Wholesale involves purchasing large quantities of products directly from manufacturers or distributors at discounted rates, enabling businesses to resell at competitive prices. Social sourcing leverages social networks and platforms to identify and procure products, often emphasizing unique or niche items through community recommendations. While wholesale ensures consistent supply and cost efficiency, social sourcing offers greater variety and personalized product discovery.
Table of Comparison
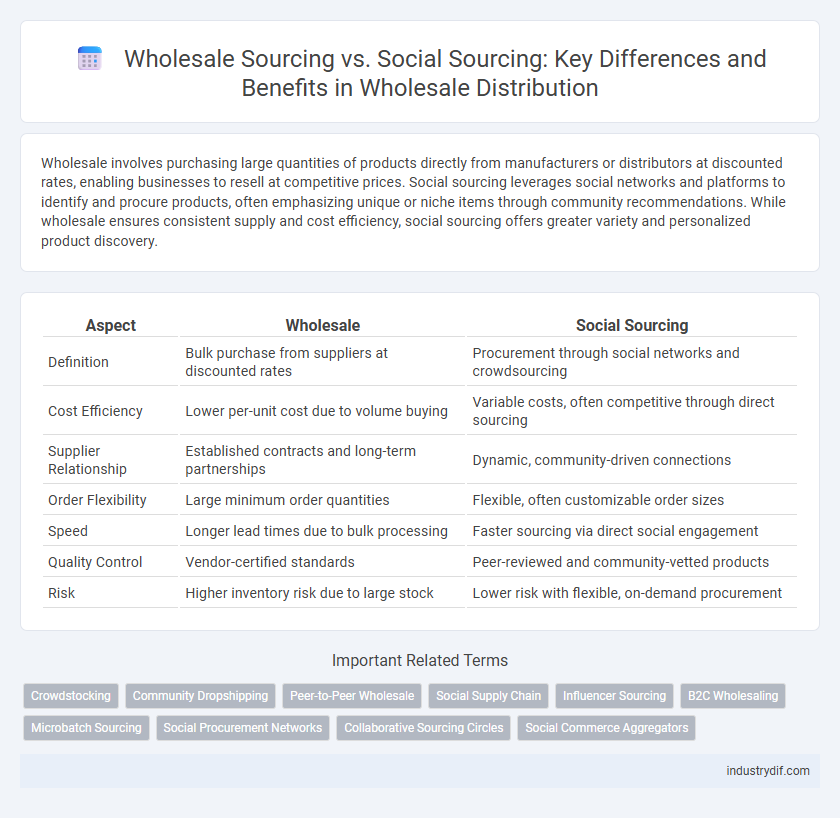
| Aspect | Wholesale | Social Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bulk purchase from suppliers at discounted rates | Procurement through social networks and crowdsourcing |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower per-unit cost due to volume buying | Variable costs, often competitive through direct sourcing |
| Supplier Relationship | Established contracts and long-term partnerships | Dynamic, community-driven connections |
| Order Flexibility | Large minimum order quantities | Flexible, often customizable order sizes |
| Speed | Longer lead times due to bulk processing | Faster sourcing via direct social engagement |
| Quality Control | Vendor-certified standards | Peer-reviewed and community-vetted products |
| Risk | Higher inventory risk due to large stock | Lower risk with flexible, on-demand procurement |
Definition of Wholesale and Social Sourcing
Wholesale involves purchasing large quantities of goods directly from manufacturers or distributors at reduced prices for resale to retailers or consumers, emphasizing bulk transactions and supply chain efficiency. Social sourcing leverages social networks and community engagement to discover and procure products or services, prioritizing collaboration, transparency, and often localized or niche market opportunities. Both strategies differ fundamentally in scale, relationship dynamics, and sourcing methodology within supply chain management.
Core Differences Between Wholesale and Social Sourcing
Wholesale involves purchasing large quantities of products directly from manufacturers or distributors to resell at a profit, emphasizing bulk transactions and fixed pricing structures. Social sourcing leverages online platforms and peer networks to discover, evaluate, and procure products or suppliers, focusing on transparency, collaboration, and community-driven recommendations. The core differences lie in the transaction scale, procurement approach, and reliance on digital social interactions versus traditional bulk buying methods.
Key Advantages of Wholesale
Wholesale offers significant advantages such as bulk purchasing discounts, enabling businesses to reduce per-unit costs and increase profit margins. It ensures consistent product availability and reliable supply chains, critical for maintaining inventory levels and meeting customer demand. Additionally, wholesale transactions often involve established vendors with reputations for quality, fostering trust and long-term business relationships.
Key Benefits of Social Sourcing
Social sourcing leverages the power of networks and community engagement to drive authentic product discovery and rapid demand generation. It enables real-time feedback and insights from end-users, enhancing product relevance and market responsiveness compared to traditional wholesale channels. Businesses benefit from increased brand trust, lower acquisition costs, and scalable, organic growth through targeted social interactions.
Pricing Structures: Wholesale vs Social Sourcing
Wholesale pricing structures typically involve bulk purchasing with fixed rates, allowing businesses to benefit from volume discounts and predictable cost management. Social sourcing pricing is often more flexible, based on dynamic negotiations influenced by social networks and real-time market trends, leading to variable but potentially lower prices. Understanding these distinctions helps businesses optimize procurement costs by aligning their buying strategy with either standardized wholesale contracts or adaptive social sourcing agreements.
