Off-site construction involves fabricating building components in a controlled factory environment before transporting them to the construction site for assembly, enhancing efficiency and reducing onsite labor. Modular construction, a subset of off-site methods, manufactures fully equipped, prefabricated modules that are assembled on-site, enabling faster project completion and consistent quality control. Both approaches minimize construction waste, improve safety, and accelerate timelines compared to traditional on-site building processes.
Table of Comparison
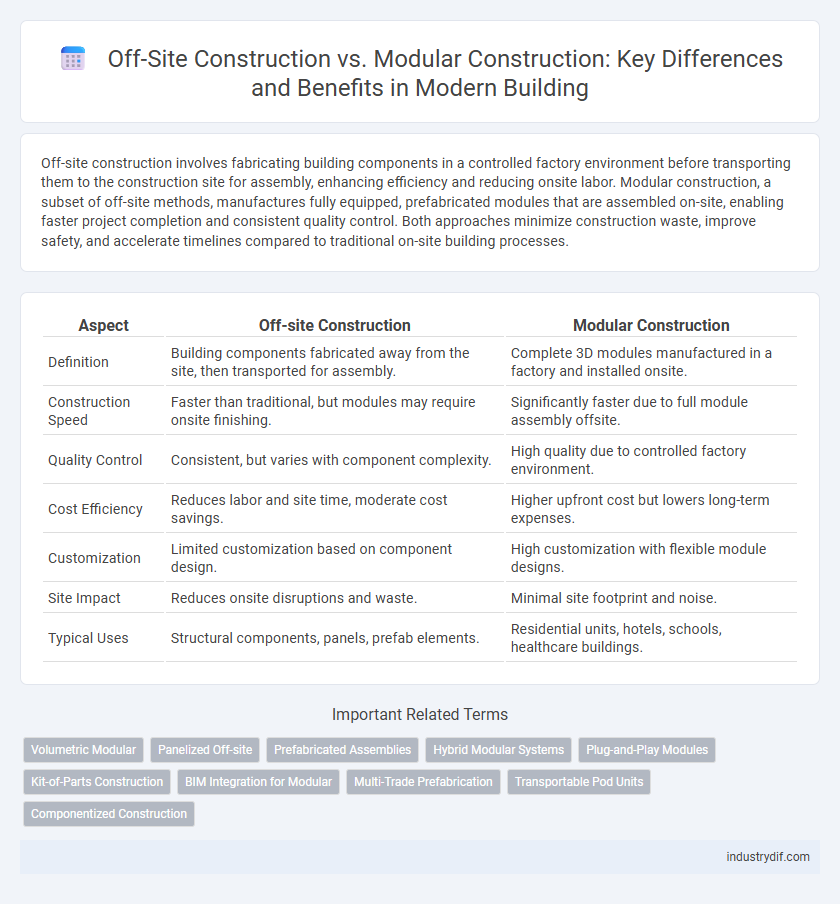
| Aspect | Off-site Construction | Modular Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Building components fabricated away from the site, then transported for assembly. | Complete 3D modules manufactured in a factory and installed onsite. |
| Construction Speed | Faster than traditional, but modules may require onsite finishing. | Significantly faster due to full module assembly offsite. |
| Quality Control | Consistent, but varies with component complexity. | High quality due to controlled factory environment. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces labor and site time, moderate cost savings. | Higher upfront cost but lowers long-term expenses. |
| Customization | Limited customization based on component design. | High customization with flexible module designs. |
| Site Impact | Reduces onsite disruptions and waste. | Minimal site footprint and noise. |
| Typical Uses | Structural components, panels, prefab elements. | Residential units, hotels, schools, healthcare buildings. |
Understanding Off-site Construction: Definition and Scope
Off-site construction involves fabricating building components in a controlled factory environment before transporting them to the site for assembly, reducing construction time and improving quality control. This method encompasses modular construction, panelized systems, and prefabricated assemblies, each varying in complexity and integration level. Understanding off-site construction's scope requires recognizing its potential to enhance efficiency, minimize waste, and improve site safety through advanced manufacturing techniques.
What is Modular Construction? Key Features and Concepts
Modular construction involves fabricating building sections, or modules, in a controlled factory environment before transporting them to the site for assembly. Key features include precise manufacturing, reduced construction time, improved quality control, and enhanced sustainability through minimized waste. This method leverages repeatable design elements and integrated systems, enabling efficient project delivery and greater cost predictability compared to traditional off-site construction approaches.
Core Differences: Off-site Construction vs Modular Construction
Off-site construction involves fabricating building components or entire sections in a controlled factory environment before transporting them to the site for assembly, emphasizing efficiency and reduced on-site labor. Modular construction is a subset of off-site construction that produces fully finished, three-dimensional modules or units, which are then delivered and assembled on-site to form complete buildings. The core difference lies in modular construction delivering near-complete, volumetric units, whereas off-site construction includes both component-level and panelized systems requiring more extensive on-site integration.
Advantages of Off-site Construction in Modern Projects
Off-site construction offers significant advantages in modern projects by enabling faster project timelines and reducing on-site disruptions through prefabrication in controlled environments. This method improves quality control and minimizes waste, contributing to sustainable building practices and cost savings. Enhanced safety conditions are ensured as workers operate in factory settings rather than unpredictable job sites, advancing overall project efficiency.
Benefits of Modular Construction: Speed, Quality, and Flexibility
Modular construction accelerates project timelines by enabling simultaneous site preparation and module fabrication, reducing overall construction duration by up to 50%. Factory-controlled environments ensure higher quality standards with consistent materials and precise assembly, minimizing defects and rework. This method offers unmatched flexibility, allowing easy customization, scalability, and adaptability to design changes without disrupting ongoing site activities.
