Blueprints provide a traditional two-dimensional representation of building designs, capturing the essential architectural and structural details needed for construction. Digital twin models go beyond static visuals by offering a dynamic, real-time simulation of the physical building, integrating data from sensors and IoT to monitor performance and predict issues. This advanced technology enhances project management, enabling proactive maintenance, increased efficiency, and better decision-making throughout the construction lifecycle.
Table of Comparison
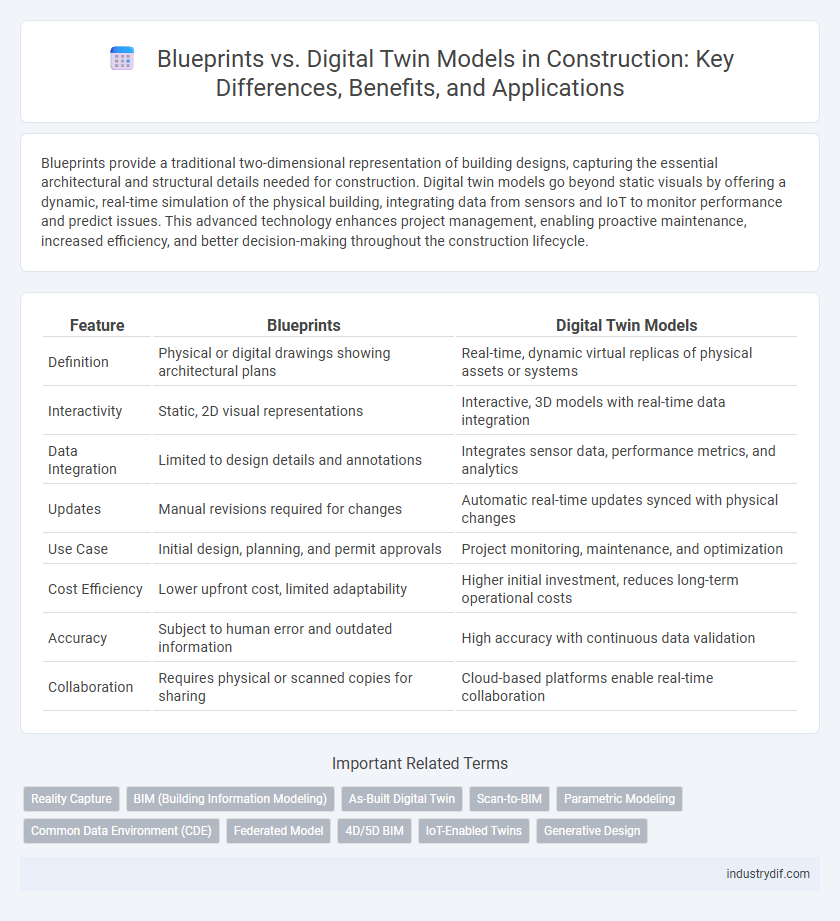
| Feature | Blueprints | Digital Twin Models |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical or digital drawings showing architectural plans | Real-time, dynamic virtual replicas of physical assets or systems |
| Interactivity | Static, 2D visual representations | Interactive, 3D models with real-time data integration |
| Data Integration | Limited to design details and annotations | Integrates sensor data, performance metrics, and analytics |
| Updates | Manual revisions required for changes | Automatic real-time updates synced with physical changes |
| Use Case | Initial design, planning, and permit approvals | Project monitoring, maintenance, and optimization |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower upfront cost, limited adaptability | Higher initial investment, reduces long-term operational costs |
| Accuracy | Subject to human error and outdated information | High accuracy with continuous data validation |
| Collaboration | Requires physical or scanned copies for sharing | Cloud-based platforms enable real-time collaboration |
Introduction to Blueprints and Digital Twin Models
Blueprints are traditional, two-dimensional technical drawings used in construction to detail the design, dimensions, and specifications of a building project. Digital Twin Models are advanced, dynamic replicas of physical assets created using real-time data, allowing for continuous monitoring and simulation. While blueprints provide static visual plans, Digital Twin Models enable enhanced decision-making through accurate, real-time representation of construction progress and performance.
Evolution of Construction Documentation Methods
Blueprints have long served as the primary medium for construction documentation, providing detailed 2D representations of architectural plans and specifications. Digital twin models represent an advanced evolution, offering dynamic, real-time 3D simulations that integrate data from various construction phases for enhanced accuracy and project management. This transition from static blueprints to interactive digital twins improves collaboration, reduces errors, and accelerates decision-making throughout the construction lifecycle.
Key Features of Traditional Blueprints
Traditional blueprints provide detailed architectural and engineering drawings with precise measurements, scale representations, and standardized symbols critical for on-site construction and fabrication. These physical documents enable direct interpretation of structural elements, material specifications, and spatial relationships, facilitating clear communication among builders, contractors, and inspectors. Despite limitations in interactivity and real-time updates, blueprints remain essential for regulatory compliance and detailed project documentation in conventional construction workflows.
Defining Digital Twin Models in Construction
Digital twin models in construction are advanced digital replicas of physical assets, incorporating real-time data to simulate, predict, and optimize building performance throughout its lifecycle. Unlike traditional blueprints, digital twins enable dynamic visualization and analysis by integrating BIM (Building Information Modeling) with IoT sensors and analytics platforms. This technology enhances project management, reduces operational costs, and improves decision-making by providing a comprehensive, data-driven virtual environment of the construction site.