Supply Chain Management Comparison
Wholesale supply chain management emphasizes bulk purchasing, centralized inventory control, and streamlined logistics to optimize cost efficiency and scalability. Social sourcing relies on decentralized networks and real-time consumer insights, enhancing flexibility but often increasing complexity in tracking and fulfillment. Comparing both, wholesale offers predictability and volume discounts, while social sourcing enables agile demand response and personalized supplier relationships.
Market Reach and Customer Engagement
Wholesale enables businesses to achieve extensive market reach by distributing large quantities of products to retailers and various sales channels, ensuring widespread product availability. Social sourcing emphasizes direct customer engagement through social media platforms, fostering personalized interactions and community-driven brand loyalty. Combining wholesale's broad distribution with social sourcing's interactive engagement can optimize both market expansion and customer retention.
Technology Integration in Wholesale and Social Sourcing
Technology integration in wholesale streamlines inventory management, automates order processing, and enhances supply chain visibility through advanced ERP systems and IoT sensors. Social sourcing leverages AI-driven platforms and social media analytics to identify emerging trends, connect with niche suppliers, and enable real-time collaboration. Both approaches benefit from cloud-based solutions and data analytics, but wholesale places greater emphasis on operational efficiency while social sourcing prioritizes dynamic supplier engagement.
Challenges in Wholesale and Social Sourcing
Wholesale faces challenges such as managing large inventory volumes, negotiating bulk pricing, and maintaining consistent supply chain reliability to meet business demands. Social sourcing struggles with quality control, scalability, and ensuring supplier credibility due to decentralized and diverse supplier networks. Both models require robust logistical planning and technology integration to overcome inefficiencies and meet market expectations.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Wholesale offers bulk purchasing at discounted rates, ideal for businesses seeking consistent inventory and predictable pricing, while social sourcing leverages community-driven, often smaller-scale suppliers to foster unique product variety and flexible terms. Evaluating factors such as order volume, supply chain reliability, and target market preferences helps determine whether a wholesale or social sourcing model aligns best with your operational goals. Selecting the right sourcing strategy directly impacts cost efficiency, product differentiation, and scalability in competitive marketplaces.
Related Important Terms
Crowdstocking
Wholesale involves bulk purchasing from manufacturers or distributors to resell at scale, while social sourcing leverages community networks to aggregate demand and supply. Crowdstocking, a hybrid model within social sourcing, enables groups of buyers to collectively place large orders, reducing costs and increasing bargaining power compared to traditional wholesale channels.
Community Dropshipping
Community dropshipping in wholesale leverages local networks to streamline product distribution and reduce inventory risks, enhancing supply chain efficiency. This model contrasts with traditional wholesale by emphasizing direct engagement with community members, who act as micro-suppliers and resellers, driving localized sales growth.
Peer-to-Peer Wholesale
Peer-to-peer wholesale leverages decentralized networks where businesses directly connect, bypassing traditional intermediaries to reduce costs and increase efficiency in bulk product distribution. Unlike social sourcing, which relies heavily on social media and influencer marketing for demand generation, peer-to-peer wholesale emphasizes trust and transparency within industry-specific communities to optimize supply chain dynamics.
Social Supply Chain
Social supply chain leverages digital platforms and community networks to source products directly from suppliers, enhancing transparency and agility in procurement compared to traditional wholesale models. Emphasizing collaboration and real-time data exchange, social sourcing reduces lead times and fosters sustainable supplier relationships essential for modern wholesale scalability.
Influencer Sourcing
Wholesale involves bulk purchasing directly from manufacturers or distributors, ensuring consistent supply and pricing control for retailers. Influencer sourcing leverages social media personalities to promote products, creating authentic engagement but often requiring flexible order quantities compared to traditional wholesale's fixed minimums.
B2C Wholesaling
B2C wholesaling streamlines bulk product distribution directly to consumers, enhancing inventory accessibility and reducing costs compared to social sourcing methods that rely on peer-to-peer transactions. This approach enables businesses to maintain consistent supply chains and leverage volume discounts, optimizing profitability and customer satisfaction.
Microbatch Sourcing
Microbatch sourcing in wholesale leverages small, specialized production runs to fulfill bulk orders with greater customization and reduced inventory risk. Compared to social sourcing, microbatch sourcing optimizes supply chain agility by enabling precise demand matching and minimizing overproduction in large-scale wholesale operations.
Social Procurement Networks
Social procurement networks enhance transparency and collaboration in wholesale by connecting buyers and suppliers through digital platforms, enabling real-time communication and trust-building. These networks streamline sourcing processes by leveraging social relationships and shared data, reducing costs and improving supplier diversity compared to traditional wholesale methods.
Collaborative Sourcing Circles
Collaborative Sourcing Circles in wholesale leverage collective buying power by uniting multiple buyers to negotiate better prices and terms directly with suppliers, reducing costs and increasing efficiency compared to traditional wholesale methods. Social sourcing enhances transparency and trust through shared feedback and recommendations within these circles, fostering stronger supplier relationships and more informed purchasing decisions.
Social Commerce Aggregators
Social Commerce Aggregators consolidate consumer demand by leveraging peer recommendations and user-generated content, offering wholesalers direct access to engaged, niche markets. This model enhances product visibility and accelerates sales cycles compared to traditional wholesale distribution channels.
Wholesale vs Social Sourcing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com