Wholesale involves bulk purchasing directly from suppliers to resell at competitive prices, emphasizing large volumes and long-term supplier relationships. Social commerce leverages social media platforms to enable direct selling through user engagement and influencer marketing, focusing on convenience and personalized shopping experiences. Both models drive sales growth but cater to different consumer behaviors and business strategies in the digital marketplace.
Table of Comparison
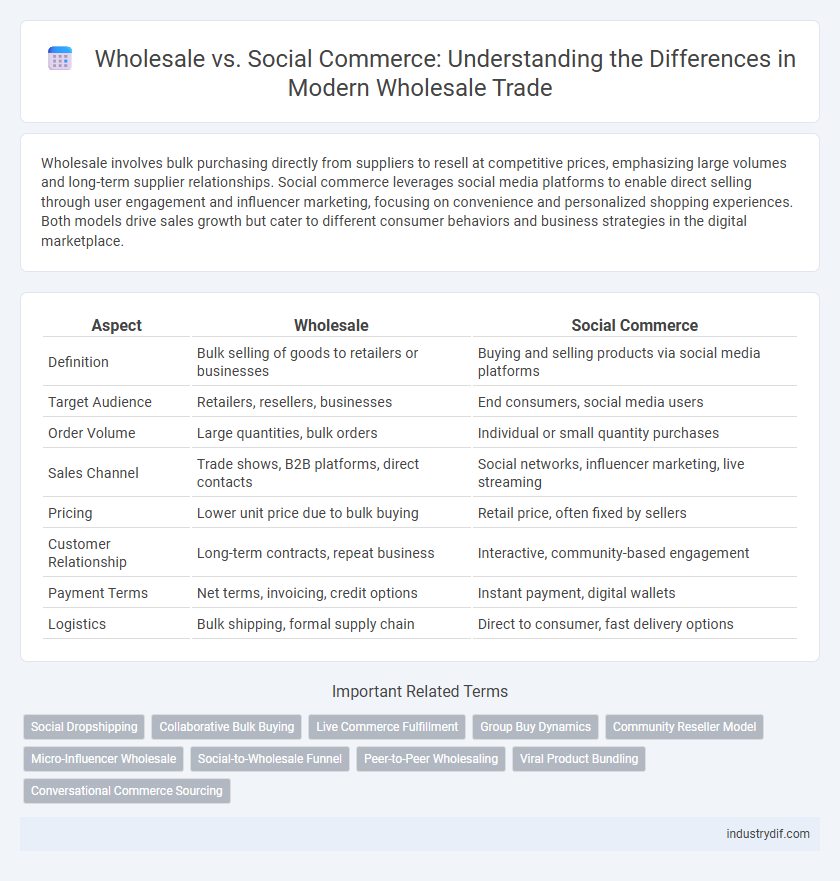
| Aspect | Wholesale | Social Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bulk selling of goods to retailers or businesses | Buying and selling products via social media platforms |
| Target Audience | Retailers, resellers, businesses | End consumers, social media users |
| Order Volume | Large quantities, bulk orders | Individual or small quantity purchases |
| Sales Channel | Trade shows, B2B platforms, direct contacts | Social networks, influencer marketing, live streaming |
| Pricing | Lower unit price due to bulk buying | Retail price, often fixed by sellers |
| Customer Relationship | Long-term contracts, repeat business | Interactive, community-based engagement |
| Payment Terms | Net terms, invoicing, credit options | Instant payment, digital wallets |
| Logistics | Bulk shipping, formal supply chain | Direct to consumer, fast delivery options |
Understanding Wholesale and Social Commerce
Wholesale involves purchasing goods in bulk directly from manufacturers or distributors at discounted prices, enabling retailers to sell products at competitive rates. Social commerce integrates e-commerce with social media platforms, allowing users to discover and buy products through social interactions, reviews, and influencer recommendations. Understanding the differences helps businesses optimize supply chain strategies and leverage social networks to boost sales and customer engagement.
Key Differences Between Wholesale and Social Commerce
Wholesale involves bulk purchasing directly from manufacturers or distributors, enabling businesses to obtain goods at lower costs for resale. Social commerce centers on selling products through social media platforms, leveraging influencer marketing and user engagement to drive sales. Key differences lie in the target audience, transaction scale, and marketing strategies, with wholesale focusing on B2B bulk orders and social commerce emphasizing B2C personalized shopping experiences.
Advantages of Wholesale Models
Wholesale models offer significant advantages including bulk purchasing discounts, streamlined supply chain management, and consistent inventory availability, which are essential for businesses targeting large-scale distribution. Unlike social commerce, wholesale facilitates direct relationships between manufacturers and retailers, reducing intermediary costs and enhancing pricing competitiveness. The scalability of wholesale operations supports sustained growth and market penetration across diverse geographic regions.
Benefits of Social Commerce Platforms
Social commerce platforms enhance customer engagement by integrating shopping experiences directly within social media, increasing conversion rates and reducing friction in the buyer journey. They offer real-time customer feedback and influencer partnerships, driving targeted marketing and building trust through peer recommendations. These platforms provide scalable solutions for small and medium enterprises to reach wider audiences without the traditional overheads associated with wholesale distribution.
Target Markets: Wholesale vs Social Commerce
Wholesale primarily targets businesses, retailers, and large-scale buyers seeking bulk purchases and consistent supply chains. Social commerce focuses on individual consumers influenced by social media trends and peer recommendations, leveraging platforms like Instagram and TikTok for direct engagement. Targeting strategies in wholesale emphasize B2B relationships and volume discounts, while social commerce aims to drive impulse purchases and personalized experiences through social interactions.