Advantages of Blueprints in Construction Projects
Blueprints provide a tangible, large-scale visual reference that enhances on-site communication and spatial understanding among construction teams. Their durability and ease of annotation allow quick modifications and immediate access without reliance on electronic devices or software. Blueprints also ensure compatibility across all stages of construction, reducing technical barriers and facilitating regulatory inspections.
Benefits of Digital Twin Models for Modern Builds
Digital Twin Models offer real-time data integration and simulation capabilities unmatched by traditional blueprints, enabling predictive maintenance and efficient resource management. These models enhance collaboration by providing a dynamic, 3D visual representation accessible across project phases, reducing errors and accelerating decision-making. Leveraging IoT sensors and AI analytics, Digital Twin Models optimize building performance, sustainability, and cost-efficiency throughout a construction project's lifecycle.
Challenges with Blueprint Usage Today
Blueprints face challenges such as limited real-time updates and difficulty accommodating design changes, which slow project adaptations and increase errors. Physical degradation and storage issues further complicate blueprint reliability and accessibility on-site. In contrast, digital twin models provide dynamic, instantly updated representations that enhance accuracy and collaboration in construction projects.
Limitations and Barriers to Digital Twin Adoption
Blueprints provide static, two-dimensional representations that lack real-time data integration and predictive analytics, limiting their adaptability during construction phases. Digital twin models face barriers such as high implementation costs, complex data interoperability challenges, and the need for skilled personnel to manage and analyze continuous data streams. Furthermore, concerns about data security, integration with legacy systems, and resistance to change within construction teams hinder widespread digital twin adoption.
Integration of Blueprints and Digital Twins in Workflows
Integrating blueprints with digital twin models enhances construction workflows by combining detailed 2D design plans with real-time 3D data analytics, enabling precise project monitoring and predictive maintenance. This fusion supports collaboration across multidisciplinary teams through cloud-based platforms, improving data accuracy and decision-making efficiency. Leveraging IoT sensors and BIM data synchronizes physical and digital assets, streamlining construction scheduling and resource allocation.
Future Trends: From Blueprints to Intelligent Models
Digital twin models represent a transformative shift in construction, enabling real-time monitoring, simulation, and predictive maintenance beyond static blueprints. These intelligent models integrate IoT sensors, AI analytics, and BIM data, enhancing project accuracy and operational efficiency. Future trends emphasize augmented reality and machine learning integration to facilitate proactive decision-making and reduce costly errors on-site.
Related Important Terms
Reality Capture
Blueprints provide static, two-dimensional representations of construction designs, while digital twin models integrate reality capture technologies such as 3D scanning and photogrammetry to create dynamic, real-time, and highly accurate virtual replicas of physical structures. This advanced integration enhances project monitoring, facilitates predictive maintenance, and supports data-driven decision-making throughout the construction lifecycle.
BIM (Building Information Modeling)
Blueprints provide static, two-dimensional representations of construction projects, while digital twin models leverage BIM (Building Information Modeling) to create dynamic, data-rich, and interactive virtual replicas that enhance real-time decision-making and facility management. BIM integrates multidisciplinary data into digital twins, improving accuracy, collaboration, and lifecycle management throughout construction and operation phases.
As-Built Digital Twin
As-built digital twin models provide real-time, precise representations of constructed assets by integrating sensor data and BIM information, surpassing traditional blueprints in accuracy and operational insights. These models enable enhanced facility management, predictive maintenance, and lifecycle optimization by reflecting the exact, current state of built environments.
Scan-to-BIM
Scan-to-BIM technology converts detailed 3D laser scans into precise digital twin models, offering enhanced accuracy and real-time data over traditional blueprints in construction. These digital twins enable improved project visualization, clash detection, and facility management by integrating as-built conditions into a dynamic, interactive platform.
Parametric Modeling
Parametric modeling in digital twin models allows real-time updates and precise simulation of construction elements, far surpassing static blueprints by enabling dynamic adjustments based on project data. This technology enhances collaboration and accuracy in design, construction planning, and facility management by integrating multidimensional parameters into a cohesive virtual representation.
Common Data Environment (CDE)
Blueprints serve as traditional, static construction plans, while digital twin models offer dynamic, real-time data integration within a Common Data Environment (CDE) to enhance collaboration and project accuracy. The CDE centralizes access to both digital twins and blueprint documents, enabling seamless updates, version control, and improved communication across all stakeholders in the construction lifecycle.
Federated Model
Federated models integrate multiple digital twin datasets and blueprints into a unified platform, enabling seamless collaboration and real-time updates across construction stakeholders. This approach enhances accuracy and efficiency by synchronizing architectural, structural, and MEP systems within a comprehensive digital representation.
4D/5D BIM
4D/5D BIM integrates time and cost dimensions into digital twin models, enabling real-time project scheduling and budget analysis, which surpasses the static nature of traditional blueprints. This advanced technology enhances construction planning accuracy, risk management, and decision-making efficiency throughout the project lifecycle.
IoT-Enabled Twins
Blueprints provide static, two-dimensional representations of construction designs, while IoT-enabled digital twin models offer dynamic, real-time monitoring and simulation of building performance through sensor integration. These digital twins enhance project management by enabling predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and improved operational efficiency across the construction lifecycle.
Generative Design
Blueprints provide static, detailed architectural plans, whereas Digital Twin Models integrate real-time data for dynamic simulation and performance analysis in construction projects. Generative design within Digital Twins leverages AI algorithms to optimize structural efficiency, material usage, and cost, enabling adaptive, data-driven decision-making beyond traditional blueprint constraints.
Blueprints vs Digital Twin Models Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com