Limitations and Challenges: Off-site vs Modular Methods
Off-site construction faces challenges related to transportation logistics, limited customization on-site, and high initial capital investment for factory setup. Modular construction encounters limitations such as design constraints due to module size, potential integration issues during assembly, and strict adherence to building codes across jurisdictions. Both methods require skilled labor and precise coordination to address structural integrity and quality control throughout the fabrication and installation processes.
Cost Comparison: Off-site Construction vs Modular Construction
Off-site construction typically offers cost savings through reduced labor expenses and faster project timelines by fabricating components in controlled factory settings. Modular construction, a subset of off-site methods, often incurs higher upfront costs due to the complexity of assembling complete modules but delivers lower overall costs by minimizing on-site labor and shortening construction schedules. Careful cost analysis reveals that while off-site construction reduces material waste and site disruptions, modular construction provides predictable budgeting and significant savings in project duration, influencing total project expenditure.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact of Both Methods
Off-site construction reduces waste and energy consumption by fabricating building components in controlled factory settings, minimizing site disturbance and material overruns. Modular construction, a subset of off-site methods, enhances sustainability by enabling precise resource management and faster assembly, which cuts down emissions from prolonged on-site activities. Both methods promote environmental benefits through improved quality control and the potential for greater recycling of materials compared to traditional construction.
Applications and Project Types Suited for Each Approach
Off-site construction excels in large-scale infrastructure projects such as bridges, highways, and utility installations, offering enhanced quality control and reduced on-site disruption. Modular construction suits residential buildings, hotels, and healthcare facilities, enabling faster assembly and improved scalability through factory-built modules. Both methods optimize project timelines and cost efficiency but are selected based on project complexity and customization requirements.
Future Trends in Off-site and Modular Construction Technologies
Future trends in off-site and modular construction technologies emphasize automation, integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM), and the increased use of sustainable materials to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Advanced robotics and AI-driven machinery are being developed to accelerate precision assembly while minimizing labor costs and errors. The adoption of smart factory systems and digital twins is set to transform production processes, enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of construction projects.
Related Important Terms
Volumetric Modular
Volumetric modular construction involves manufacturing fully finished, three-dimensional building modules off-site, which are then transported and assembled on-site, significantly reducing construction time and improving quality control. Compared to traditional off-site methods that may focus on component fabrication, volumetric modular provides complete, volumetric units that integrate electrical, plumbing, and interior finishes, enhancing efficiency and minimizing on-site labor.
Panelized Off-site
Panelized off-site construction involves fabricating wall, floor, and roof panels in a controlled factory environment, enabling precise quality control and faster on-site assembly compared to traditional modular construction, which typically delivers fully assembled volumetric units. This method reduces on-site labor and material waste while allowing greater flexibility in architectural design and customization.
Prefabricated Assemblies
Prefabricated assemblies in off-site construction are manufactured in controlled factory environments and transported to the site for assembly, enabling faster project timelines and reduced on-site labor costs. Modular construction involves creating fully finished modules that are pre-assembled with mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems, allowing for high-quality standards and minimal disruption during installation.
Hybrid Modular Systems
Hybrid modular systems combine off-site construction's efficiency with modular construction's flexibility, enabling faster project completion and enhanced quality control by integrating pre-fabricated components with traditional building methods. This innovative approach reduces on-site labor costs and minimizes construction waste while maintaining design adaptability for complex architectural requirements.
Plug-and-Play Modules
Off-site construction leverages plug-and-play modules that are pre-fabricated in controlled factory environments, enabling faster project timelines and reduced on-site labor costs. Modular construction enhances efficiency by integrating these standardized, transportable units directly into building frameworks, minimizing on-site assembly and improving quality control.
Kit-of-Parts Construction
Kit-of-Parts Construction in off-site construction consists of pre-engineered, standardized components manufactured in controlled environments and assembled on-site, enhancing precision and reducing waste. Unlike traditional modular construction, which delivers fully built modules, Kit-of-Parts offers flexibility in design and customization by enabling on-site assembly of individual parts.
BIM Integration for Modular
Modular construction leverages Building Information Modeling (BIM) integration to streamline design accuracy, enhance collaboration, and improve project timelines by allowing detailed 3D modeling and real-time data sharing between off-site factories and on-site assemblies. Off-site construction benefits from BIM by facilitating precise component fabrication and reducing errors, but modular construction's standardized units maximize BIM's capabilities for efficient manufacturing and assembly processes.
Multi-Trade Prefabrication
Multi-trade prefabrication in off-site construction integrates various trades such as electrical, plumbing, and HVAC into preassembled modules, enhancing efficiency and reducing on-site labor time. Modular construction leverages this approach by delivering fully finished, multi-trade units to the site, accelerating project timelines and improving quality control through factory-based assembly.
Transportable Pod Units
Transportable pod units in off-site construction streamline project timelines by enabling simultaneous site preparation and unit fabrication, resulting in reduced labor costs and waste. Modular construction leverages these prefabricated pods for rapid assembly, enhancing quality control and minimizing on-site disruptions while ensuring structural integrity during transport.
Componentized Construction
Componentized construction in off-site construction involves fabricating building components separately before transportation to the site, enabling streamlined assembly and reduced on-site labor. Modular construction extends this by assembling entire modules off-site, offering increased efficiency and consistent quality through factory-controlled environments.
Off-site Construction vs Modular Construction Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com