Pricing Strategies in Wholesale and Social Commerce
Wholesale pricing strategies prioritize volume discounts and bulk purchase incentives to attract retailers and maximize large-scale sales. Social commerce employs dynamic pricing, personalized offers, and flash sales to engage individual consumers and drive impulse purchases through social platforms. The contrast lies in wholesale's emphasis on cost-efficiency per unit versus social commerce's focus on consumer behavior and real-time pricing adjustments.
Supply Chain Management: Wholesale vs Social Commerce
Wholesale supply chain management emphasizes bulk purchasing, centralized warehousing, and long-term vendor relationships to optimize inventory turnover and reduce costs. Social commerce supply chains prioritize agility, real-time demand forecasting, and integration with digital platforms to swiftly respond to consumer trends and personalize product offerings. Efficient coordination in wholesale supports large-scale distribution, while social commerce depends on seamless digital infrastructure and rapid fulfillment for fragmented, direct-to-consumer sales.
Technology’s Role in Wholesale and Social Commerce
Technology revolutionizes wholesale by enabling advanced inventory management systems, real-time data analytics, and automated order processing, which streamline supply chain efficiency. In social commerce, technology integrates social media platforms with seamless checkout experiences, leveraging AI-driven personalized recommendations to boost consumer engagement. Both sectors harness cloud computing and mobile applications to enhance connectivity and scalability, transforming traditional retail landscapes.
Marketing Approaches: Wholesale vs Social Commerce
Wholesale marketing strategies emphasize bulk selling, long-term contracts, and direct relationships with retailers to achieve economies of scale and consistent market penetration. Social commerce leverages social media platforms for personalized marketing, influencer collaborations, and real-time customer engagement to drive immediate consumer purchases. Data-driven targeting and content personalization differentiate social commerce, while wholesale relies on supply chain efficiency and volume-based pricing.
Future Trends in Wholesale and Social Commerce
Future trends in wholesale emphasize automation, AI-driven inventory management, and seamless integration with digital platforms to enhance efficiency and scalability. Social commerce is evolving through personalized shopping experiences, influencer partnerships, and augmented reality, driving direct consumer engagement and sales. Both sectors increasingly leverage data analytics and omnichannel strategies to optimize supply chains and customer journeys in a digitally connected marketplace.
Related Important Terms
Social Dropshipping
Social dropshipping leverages social commerce platforms to directly connect sellers with consumers, bypassing traditional wholesale inventories and reducing upfront costs. This model accelerates market entry for small businesses by utilizing influencer marketing and real-time consumer engagement to drive sales without managing physical stock.
Collaborative Bulk Buying
Collaborative bulk buying in wholesale enables multiple buyers to combine orders, unlocking significant discounts and reducing per-unit costs by leveraging collective purchasing power. Social commerce enhances this process by facilitating seamless communication and coordination among buyers through integrated social platforms, streamlining group negotiations and order management.
Live Commerce Fulfillment
Wholesale leverages bulk inventory management and streamlined supply chain logistics to optimize Live Commerce Fulfillment, enabling faster delivery and reduced costs compared to Social Commerce models. Integrating real-time order processing systems in wholesale enhances Live Commerce by ensuring accurate stock availability and seamless large-scale distribution.
Group Buy Dynamics
Wholesale leverages bulk purchasing power to reduce costs and maximize margins, while social commerce harnesses group buy dynamics to aggregate individual consumer demand, unlocking exclusive discounts through collective bargaining. Group buying in social commerce fosters community-driven purchasing behavior, enabling smaller buyers to access wholesale-like prices by pooling orders together.
Community Reseller Model
The Community Reseller Model leverages social networks to enable individuals to sell wholesale products directly within their communities, blending traditional wholesale scale with social commerce dynamics. This model fosters trust and personalized engagement, driving higher conversion rates compared to conventional wholesale channels that rely on bulk transactions without direct consumer interaction.
Micro-Influencer Wholesale
Micro-influencer wholesale leverages niche audiences to drive targeted bulk sales, combining the reach of small-scale influencers with traditional wholesale distribution channels. This approach enhances brand authenticity and customer engagement compared to broader social commerce strategies, optimizing conversion rates through personalized influencer endorsements.
Social-to-Wholesale Funnel
The Social-to-Wholesale funnel integrates social commerce strategies to drive bulk purchasing by leveraging influencer marketing, user-generated content, and real-time social interactions that boost brand trust and streamline order acquisition. This approach enhances wholesale scalability by converting engaged social audiences into consistent wholesale buyers through targeted social campaigns and data-driven customer insights.
Peer-to-Peer Wholesaling
Peer-to-Peer Wholesaling merges wholesale efficiency with social commerce dynamics by enabling direct transactions between individual sellers and buyers, reducing intermediaries and fostering trust through personal networks. This model leverages digital platforms to facilitate bulk purchasing within social circles, enhancing scalability and access to diverse products compared to traditional wholesale channels.
Viral Product Bundling
Wholesale leverages bulk purchases to maximize profit margins by offering discounted rates on large quantities, while social commerce drives sales through peer recommendations and viral product bundling strategies that enhance customer engagement. Viral product bundling in social commerce boosts average order value by combining complementary items into shareable deals, creating rapid spread and higher conversion rates compared to traditional wholesale distribution.
Conversational Commerce Sourcing
Wholesale enables bulk purchasing from suppliers, streamlining inventory management and reducing per-unit costs, while social commerce leverages conversational commerce sourcing through direct interactions and personalized recommendations on social platforms to enhance buyer engagement and accelerate decision-making. Integrating conversational commerce sourcing in social channels facilitates real-time negotiation and tailored product discovery, bridging the efficiency of wholesale distribution with the dynamic, relationship-driven nature of social commerce.
Wholesale vs Social Commerce Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com