enhancing route flexibility and service coverage.
Virtual Bus Stops
Virtual bus stops in shuttle service offer fixed, pre-determined pickup points that optimize route efficiency and reduce wait times. In microtransit, virtual stops adapt dynamically based on passenger demand, enhancing flexibility and coverage across urban and suburban areas.
Low-Occupancy Microtransit
Low-occupancy microtransit offers flexible, on-demand routes that adapt to real-time passenger needs, contrasting with the fixed schedules and routes of traditional shuttle services. This approach reduces operational costs and vehicle emissions while enhancing accessibility in low-density areas by efficiently matching supply with demand.
Demand-Responsive Transport (DRT)
Shuttle service typically operates on fixed routes and schedules, while microtransit leverages demand-responsive transport (DRT) technology to provide flexible, on-demand routing based on real-time passenger requests. DRT enhances efficiency and reduces wait times by dynamically adjusting routes, making microtransit a scalable solution for urban and suburban mobility challenges.
Geofenced Service Zones
Shuttle services typically operate within fixed routes and clearly defined geofenced service zones, ensuring predictable travel paths and schedules. Microtransit leverages dynamic routing within flexible geofenced zones, optimizing real-time passenger demand and expanding service coverage efficiently.
Shuttle Service vs Microtransit Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com